
Chemical pesticides vs organic pesticides Illustration
Chemical pesticides provide rapid and effective pest control by targeting a wide range of insects and weeds but often pose risks to human health and the environment due to their toxic residues. Organic pesticides, derived from natural sources, offer a safer alternative with lower environmental impact and reduced toxicity, promoting sustainable agriculture. Choosing between chemical and organic pesticides depends on balancing the need for immediate pest management and long-term ecological safety.
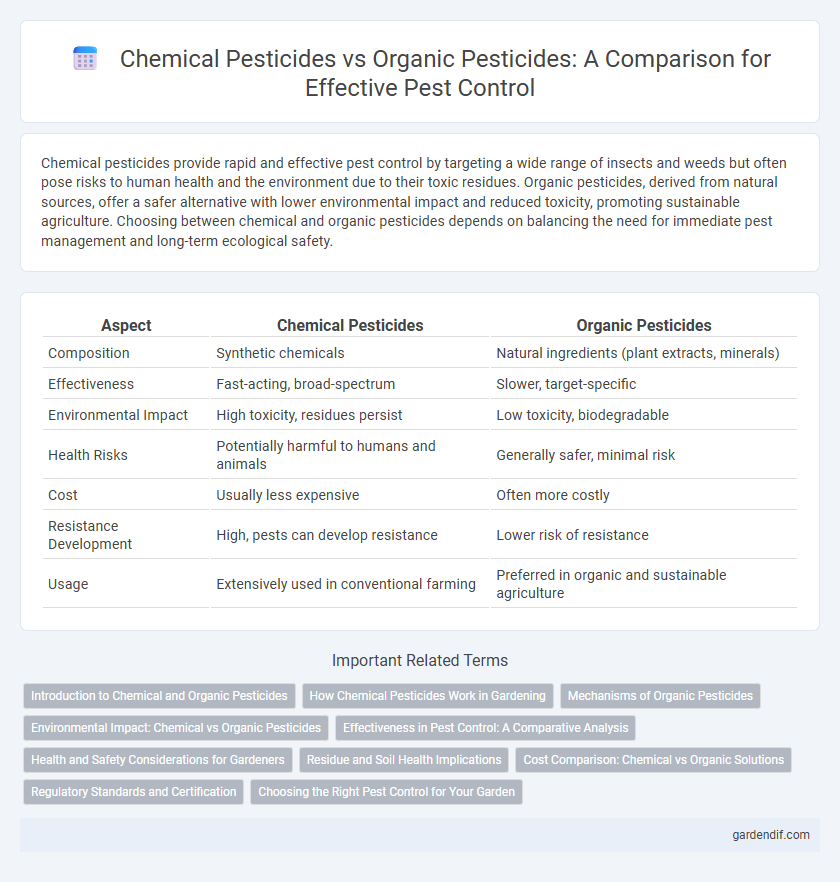
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Chemical Pesticides | Organic Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic chemicals | Natural ingredients (plant extracts, minerals) |
| Effectiveness | Fast-acting, broad-spectrum | Slower, target-specific |
| Environmental Impact | High toxicity, residues persist | Low toxicity, biodegradable |
| Health Risks | Potentially harmful to humans and animals | Generally safer, minimal risk |
| Cost | Usually less expensive | Often more costly |
| Resistance Development | High, pests can develop resistance | Lower risk of resistance |
| Usage | Extensively used in conventional farming | Preferred in organic and sustainable agriculture |
Introduction to Chemical and Organic Pesticides
Chemical pesticides are synthetic compounds widely used for rapid and effective control of pests in agricultural and urban settings, offering high potency but raising concerns about environmental impact and human health. Organic pesticides, derived from natural sources such as plants, microorganisms, or minerals, provide eco-friendly alternatives with lower toxicity and reduced persistence in ecosystems. Understanding the differences in composition, application methods, and effects on biodiversity is crucial for integrated pest management strategies aiming to balance efficacy and sustainability.
How Chemical Pesticides Work in Gardening
Chemical pesticides work in gardening by targeting specific pests through neurotoxic compounds that disrupt the nervous system or by interfering with essential biological processes such as reproduction and feeding. These synthetic chemicals offer rapid and effective pest control but can also impact non-target organisms and soil health. Understanding the mode of action and environmental impact of chemical pesticides is crucial for optimizing their use in integrated pest management strategies.
Mechanisms of Organic Pesticides
Organic pesticides primarily rely on natural substances such as plant extracts, essential oils, and microbial agents to control pests by disrupting their physiological processes or repelling them without harmful residues. These mechanisms include targeting the nervous system of insects, inhibiting their growth and reproduction, or inducing deterrence through volatile compounds. Unlike chemical pesticides, organic alternatives often enhance soil health and biodiversity while reducing chemical resistance in pest populations.
Environmental Impact: Chemical vs Organic Pesticides
Chemical pesticides often contribute to soil degradation, water contamination, and harm to non-target species, leading to long-term environmental damage. Organic pesticides, derived from natural sources, tend to break down more quickly and pose fewer risks to ecosystems and beneficial organisms. This reduced environmental footprint makes organic options a more sustainable choice for pest management.
Effectiveness in Pest Control: A Comparative Analysis
Chemical pesticides offer rapid and broad-spectrum pest control by targeting specific physiological processes in insects, often resulting in immediate reduction of pest populations. Organic pesticides, derived from natural substances like neem oil or pyrethrin, provide effective pest suppression with lower environmental toxicity but may require more frequent applications. Studies show chemical pesticides achieve higher short-term effectiveness, whereas organic pesticides support sustainable pest management with reduced risks of resistance and environmental impact.
Health and Safety Considerations for Gardeners
Chemical pesticides often contain synthetic compounds that can pose health risks such as skin irritation, respiratory problems, and long-term toxicity if proper protective measures are not used. Organic pesticides, derived from natural sources like plant extracts or beneficial microbes, generally present fewer hazards and are safer for gardeners to handle, reducing chemical exposure and contamination. Choosing organic options supports sustainable gardening practices by minimizing environmental impact and protecting the health of both gardeners and surrounding ecosystems.
Residue and Soil Health Implications
Chemical pesticides often leave harmful residues that persist in soil and water, potentially disrupting microbial ecosystems and harming beneficial organisms. Organic pesticides, made from natural substances, generally break down more quickly and pose less risk of long-term soil contamination. Maintaining soil health benefits from reduced chemical residue accumulation, which supports biodiversity and sustainable agricultural practices.
Cost Comparison: Chemical vs Organic Solutions
Chemical pesticides generally offer lower upfront costs compared to organic pesticides due to mass production and synthetic ingredients. Organic pesticides often have higher initial expenses but provide long-term benefits such as improved soil health and reduced environmental impact. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires factoring in recurring application rates, potential resistance development, and regulatory compliance expenses.
Regulatory Standards and Certification
Chemical pesticides are subject to stringent regulatory standards established by agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, which mandate rigorous testing for toxicity, environmental impact, and residue levels before approval. Organic pesticides must comply with certification programs like the USDA National Organic Program (NOP), which enforces strict guidelines on ingredient sourcing and prohibits synthetic chemical components. Compliance with these regulatory frameworks ensures that both chemical and organic pesticides meet safety, efficacy, and environmental protection criteria vital for sustainable pest management.
Choosing the Right Pest Control for Your Garden
Chemical pesticides offer fast and effective pest elimination but may harm beneficial insects and soil health, risking long-term garden sustainability. Organic pesticides rely on natural ingredients like neem oil or insecticidal soap, promoting ecological balance and reducing chemical residues. Selecting the right pest control involves assessing pest severity, crop type, and environmental impact to maintain a healthy, thriving garden ecosystem.
Chemical pesticides vs organic pesticides Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com