
Diatomaceous earth vs Clay dust Illustration
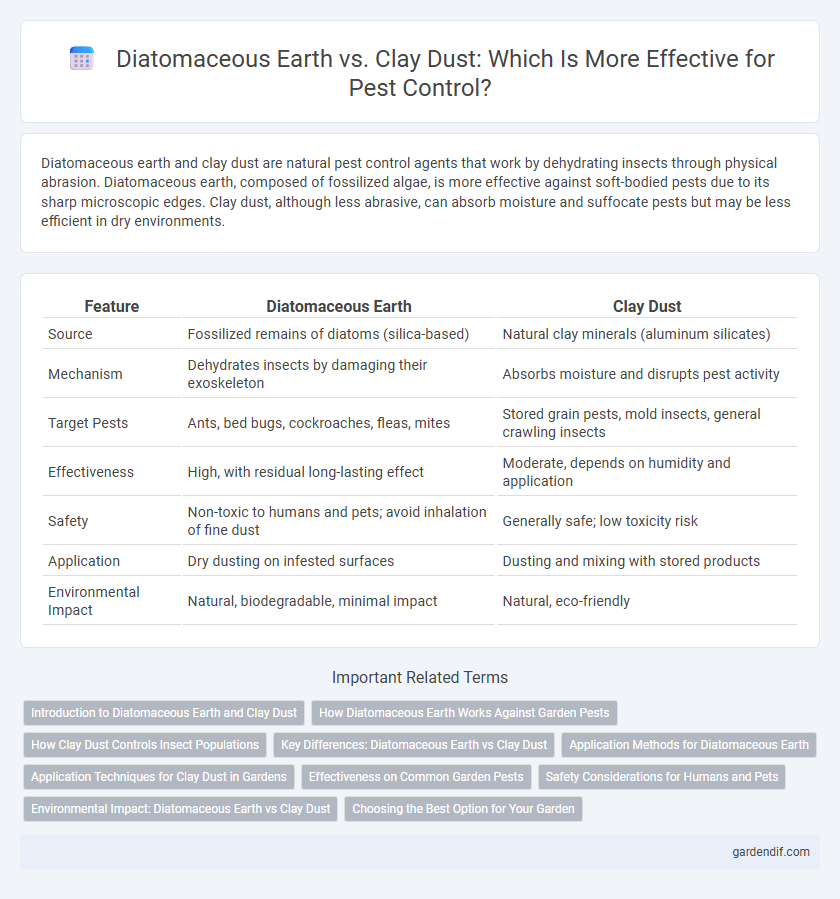
Diatomaceous earth and clay dust are natural pest control agents that work by dehydrating insects through physical abrasion. Diatomaceous earth, composed of fossilized algae, is more effective against soft-bodied pests due to its sharp microscopic edges. Clay dust, although less abrasive, can absorb moisture and suffocate pests but may be less efficient in dry environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Diatomaceous Earth | Clay Dust |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fossilized remains of diatoms (silica-based) | Natural clay minerals (aluminum silicates) |
| Mechanism | Dehydrates insects by damaging their exoskeleton | Absorbs moisture and disrupts pest activity |
| Target Pests | Ants, bed bugs, cockroaches, fleas, mites | Stored grain pests, mold insects, general crawling insects |
| Effectiveness | High, with residual long-lasting effect | Moderate, depends on humidity and application |
| Safety | Non-toxic to humans and pets; avoid inhalation of fine dust | Generally safe; low toxicity risk |
| Application | Dry dusting on infested surfaces | Dusting and mixing with stored products |
| Environmental Impact | Natural, biodegradable, minimal impact | Natural, eco-friendly |
Introduction to Diatomaceous Earth and Clay Dust
Diatomaceous earth is a naturally occurring, silica-based powder derived from fossilized diatoms, used as a non-toxic insecticide for pest control by physically damaging insect exoskeletons. Clay dust, composed primarily of fine mineral particles such as bentonite or kaolin, works by absorbing lipids from insect exoskeletons, leading to desiccation and death. Both substances offer environmentally friendly pest management alternatives, with diatomaceous earth favored for its mechanical action and clay dust valued for its moisture-absorbing properties.
How Diatomaceous Earth Works Against Garden Pests
Diatomaceous earth combats garden pests through its abrasive, microscopic silica particles that damage the exoskeletons of insects like aphids, ants, and beetles, causing dehydration and death. This natural, non-toxic powder adheres to pests as they crawl through treated areas, providing effective pest control without harmful chemicals. Unlike clay dust, which primarily absorbs moisture, diatomaceous earth physically disrupts pest physiology, making it a preferred choice for organic garden pest management.
How Clay Dust Controls Insect Populations
Clay dust controls insect populations by physically abrading the protective waxy layer on insect exoskeletons, leading to dehydration and death. Its fine particles adhere to pests like ants, bed bugs, and cockroaches, disrupting their mobility and respiration. Unlike diatomaceous earth, clay dust's mineral composition offers a unique abrasive effect that enhances its pest control efficiency.
Key Differences: Diatomaceous Earth vs Clay Dust
Diatomaceous earth is composed of fossilized algae shells with abrasive and absorbent properties that damage insect exoskeletons, leading to dehydration. Clay dust, primarily made of fine mineral particles like bentonite or kaolin, works by absorbing moisture and creating a physical barrier but lacks the abrasive action of diatomaceous earth. The key differences lie in their mechanisms, where diatomaceous earth causes physical damage to pests, while clay dust mainly disrupts pests through moisture absorption and surface coverage.
Application Methods for Diatomaceous Earth
Diatomaceous earth is applied by dusting it directly onto pest-prone surfaces or mixing it with water for spray applications, ensuring thorough coverage and contact with insects. It is most effective in dry environments where moisture does not reduce its insecticidal properties. Clay dust, unlike diatomaceous earth, is primarily used as a soil amendment and does not offer the same pest control benefits when applied in the same manner.
Application Techniques for Clay Dust in Gardens
Clay dust is applied in gardens primarily as a natural pest control method by creating a barrier that deters soft-bodied insects such as slugs and aphids from reaching plants. The dust should be evenly spread in a thin layer around the base of plants, ensuring dry conditions for maximum adhesion and effectiveness. Reapplication is necessary after rainfall or overhead watering to maintain the protective coating and continuous pest deterrence.
Effectiveness on Common Garden Pests
Diatomaceous earth is highly effective against common garden pests such as aphids, slugs, and ants by physically damaging their exoskeletons and causing dehydration. Clay dust, while less commonly used, can repel certain insects by creating a barrier but lacks the desiccating properties of diatomaceous earth. Studies show diatomaceous earth provides longer-lasting pest control in moist garden environments compared to clay dust, which tends to wash away more easily.
Safety Considerations for Humans and Pets
Diatomaceous earth is considered safer for humans and pets due to its natural, non-toxic composition, primarily consisting of fossilized algae that mechanically disrupts pest exoskeletons without chemical exposure. Clay dust, while effective in pest control, can pose respiratory risks if inhaled excessively, making protective measures essential during application. Choosing diatomaceous earth over clay dust reduces potential health hazards, especially in homes with children or animals, due to its minimal irritation and safer handling profile.
Environmental Impact: Diatomaceous Earth vs Clay Dust
Diatomaceous earth is composed of fossilized algae, making it a natural and biodegradable pest control option with minimal environmental toxicity. Clay dust, typically derived from finely ground minerals, can pose respiratory hazards and may contribute to soil compaction, affecting local ecosystems negatively. The ecological footprint of diatomaceous earth tends to be lower, promoting sustainable pest management practices without chemical residues.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Garden
Diatomaceous earth offers an effective, natural pest control solution by targeting a wide range of insects through its abrasive silica structure, making it ideal for organic gardens. Clay dust provides residual benefits by smothering soft-bodied pests and improving soil quality with its mineral content, which can enhance plant health. Selecting the best option depends on your garden's pest types and soil needs, with diatomaceous earth favored for insect deterrence and clay dust preferred for soil enrichment and pest suppression.
Diatomaceous earth vs Clay dust Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com