
trap cropping vs border planting Illustration
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops that attract pests away from the main crop, effectively reducing pest damage by concentrating pests on sacrificial plants. Border planting creates physical or biological barriers around the main crop using plants that repel or deter pests, preventing them from reaching the valuable crops. Both strategies leverage plant diversification to manage pest populations sustainably and reduce reliance on chemical pesticides.
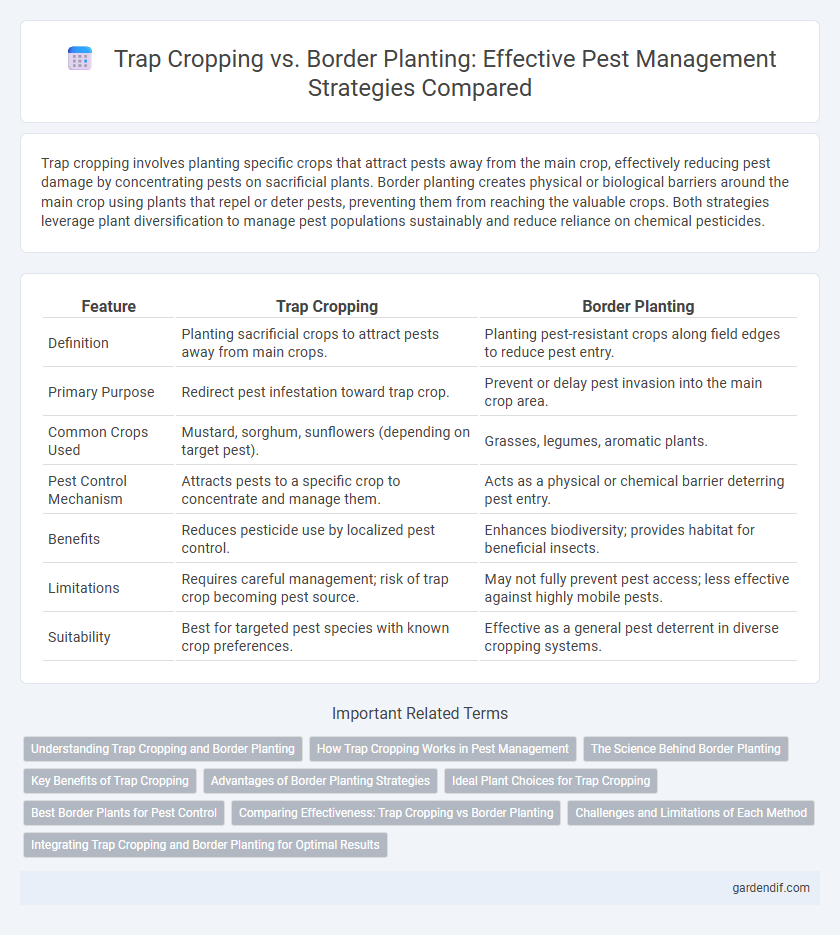
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Trap Cropping | Border Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planting sacrificial crops to attract pests away from main crops. | Planting pest-resistant crops along field edges to reduce pest entry. |
| Primary Purpose | Redirect pest infestation toward trap crop. | Prevent or delay pest invasion into the main crop area. |
| Common Crops Used | Mustard, sorghum, sunflowers (depending on target pest). | Grasses, legumes, aromatic plants. |
| Pest Control Mechanism | Attracts pests to a specific crop to concentrate and manage them. | Acts as a physical or chemical barrier deterring pest entry. |
| Benefits | Reduces pesticide use by localized pest control. | Enhances biodiversity; provides habitat for beneficial insects. |
| Limitations | Requires careful management; risk of trap crop becoming pest source. | May not fully prevent pest access; less effective against highly mobile pests. |
| Suitability | Best for targeted pest species with known crop preferences. | Effective as a general pest deterrent in diverse cropping systems. |
Understanding Trap Cropping and Border Planting
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops that attract pests away from the main crop, effectively reducing pest damage by concentrating pests in controlled areas. Border planting utilizes certain plants along the edges of fields to create a physical or chemical barrier that deters or distracts pests from entering the main crop zone. Both strategies enhance integrated pest management by targeting pest behavior and movement, minimizing pesticide usage and crop losses.
How Trap Cropping Works in Pest Management
Trap cropping functions by planting a highly attractive crop species near the main crop to divert pest insects away, reducing damage to the primary plants. This method exploits pest behavior and feeding preferences, concentrating pests in a manageable area where they can be controlled through targeted treatments or removal. Effective trap cropping enhances integrated pest management by lowering pesticide use and preserving crop health.
The Science Behind Border Planting
Border planting involves strategically placing specific plants around crop fields to attract and contain pests, exploiting insect behavior and host preference. Scientific studies reveal that this method disrupts pest colonization by providing a trap zone, reducing pest pressure on the main crops. The effectiveness of border planting depends on selecting the right plant species that act as attractants or repellents based on pest ecology and life cycle.
Key Benefits of Trap Cropping
Trap cropping effectively reduces pest populations by attracting pests away from main crops, minimizing damage and pesticide usage. It enhances integrated pest management by promoting natural pest control through habitat for beneficial insects. Compared to border planting, trap cropping offers targeted pest diversion, resulting in higher crop yields and sustainable pest suppression.
Advantages of Border Planting Strategies
Border planting strategies enhance pest management by creating a physical barrier that reduces pest entry into main crops, promoting ecological balance through habitat diversification. This method fosters the presence of natural predators and beneficial insects, thereby minimizing the need for chemical pesticides and supporting sustainable agriculture. Crop yield improves as border plants suppress pest populations more effectively than trap cropping, which often attracts pests closer to the main crop.
Ideal Plant Choices for Trap Cropping
Ideal plant choices for trap cropping include species that are more attractive to pests than the main crop, such as mustard for aphids or radish for flea beetles. Effective trap crops must have a strong pest-attracting chemical profile and quick growth to lure pests away from valuable plants. Selecting trap crops with synchronized growth cycles and pest-specific appeal ensures enhanced pest management and crop protection.
Best Border Plants for Pest Control
Effective border plants for pest control include marigolds, nasturtiums, and chives, which repel harmful insects while attracting beneficial predators. These plants create a natural barrier that reduces pest invasion into main crops by disrupting pest movement and feeding patterns. Choosing diverse border plants enhances biodiversity and strengthens integrated pest management strategies in agricultural systems.
Comparing Effectiveness: Trap Cropping vs Border Planting
Trap cropping attracts pests away from main crops by using sacrificial plants, significantly reducing pest damage and minimizing pesticide use. Border planting creates a physical or ecological barrier, which can deter pest movement but is generally less effective at diverting pests compared to trap cropping. Studies show trap cropping provides more targeted pest control and higher crop yield protection than border planting in integrated pest management programs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Trap cropping faces challenges such as the risk of attracting more pests than can be managed, requiring precise timing and maintenance to prevent pest spillover into main crops. Border planting is limited by its dependence on crop and pest species compatibility, often providing inconsistent pest suppression due to variable pest behavior and environmental factors. Both methods require careful monitoring and integration with other pest management strategies to be effective.
Integrating Trap Cropping and Border Planting for Optimal Results
Integrating trap cropping and border planting enhances pest management by strategically positioning sacrificial plants to lure pests away from the main crop while establishing protective barriers that restrict pest movement. This combined approach maximizes pest suppression, reduces reliance on chemical controls, and promotes healthier crop growth. Empirical studies show that synchronizing trap crops with border planting increases pest diversion efficiency by up to 40%, optimizing integrated pest management strategies.
trap cropping vs border planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com