
Organic pesticides vs Synthetic pesticides Illustration
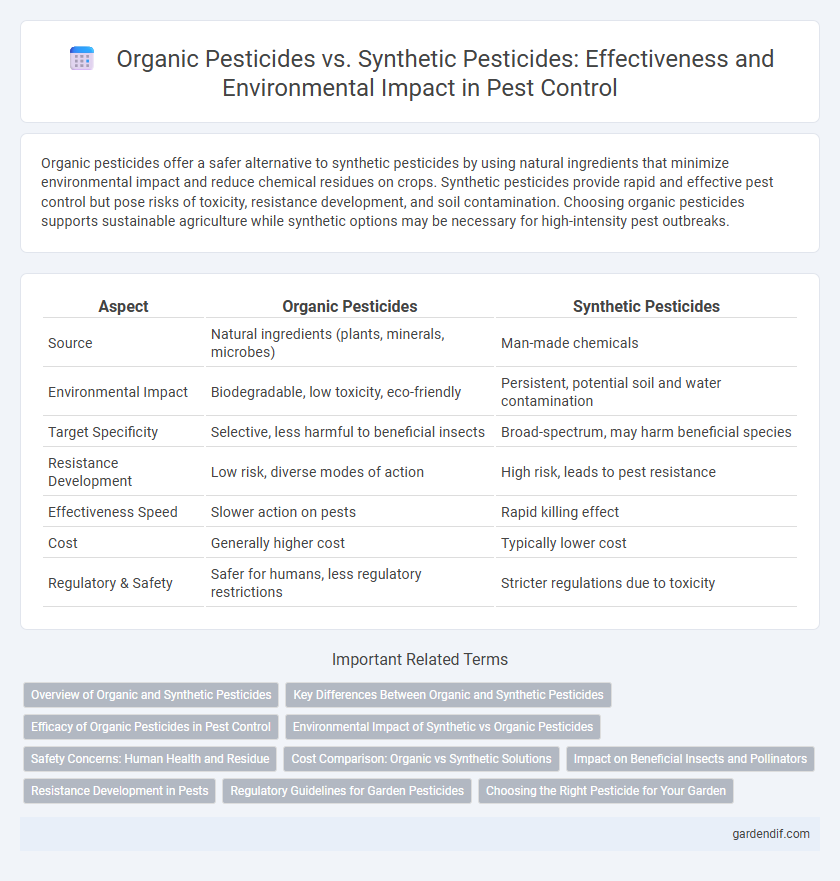
Organic pesticides offer a safer alternative to synthetic pesticides by using natural ingredients that minimize environmental impact and reduce chemical residues on crops. Synthetic pesticides provide rapid and effective pest control but pose risks of toxicity, resistance development, and soil contamination. Choosing organic pesticides supports sustainable agriculture while synthetic options may be necessary for high-intensity pest outbreaks.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Organic Pesticides | Synthetic Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural ingredients (plants, minerals, microbes) | Man-made chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity, eco-friendly | Persistent, potential soil and water contamination |
| Target Specificity | Selective, less harmful to beneficial insects | Broad-spectrum, may harm beneficial species |
| Resistance Development | Low risk, diverse modes of action | High risk, leads to pest resistance |
| Effectiveness Speed | Slower action on pests | Rapid killing effect |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Typically lower cost |
| Regulatory & Safety | Safer for humans, less regulatory restrictions | Stricter regulations due to toxicity |
Overview of Organic and Synthetic Pesticides
Organic pesticides are derived from natural sources such as plants, minerals, or microorganisms, offering biodegradable and environmentally friendly pest control solutions. Synthetic pesticides, created through chemical synthesis, tend to have higher potency and longer-lasting effects but may pose greater risks to human health and ecosystems. Both types play critical roles in integrated pest management, balancing efficacy with safety and sustainability concerns.
Key Differences Between Organic and Synthetic Pesticides
Organic pesticides, derived from natural sources such as plants, minerals, and microorganisms, typically break down more rapidly in the environment, reducing long-term ecological impact. Synthetic pesticides, manufactured through chemical processes, often provide more consistent and targeted pest control but may persist longer in soil and water, raising concerns about toxicity and bioaccumulation. The key differences lie in their chemical composition, environmental persistence, and potential effects on non-target organisms and human health.
Efficacy of Organic Pesticides in Pest Control
Organic pesticides exhibit effective pest control by utilizing natural compounds such as neem oil, pyrethrin, and spinosad, which target specific pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects and the environment. These substances often degrade faster than synthetic chemicals, reducing the risk of residue buildup and resistance development in pest populations. Studies indicate organic pesticides can maintain adequate control levels in integrated pest management systems, especially when applied preventively or combined with cultural practices.
Environmental Impact of Synthetic vs Organic Pesticides
Synthetic pesticides often pose significant risks to ecosystems due to their persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity to non-target species such as beneficial insects and aquatic life. Organic pesticides, derived from natural sources like plant extracts and microorganisms, generally break down more quickly and have a reduced environmental footprint. Studies indicate that organic pesticides contribute less to soil and water contamination, promoting biodiversity and sustainable pest management.
Safety Concerns: Human Health and Residue
Organic pesticides generally pose fewer safety concerns for human health due to their natural ingredients and lower toxicity levels, reducing the risk of harmful residue on food crops. Synthetic pesticides, while often more effective at pest control, carry higher risks of chemical residues that can persist on produce and potentially contribute to chronic health issues. Regulatory agencies frequently monitor residue levels to ensure synthetic pesticide exposure remains within safe limits, but concerns about long-term effects and environmental accumulation persist.
Cost Comparison: Organic vs Synthetic Solutions
Organic pesticides generally have higher upfront costs compared to synthetic pesticides due to the natural ingredients and slower production processes involved. Synthetic pesticides are often more cost-effective in large-scale applications because of mass production and longer shelf life. However, long-term expenses may favor organic options as they reduce pest resistance and environmental damage, lowering the need for repeated treatments.
Impact on Beneficial Insects and Pollinators
Organic pesticides generally have a lower toxicity to beneficial insects and pollinators compared to synthetic pesticides, helping preserve essential ecosystem services like pollination and natural pest control. Synthetic pesticides often contain chemical compounds that can cause sub-lethal effects or mortality in bees, butterflies, and other beneficial arthropods, disrupting pollination cycles and biodiversity. Understanding the differential impact on beneficial insects highlights the importance of choosing pest management strategies that protect these crucial contributors to agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
Resistance Development in Pests
Organic pesticides generally slow resistance development in pests due to their complex mixtures of active compounds, which reduce the likelihood of pests adapting quickly. Synthetic pesticides often target specific biochemical pathways, leading to faster resistance buildup as pests develop genetic mutations against a single mode of action. Overreliance on synthetic pesticides accelerates resistance, necessitating integrated pest management strategies combining both organic and synthetic solutions to sustain efficacy.
Regulatory Guidelines for Garden Pesticides
Regulatory guidelines for garden pesticides differentiate strictly between organic and synthetic pesticides, emphasizing safety and environmental impact. Organic pesticides often undergo rigorous evaluation to ensure they meet standards for biodegradability and non-toxicity to beneficial insects, aligning with organic gardening certifications. Synthetic pesticides are regulated with detailed restrictions on chemical composition, application rates, and residue limits to minimize risks to human health and ecosystems, as enforced by agencies like the EPA and EU's EFSA.
Choosing the Right Pesticide for Your Garden
Organic pesticides offer environmentally friendly pest control by using natural ingredients that minimize harm to beneficial insects and soil health. Synthetic pesticides provide fast-acting, targeted solutions but may contribute to resistance and environmental pollution. Selecting the right pesticide depends on your garden's specific pest issues, plant types, and your preference for sustainability versus immediate efficacy.
Organic pesticides vs Synthetic pesticides Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com