
Heirloom vs Hybrid Illustration
Heirloom plants are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, prized for their genetic diversity, unique flavors, and adaptability to local growing conditions. Hybrid plants result from crossbreeding two different parent plants to produce offspring with specific desired traits such as increased yield, disease resistance, or uniformity. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid seeds depends on whether gardeners prioritize traditional characteristics and seed saving or enhanced performance and consistency.
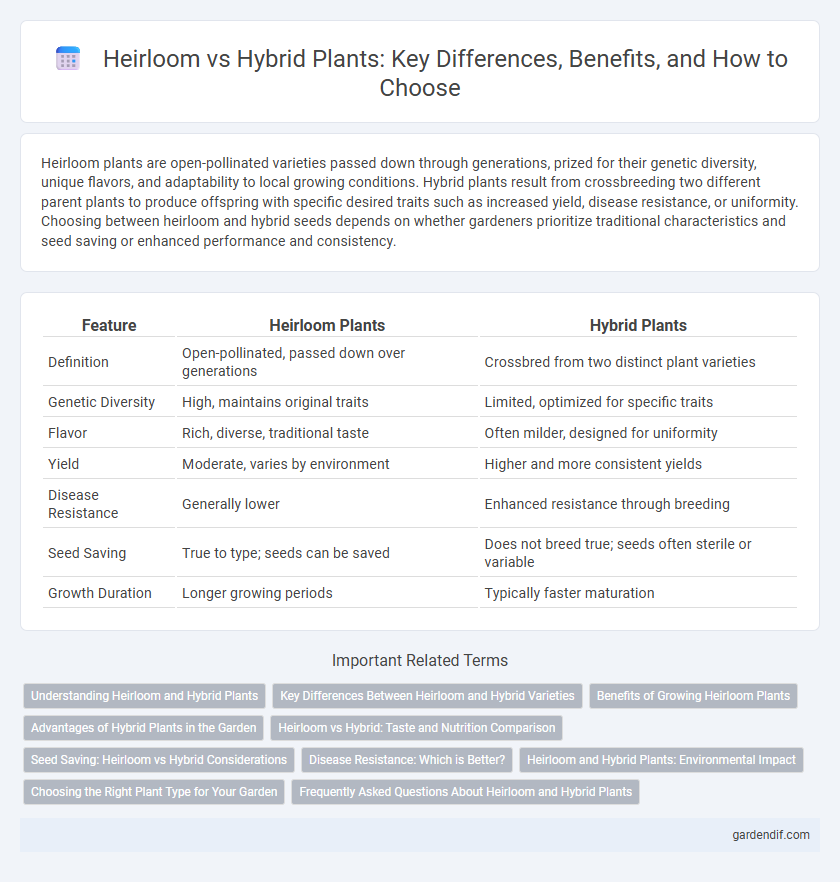
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom Plants | Hybrid Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Open-pollinated, passed down over generations | Crossbred from two distinct plant varieties |
| Genetic Diversity | High, maintains original traits | Limited, optimized for specific traits |
| Flavor | Rich, diverse, traditional taste | Often milder, designed for uniformity |
| Yield | Moderate, varies by environment | Higher and more consistent yields |
| Disease Resistance | Generally lower | Enhanced resistance through breeding |
| Seed Saving | True to type; seeds can be saved | Does not breed true; seeds often sterile or variable |
| Growth Duration | Longer growing periods | Typically faster maturation |
Understanding Heirloom and Hybrid Plants
Heirloom plants are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, known for their stable traits and rich genetic diversity. Hybrid plants result from crossbreeding two distinct parent varieties to enhance specific characteristics such as disease resistance or yield. Understanding the differences helps gardeners choose between traditional flavors and uniform performance.
Key Differences Between Heirloom and Hybrid Varieties
Heirloom plant varieties are open-pollinated and maintain genetic traits passed down through generations, resulting in diverse flavors and colors. Hybrid plants are created by crossbreeding two distinct parent varieties to enhance specific qualities such as disease resistance, yield, and uniformity. Unlike hybrids, heirlooms offer true-to-type seeds that retain original characteristics, making them preferable for seed saving and preserving biodiversity.
Benefits of Growing Heirloom Plants
Growing heirloom plants preserves genetic diversity and offers unique flavors and textures not found in hybrid varieties. These plants adapt well to local climates and soil conditions, often requiring fewer chemical inputs and promoting sustainable gardening practices. Heirloom seeds can be saved and shared, ensuring the continuation of traditional plant varieties for future generations.
Advantages of Hybrid Plants in the Garden
Hybrid plants offer increased disease resistance and higher yields compared to heirloom varieties, making them ideal for gardeners seeking robust and productive crops. Their consistent traits, such as uniform size and flavor, enhance commercial appeal and simplify harvesting. These plants often adapt better to varying environmental conditions, providing greater resilience in diverse garden settings.
Heirloom vs Hybrid: Taste and Nutrition Comparison
Heirloom plants are prized for their superior taste and rich nutritional profiles, often retaining more natural sugars, antioxidants, and essential vitamins compared to hybrid varieties. Hybrids are bred primarily for yield, disease resistance, and uniformity, which can sometimes result in compromised flavor and nutrient density. Consumers seeking a more authentic eating experience and enhanced nutrient intake often prefer heirloom varieties over hybrids.
Seed Saving: Heirloom vs Hybrid Considerations
Heirloom seeds maintain genetic stability, making them ideal for seed saving as they reliably reproduce true-to-type plants year after year. Hybrid seeds often yield vigorous plants initially but produce unpredictable traits in saved seeds, leading to inconsistent crop quality. Gardeners prioritizing sustainable seed saving should choose heirloom varieties for dependable regeneration and preservation of plant heritage.
Disease Resistance: Which is Better?
Heirloom plants often showcase superior genetic diversity, which can contribute to natural disease resistance, though they may lack consistency in performance. Hybrid plants are bred specifically for enhanced disease resistance, offering more reliable protection against common pathogens. Selecting between heirloom and hybrid varieties depends on whether genetic diversity or targeted disease resistance is the priority for your crop management.
Heirloom and Hybrid Plants: Environmental Impact
Heirloom plants, grown from seeds passed down through generations, promote biodiversity and support sustainable agriculture by preserving genetic diversity. Hybrid plants, bred for higher yields and disease resistance, often require more chemical inputs and can reduce genetic variation in crop populations. Choosing heirloom varieties helps maintain resilient ecosystems, while hybrids can contribute to increased resource use and environmental strain.
Choosing the Right Plant Type for Your Garden
Heirloom plants offer genetic diversity and rich flavors, making them ideal for gardeners prioritizing natural seed saving and traditional varieties. Hybrid plants provide enhanced disease resistance, higher yields, and faster growth, suitable for those seeking reliable crop performance and uniformity. Selecting the right plant type depends on your garden goals, whether preserving heritage traits or maximizing productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Heirloom and Hybrid Plants
Heirloom plants are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, prized for their rich flavor and genetic diversity, while hybrid plants result from controlled crossbreeding to enhance traits like disease resistance and yield. Frequently asked questions often address differences in seed saving, where heirlooms can be replanted with consistent traits, unlike hybrids that may produce unpredictable offspring. Many gardeners seek guidance on which type suits their needs, with heirlooms favored for organic gardening and hybrids chosen for uniformity and robustness in challenging environments.
Heirloom vs Hybrid Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com