
Diatomaceous earth vs Slug pellets Illustration
Diatomaceous earth offers a natural, non-toxic alternative to slug pellets by physically damaging the exoskeletons of slugs, causing dehydration and death without harmful chemicals. Slug pellets typically contain metaldehyde or iron phosphate, which can be effective but pose risks to pets, wildlife, and the environment if misused. Using diatomaceous earth promotes a safer, eco-friendly approach to pest control, minimizing collateral damage while maintaining garden health.
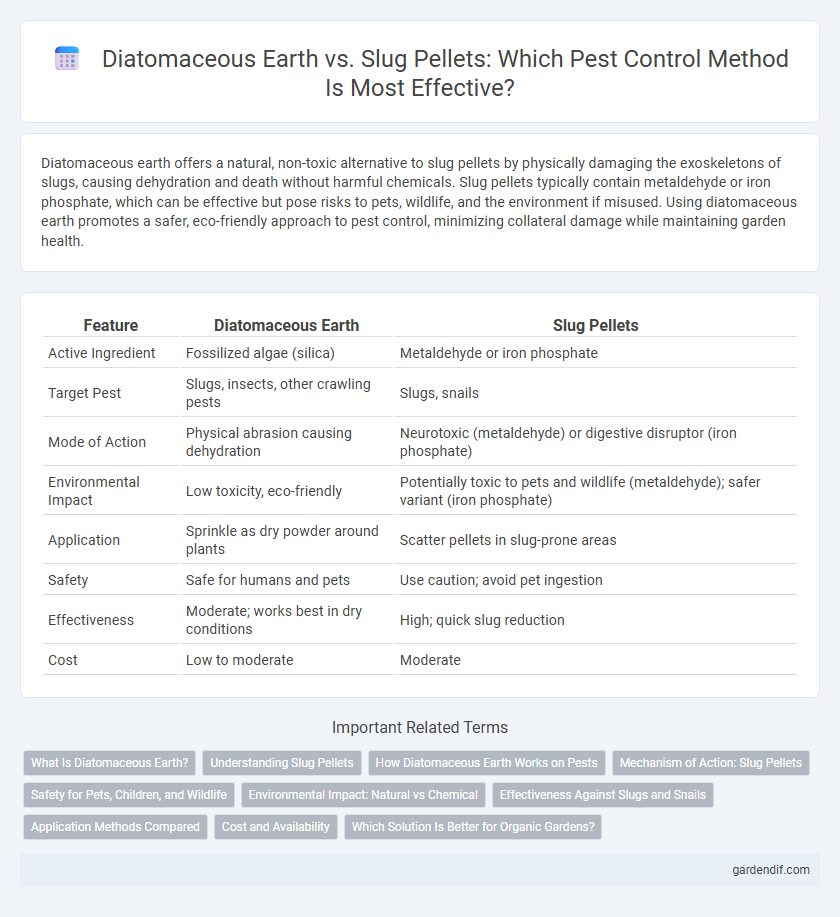
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Diatomaceous Earth | Slug Pellets |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Fossilized algae (silica) | Metaldehyde or iron phosphate |
| Target Pest | Slugs, insects, other crawling pests | Slugs, snails |
| Mode of Action | Physical abrasion causing dehydration | Neurotoxic (metaldehyde) or digestive disruptor (iron phosphate) |
| Environmental Impact | Low toxicity, eco-friendly | Potentially toxic to pets and wildlife (metaldehyde); safer variant (iron phosphate) |
| Application | Sprinkle as dry powder around plants | Scatter pellets in slug-prone areas |
| Safety | Safe for humans and pets | Use caution; avoid pet ingestion |
| Effectiveness | Moderate; works best in dry conditions | High; quick slug reduction |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate |
What Is Diatomaceous Earth?
Diatomaceous earth is a natural, silica-based powder derived from fossilized remains of diatoms, microscopic algae with hard shells. It acts as a non-toxic pest control agent by physically damaging the exoskeletons of slugs and other insects, causing dehydration and death. Unlike chemical slug pellets, diatomaceous earth provides an eco-friendly option that minimizes harm to beneficial organisms and reduces environmental impact.
Understanding Slug Pellets
Slug pellets contain metaldehyde or iron phosphate, which act as chemical baits to effectively control slug populations in gardens and agricultural fields. While slug pellets provide targeted and fast-acting pest control, their toxicity to pets, wildlife, and beneficial insects demands careful handling and application. In contrast, diatomaceous earth offers a natural, non-toxic alternative by physically damaging slug exoskeletons, but it requires dry conditions and repeated applications for optimal effectiveness.
How Diatomaceous Earth Works on Pests
Diatomaceous earth eliminates pests by physically damaging their exoskeletons, causing dehydration and eventual death. Its microscopic silica particles pierce the protective outer layer of insects like slugs and other crawling pests. This natural, chemical-free method offers a safer alternative to toxic slug pellets, minimizing environmental impact while effectively reducing pest populations.
Mechanism of Action: Slug Pellets
Slug pellets contain metaldehyde or iron phosphate, which disrupt the slug's mucus production and nervous system, causing dehydration and paralysis. Upon ingestion, the toxic compounds interfere with the slug's cellular function, ultimately leading to death. This chemical mechanism is highly effective in controlling slug populations in gardens and agricultural settings.
Safety for Pets, Children, and Wildlife
Diatomaceous earth is a natural, non-toxic option that poses minimal risk to pets, children, and wildlife, making it a safer choice for pest control in homes and gardens. In contrast, traditional slug pellets often contain metaldehyde or other chemicals that can be highly toxic if ingested by animals or children, requiring careful storage and application. Choosing diatomaceous earth reduces the likelihood of accidental poisoning while effectively managing slug populations through physical dehydration.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Chemical
Diatomaceous earth offers a natural, non-toxic alternative to slug pellets, minimizing harm to beneficial insects, soil health, and water quality. Slug pellets often contain chemicals like metaldehyde, posing risks of toxicity to pets, wildlife, and contaminating ecosystems. Choosing diatomaceous earth supports sustainable pest control with a lower environmental footprint.
Effectiveness Against Slugs and Snails
Diatomaceous earth effectively controls slugs and snails by damaging their soft bodies, causing dehydration and death, while being environmentally safe and non-toxic to pets and humans. Slug pellets, containing metaldehyde or iron phosphate, deliver rapid results by poisoning slugs but pose risks to wildlife, pets, and beneficial insects. Diatomaceous earth offers a sustainable, slower-acting method that reduces slug populations without chemical residues.
Application Methods Compared
Diatomaceous earth is applied as a dry powder spread around plants or soil surfaces, creating a physical barrier that damages pests' exoskeletons upon contact. Slug pellets are typically scattered or broadcasted in granular form, releasing toxic chemicals that slugs ingest when feeding. The non-toxic, residue-free nature of diatomaceous earth makes it ideal for organic gardens, while slug pellets require careful handling due to potential environmental and pet toxicity.
Cost and Availability
Diatomaceous earth is often more cost-effective and widely available in garden centers and online compared to slug pellets, which may be pricier due to chemical ingredients. Slug pellets, though sometimes more immediately effective, can be harder to find in organic or eco-friendly varieties, increasing costs for sustainable gardeners. Bulk purchasing options for diatomaceous earth further reduce expenses and ensure steady availability throughout the gardening season.
Which Solution Is Better for Organic Gardens?
Diatomaceous earth offers a natural, non-toxic solution for controlling slugs in organic gardens by physically damaging their exoskeletons, making it safer for beneficial insects and pets. Slug pellets typically contain chemicals like metaldehyde or iron phosphate, which can be effective but may pose risks to wildlife and soil health. For organic gardening, diatomaceous earth is generally preferred due to its environmental safety and compliance with organic standards.
Diatomaceous earth vs Slug pellets Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com