
Beneficial insects vs harmful pests Illustration
Beneficial insects play a crucial role in controlling harmful pests by preying on them and reducing their populations naturally. These helpful species, such as ladybugs and parasitic wasps, contribute to maintaining ecological balance and minimizing the need for chemical pesticides. Understanding the distinction between beneficial insects and harmful pests is essential for effective integrated pest management strategies.
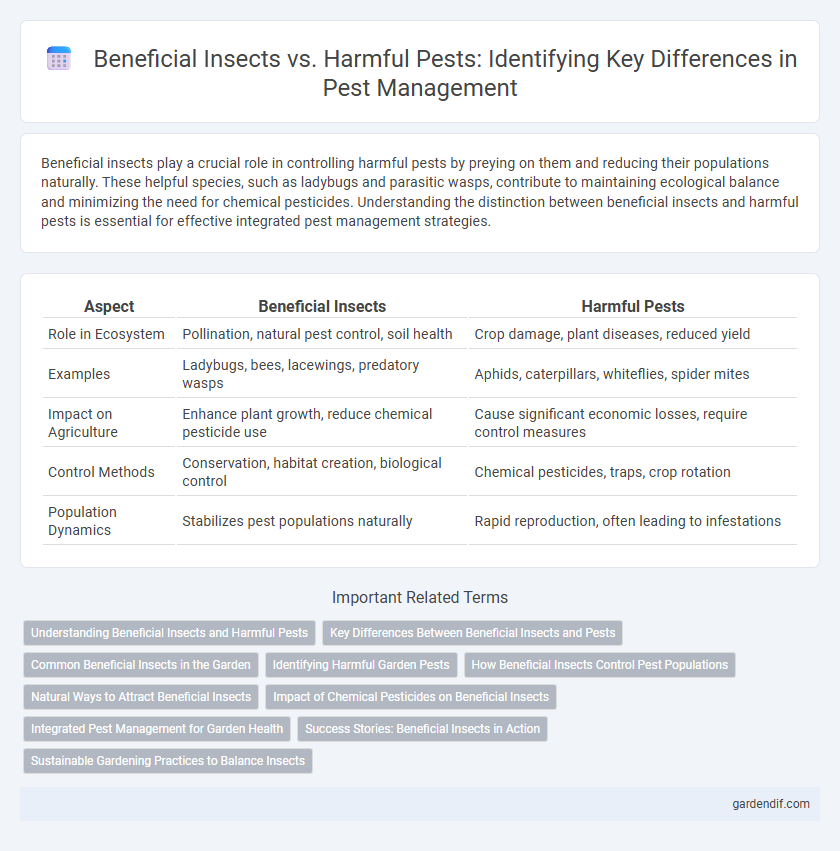
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Beneficial Insects | Harmful Pests |
|---|---|---|
| Role in Ecosystem | Pollination, natural pest control, soil health | Crop damage, plant diseases, reduced yield |
| Examples | Ladybugs, bees, lacewings, predatory wasps | Aphids, caterpillars, whiteflies, spider mites |
| Impact on Agriculture | Enhance plant growth, reduce chemical pesticide use | Cause significant economic losses, require control measures |
| Control Methods | Conservation, habitat creation, biological control | Chemical pesticides, traps, crop rotation |
| Population Dynamics | Stabilizes pest populations naturally | Rapid reproduction, often leading to infestations |
Understanding Beneficial Insects and Harmful Pests
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory beetles play a crucial role in natural pest control by feeding on harmful pests like aphids, mites, and caterpillars that damage crops and gardens. Understanding the behaviors and life cycles of these insects enables effective pest management strategies that reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and promote ecological balance. Monitoring insect populations and fostering habitats with flowering plants supports the proliferation of beneficial species, helping to suppress pest outbreaks naturally.
Key Differences Between Beneficial Insects and Pests
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, and bees play crucial roles in pollination, natural pest control, and maintaining ecological balance, whereas harmful pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites damage crops by feeding on plants and spreading diseases. Beneficial insects contribute to sustainable agriculture by reducing the need for chemical pesticides, while pests cause significant economic losses by reducing crop yield and quality. Understanding these key differences helps in implementing integrated pest management strategies that promote beneficial insect populations and suppress harmful pest outbreaks.
Common Beneficial Insects in the Garden
Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory wasps are common beneficial insects in the garden, playing crucial roles in controlling aphids, mites, and other harmful pests naturally. These insects reduce the need for chemical pesticides by preying on destructive pests that damage plants and crops. Incorporating flowering plants and maintaining habitat diversity encourages the presence of these beneficial predators, promoting a healthier and more sustainable garden ecosystem.
Identifying Harmful Garden Pests
Identifying harmful garden pests involves recognizing species such as aphids, caterpillars, and spider mites that damage plants by feeding on leaves, stems, or roots, leading to stunted growth and reduced yields. Beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory beetles naturally control these pests by preying on them, promoting a balanced ecosystem. Early detection of harmful pests enables targeted interventions, minimizing chemical use and supporting sustainable garden health.
How Beneficial Insects Control Pest Populations
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps play a crucial role in controlling pest populations by preying on harmful insects like aphids, caterpillars, and scale insects. These predatory and parasitic species naturally reduce the need for chemical pesticides by maintaining ecological balance within gardens and agricultural fields. By encouraging beneficial insect habitats through diverse planting and minimizing pesticide use, pest outbreaks can be effectively managed and crop health improved.
Natural Ways to Attract Beneficial Insects
Attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps naturally reduces harmful pest populations in gardens and farms. Planting diverse flowering plants such as dill, fennel, and yarrow provides nectar and pollen resources crucial for these insects' survival and reproduction. Creating habitats with organic mulch and avoiding chemical pesticides further supports a balanced ecosystem where beneficial insects thrive and control pests effectively.
Impact of Chemical Pesticides on Beneficial Insects
Chemical pesticides often cause significant harm to beneficial insects such as bees, ladybugs, and predatory wasps, drastically reducing their populations and disrupting natural pest control. The decline of these beneficial species leads to increased pest outbreaks, as natural predators and pollinators play essential roles in maintaining ecosystem balance and crop health. Sustainable pest management practices prioritize minimizing chemical pesticide use to protect beneficial insect populations and promote long-term agricultural productivity.
Integrated Pest Management for Garden Health
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs and predatory wasps play a crucial role in controlling harmful pests like aphids and caterpillars by naturally reducing their populations. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) combines the use of these beneficial insects with cultural, mechanical, and chemical strategies to maintain garden health while minimizing environmental impact. Emphasizing biological pest control within IPM enhances sustainable gardening practices and promotes a balanced ecosystem.
Success Stories: Beneficial Insects in Action
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps play a crucial role in controlling harmful pests like aphids, whiteflies, and caterpillars, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Successful case studies in agricultural systems demonstrate significant crop protection and yield improvement through the introduction of these natural predators. Sustainable pest management programs leveraging beneficial insects have led to decreased pest populations and increased biodiversity, showcasing their effectiveness in integrated pest management (IPM).
Sustainable Gardening Practices to Balance Insects
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings play a crucial role in sustainable gardening by naturally controlling harmful pests like aphids and caterpillars. Implementing companion planting and maintaining diverse habitats supports these helpful species, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Balanced insect populations enhance garden health, promote biodiversity, and ensure long-term pest management sustainability.
Beneficial insects vs harmful pests Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com