
Neem oil application vs insecticidal soap spray Illustration
Neem oil application offers long-lasting pest control by disrupting insect hormones and preventing reproduction, making it effective against a broad spectrum of pests. Insecticidal soap spray works by penetrating the insect's outer layer, causing dehydration and quick mortality, which is ideal for immediate pest knockdown. Both treatments are environmentally friendly, but neem oil provides residual protection, whereas insecticidal soap requires more frequent application for sustained results.
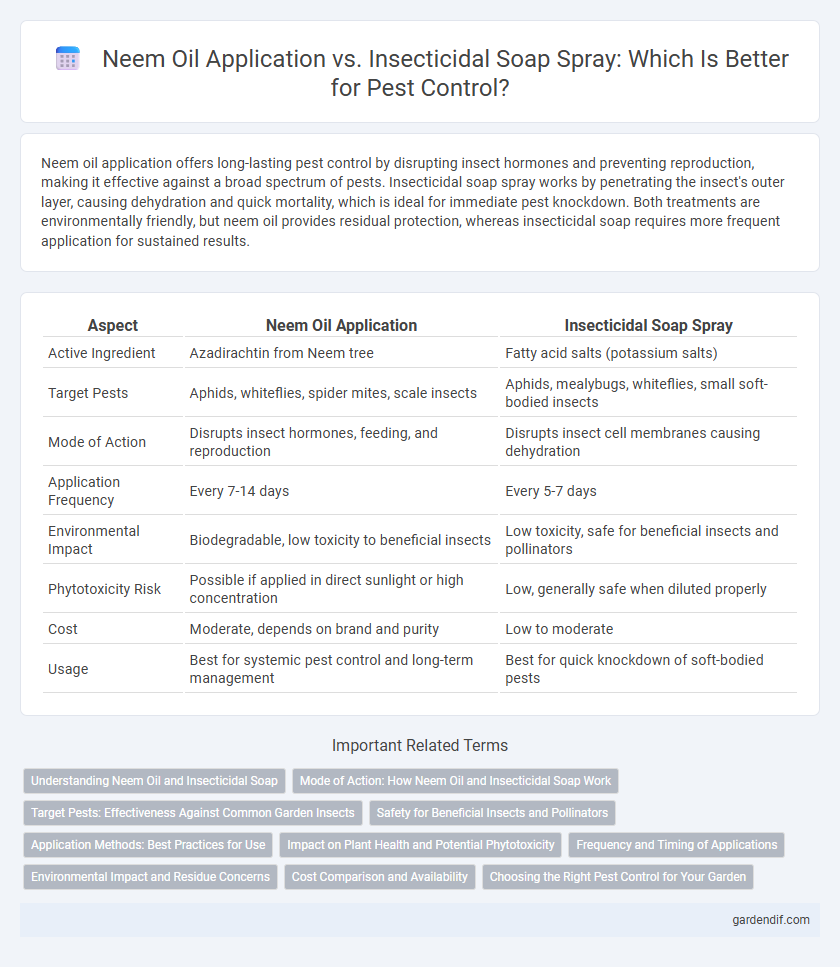
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Neem Oil Application | Insecticidal Soap Spray |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Azadirachtin from Neem tree | Fatty acid salts (potassium salts) |
| Target Pests | Aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, scale insects | Aphids, mealybugs, whiteflies, small soft-bodied insects |
| Mode of Action | Disrupts insect hormones, feeding, and reproduction | Disrupts insect cell membranes causing dehydration |
| Application Frequency | Every 7-14 days | Every 5-7 days |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity to beneficial insects | Low toxicity, safe for beneficial insects and pollinators |
| Phytotoxicity Risk | Possible if applied in direct sunlight or high concentration | Low, generally safe when diluted properly |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on brand and purity | Low to moderate |
| Usage | Best for systemic pest control and long-term management | Best for quick knockdown of soft-bodied pests |
Understanding Neem Oil and Insecticidal Soap
Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree, acts as a natural pesticide by disrupting insect hormone systems, making it effective against a broad spectrum of pests including aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. In contrast, insecticidal soap spray targets the cell membranes of soft-bodied insects, leading to dehydration and death, and is especially useful for controlling aphids, mealybugs, and thrips without harming beneficial insects. Both neem oil and insecticidal soap offer eco-friendly pest management options, with neem oil providing residual effects and systemic activity while insecticidal soap provides immediate contact control but lacks lasting protection.
Mode of Action: How Neem Oil and Insecticidal Soap Work
Neem oil works by disrupting the hormonal system of pests, inhibiting their feeding, growth, and reproduction through azadirachtin, a bioactive compound that acts as an insect growth regulator and antifeedant. Insecticidal soap spray functions by breaking down the outer protective layer of soft-bodied insects, causing dehydration and cell membrane damage leading to rapid pest mortality. Both methods are effective organic pest control options, with neem oil providing systemic effects and insecticidal soaps offering immediate contact action.
Target Pests: Effectiveness Against Common Garden Insects
Neem oil is highly effective against a wide range of common garden pests including aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, and scale insects due to its ability to disrupt insect hormones and feeding. Insecticidal soap spray primarily targets soft-bodied insects such as aphids, mealybugs, and thrips by breaking down their protective outer coating, causing dehydration. Both treatments provide organic pest control options, but neem oil offers broader pest management including fungal issues, making it suitable for diverse garden environments.
Safety for Beneficial Insects and Pollinators
Neem oil application targets pest insects while exhibiting low toxicity to beneficial insects and pollinators such as bees and ladybugs, preserving ecological balance. Insecticidal soap spray, though effective against soft-bodied pests, can harm non-target beneficial insects upon direct contact due to its broad-spectrum activity. Selecting neem oil ensures safer pest control by minimizing collateral damage to essential pollinators and natural predators vital for sustainable agriculture.
Application Methods: Best Practices for Use
Neem oil application requires thorough coverage of plant surfaces, preferably applied during early morning or late afternoon to avoid leaf burn, and should be diluted with water according to label instructions for effective pest control. Insecticidal soap spray must be sprayed directly onto pests and affected areas, ensuring repeated applications every 7-10 days for sustained efficacy, and is best used in cool, dry conditions to prevent rapid evaporation. Both methods demand careful timing and adherence to dilution rates to maximize pest suppression while minimizing plant stress.
Impact on Plant Health and Potential Phytotoxicity
Neem oil application offers broad-spectrum pest control with minimal risk of phytotoxicity when properly diluted, promoting overall plant health by targeting insect pests while preserving beneficial organisms. Insecticidal soap spray effectively disrupts soft-bodied insect pests but can cause leaf burn or spotting, particularly under high temperatures or direct sunlight, potentially stressing plants. Choosing between neem oil and insecticidal soap depends on plant sensitivity, environmental conditions, and pest type to optimize pest management without compromising plant vitality.
Frequency and Timing of Applications
Neem oil applications are most effective when applied every 7 to 14 days, preferably during early morning or late afternoon to avoid leaf burn and maximize pest control. Insecticidal soap sprays require more frequent use, often every 3 to 7 days, especially during active pest infestations, ensuring thorough coverage on the undersides of leaves. Timing applications during cooler parts of the day enhances efficacy and reduces plant stress for both treatments.
Environmental Impact and Residue Concerns
Neem oil application offers a lower environmental impact due to its biodegradable nature and targeted pest control, minimizing harm to beneficial insects. Insecticidal soap spray can leave residues that may affect soil and water quality if overused. Both methods require careful application to reduce ecological disruption and ensure safe residue levels.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Neem oil generally costs more per ounce compared to insecticidal soap spray but offers longer-lasting pest control, potentially reducing overall application frequency and expenses. Insecticidal soap sprays are widely available at garden centers and retail stores, often sold in larger, more affordable quantities suitable for regular use. Cost-effectiveness depends on the scale of treatment, with insecticidal soap favored for large infestations due to lower upfront costs and neem oil preferred for targeted, sustained pest management.
Choosing the Right Pest Control for Your Garden
Neem oil effectively targets a wide range of garden pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites by disrupting their hormonal systems and acting as a natural insecticide. Insecticidal soap spray offers a rapid knockdown of soft-bodied insects through its ability to break down their protective outer coatings, making it ideal for immediate pest infestation control. Selecting between neem oil and insecticidal soap depends on pest type and infestation severity; neem oil provides longer residual protection while insecticidal soap excels in quick pest eradication with minimal plant toxicity.
Neem oil application vs insecticidal soap spray Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com