
Flower Constancy vs Flower Generalism Illustration
Pollinators exhibiting flower constancy preferentially visit the same species of flowers, enhancing efficient pollen transfer and increasing the reproductive success of those plants. In contrast, flower generalist pollinators forage across multiple flower species, promoting genetic diversity and ecosystem resilience. Understanding the balance between flower constancy and generalism is crucial for conserving pollinator populations and maintaining plant biodiversity.
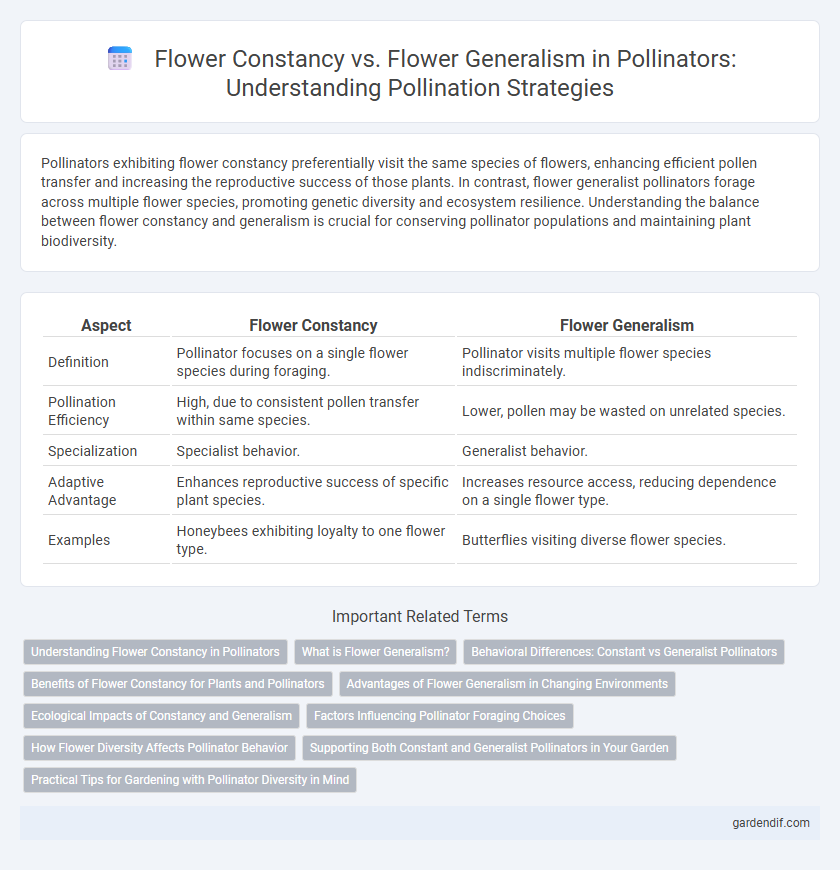
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flower Constancy | Flower Generalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pollinator focuses on a single flower species during foraging. | Pollinator visits multiple flower species indiscriminately. |
| Pollination Efficiency | High, due to consistent pollen transfer within same species. | Lower, pollen may be wasted on unrelated species. |
| Specialization | Specialist behavior. | Generalist behavior. |
| Adaptive Advantage | Enhances reproductive success of specific plant species. | Increases resource access, reducing dependence on a single flower type. |
| Examples | Honeybees exhibiting loyalty to one flower type. | Butterflies visiting diverse flower species. |
Understanding Flower Constancy in Pollinators
Flower constancy in pollinators refers to the behavior where individual pollinators consistently visit the same flower species during foraging trips, enhancing pollination efficiency and plant reproductive success. This selective visitation reduces interspecific pollen transfer, promoting specialized plant-pollinator relationships and increasing the likelihood of successful fertilization. Understanding flower constancy involves studying the cognitive mechanisms and ecological factors influencing pollinator choices, which can inform conservation strategies aimed at maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
What is Flower Generalism?
Flower generalism refers to pollinators that visit a wide variety of flowering plant species rather than specializing in a single type. These generalist pollinators contribute to the pollination of diverse plant communities, enhancing ecosystem resilience and stability. Their ability to adapt to multiple floral resources makes them vital for maintaining biodiversity and supporting agricultural productivity.
Behavioral Differences: Constant vs Generalist Pollinators
Constant pollinators exhibit flower constancy by repeatedly visiting flowers of the same species, enhancing pollination efficiency through consistent pollen transfer. Generalist pollinators display flower generalism by foraging across diverse flower species, increasing plant-pollinator network connectivity but reducing species-specific pollination fidelity. These behavioral differences impact plant reproductive success and ecological interactions, shaping pollination syndromes and biodiversity patterns.
Benefits of Flower Constancy for Plants and Pollinators
Flower constancy enhances pollination efficiency by ensuring pollen transfer occurs primarily between conspecific flowers, thus improving plant reproductive success and genetic diversity. For pollinators like bees and butterflies, specializing on a single flower type reduces handling time and learning effort, leading to more efficient foraging and increased energy gains. This mutualistic interaction supports ecosystem stability by promoting plant reproduction and sustaining pollinator populations through reliable resource exploitation.
Advantages of Flower Generalism in Changing Environments
Flower generalism enhances pollinator resilience by allowing access to diverse floral resources, ensuring consistent food supply amid fluctuating environmental conditions. This adaptability reduces dependency on any single plant species, minimizing risks from temporal or spatial variation in flower availability. Generalist pollinators play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem stability by supporting robust plant-pollinator networks across variable habitats.
Ecological Impacts of Constancy and Generalism
Flower constancy enhances pollination efficiency by promoting consistent pollen transfer within specific plant species, which supports plant reproductive success and biodiversity. In contrast, flower generalism increases cross-species pollen dispersal, potentially boosting genetic diversity and ecosystem resilience but may reduce individual plant fertilization efficiency. Understanding the balance between constancy and generalism is crucial for predicting pollinator-driven impacts on plant community dynamics and ecological stability.
Factors Influencing Pollinator Foraging Choices
Pollinator foraging choices are shaped by flower constancy, where insects repeatedly visit the same flower species, promoting efficient pollen transfer, versus flower generalism, involving visits to diverse flower types to maximize resource acquisition. Key factors influencing these behaviors include floral traits such as nectar rewards, flower color, and scent, as well as pollinator cognitive abilities and environmental resource availability. Pollinators optimize their energy intake by balancing the reliability of known floral resources against the benefits of exploring diverse flowers within their habitat.
How Flower Diversity Affects Pollinator Behavior
Flower diversity significantly influences pollinator behavior by shaping their foraging strategies between flower constancy and flower generalism. High floral diversity encourages pollinators to adopt flower generalism, allowing them to exploit a wider range of nectar and pollen sources for optimal energy intake. Conversely, low floral diversity promotes flower constancy, where pollinators repeatedly visit the same flower species to increase foraging efficiency and improve pollination accuracy.
Supporting Both Constant and Generalist Pollinators in Your Garden
Supporting both flower-constant and flower-generalist pollinators in your garden enhances biodiversity and pollination efficiency by catering to diverse foraging behaviors. Planting a variety of native flowering species that bloom at different times ensures continuous resources, attracting specialist pollinators that prefer consistent flower types and generalists that forage broadly. Creating habitats with mixed floral diversity promotes robust pollinator communities critical for ecosystem resilience and crop productivity.
Practical Tips for Gardening with Pollinator Diversity in Mind
Promote pollinator diversity by planting a variety of native flowering species with overlapping bloom periods to support both flower constancy and flower generalism behaviors. Design garden layouts that provide abundant floral resources, ensuring consistent nectar and pollen availability, which encourages efficient foraging and cross-pollination. Incorporate clusters of the same species alongside mixed-species patches to accommodate specialized and generalist pollinators, enhancing ecosystem resilience and crop yields.
Flower Constancy vs Flower Generalism Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com