
Hardy vs Tender Illustration
Hardy plants thrive in cold climates and can survive frost and freezing temperatures, making them ideal for outdoor gardens in temperate zones. Tender plants, however, are sensitive to cold and require warm, frost-free environments or indoor protection during colder months. Understanding the difference between hardy and tender plants is essential for successful gardening and plant care.
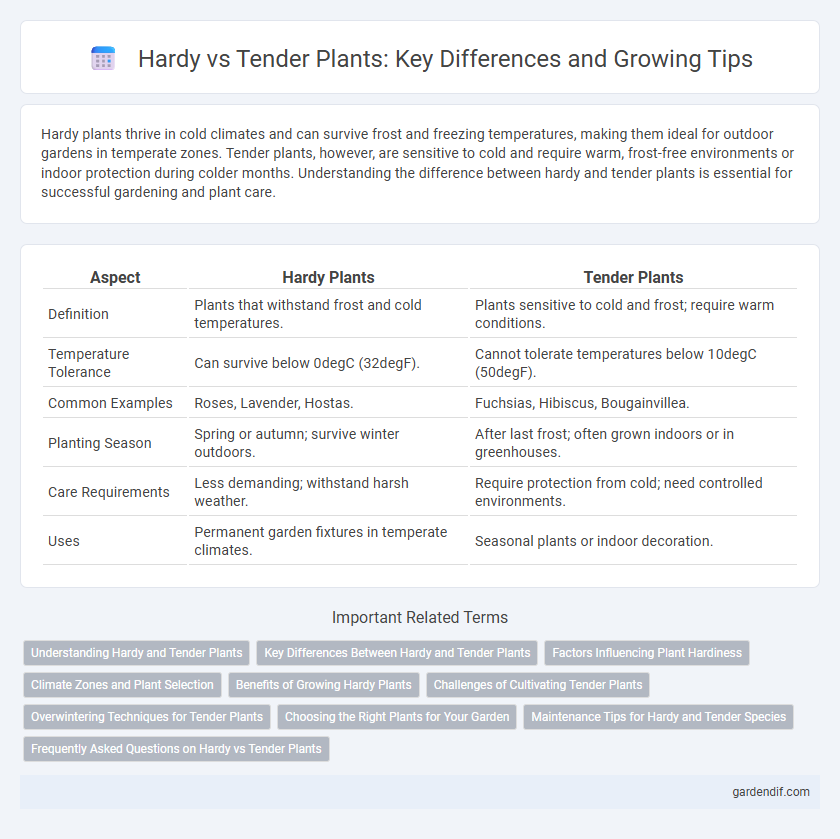
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hardy Plants | Tender Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants that withstand frost and cold temperatures. | Plants sensitive to cold and frost; require warm conditions. |
| Temperature Tolerance | Can survive below 0degC (32degF). | Cannot tolerate temperatures below 10degC (50degF). |
| Common Examples | Roses, Lavender, Hostas. | Fuchsias, Hibiscus, Bougainvillea. |
| Planting Season | Spring or autumn; survive winter outdoors. | After last frost; often grown indoors or in greenhouses. |
| Care Requirements | Less demanding; withstand harsh weather. | Require protection from cold; need controlled environments. |
| Uses | Permanent garden fixtures in temperate climates. | Seasonal plants or indoor decoration. |
Understanding Hardy and Tender Plants
Hardy plants can withstand cold temperatures and frost, making them suitable for outdoor growth in temperate and colder climates. Tender plants are sensitive to cold and require warmer conditions or indoor protection to thrive. Understanding these characteristics helps gardeners select appropriate species based on climate resilience and seasonal changes.
Key Differences Between Hardy and Tender Plants
Hardy plants withstand frost and freezing temperatures, thriving in outdoor environments with minimal protection, whereas tender plants require warmer climates and protection from cold to survive. Hardy plants often have robust root systems and thicker leaves to endure harsh weather, while tender plants typically possess delicate foliage and softer stems sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Understanding these differences guides gardeners in selecting appropriate species for their climate zones and seasonal conditions.
Factors Influencing Plant Hardiness
Plant hardiness is primarily influenced by temperature tolerance, soil type, and moisture availability, determining whether a species is classified as hardy or tender. Hardy plants can withstand frost and cold temperatures due to genetic adaptations and structural characteristics such as thicker cell walls and protective bark. Tender plants lack these adaptations, making factors like microclimate, humidity, and watering practices critical for their survival.
Climate Zones and Plant Selection
Hardy plants thrive in colder climate zones, often surviving frosts and subzero temperatures, making them ideal for USDA zones 1-7. Tender plants require warmer climates, thriving in USDA zones 8-11, where temperatures rarely drop below freezing. Selecting plants based on hardiness ensures optimal growth and survival by matching species to regional climate conditions.
Benefits of Growing Hardy Plants
Hardy plants provide numerous benefits including superior resilience to extreme weather conditions such as frost and drought, reducing the need for protective measures and minimizing plant loss. Their robust nature decreases maintenance requirements, saving time and resources on watering, fertilizing, and pest control. Cultivating hardy plants enhances garden sustainability by promoting biodiversity and supporting native wildlife habitats.
Challenges of Cultivating Tender Plants
Cultivating tender plants poses significant challenges due to their sensitivity to cold temperatures and frost, requiring controlled environments or seasonal adjustments to ensure survival. These plants often demand higher humidity, consistent watering, and protection from harsh weather conditions, increasing maintenance efforts compared to hardy species. Failure to meet these precise environmental needs can lead to stunted growth, disease susceptibility, and reduced lifespan.
Overwintering Techniques for Tender Plants
Tender plants require careful overwintering techniques to prevent frost damage, such as moving them indoors to a cool, bright location or using frost cloths and mulch outdoors to insulate roots. Hardy plants can typically withstand lower temperatures without additional protection due to their natural cold tolerance. Proper overwintering ensures tender plants survive the winter months and thrive in the growing season.
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Garden
Hardy plants thrive in cooler climates and can withstand frost, making them ideal for gardens in temperate zones. Tender plants require warmer temperatures and protection from cold, suitable for tropical or indoor gardening environments. Selecting the right plants depends on understanding your local climate, soil conditions, and the plant's tolerance to cold or heat.
Maintenance Tips for Hardy and Tender Species
Hardy plants require minimal maintenance due to their ability to withstand cold temperatures and harsh conditions, often thriving with simple watering and occasional pruning. Tender plants need more attentive care, including protection from frost, regular watering, and feeding with balanced fertilizers to support growth. Mulching around hardy species helps conserve moisture and protect roots, while tender plants benefit from indoor shelter or greenhouse environments during colder months to prevent damage.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hardy vs Tender Plants
Hardy plants can withstand frost and cold temperatures, making them suitable for outdoor planting in colder climates, while tender plants require protection from frost and thrive in warmer environments. Frequently asked questions about hardy vs tender plants often involve how to identify each type, with hardy plants typically having sturdier stems and more resilient foliage compared to the delicate leaves of tender plants. Gardeners commonly seek advice on seasonal care, with hardy plants generally needing less winter protection and tender plants benefiting from greenhouse or indoor shelter during colder months.
Hardy vs Tender Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com