
Hügelkultur vs Sheet Mulching Illustration
Hugelkultur enhances soil fertility and water retention by layering wood, compost, and soil to create raised garden beds that mimic natural forest ecosystems. Sheet mulching suppresses weeds and improves soil structure through layered organic materials, such as cardboard and mulch, decomposing directly on the ground. Both techniques promote sustainable gardening by increasing microbial activity and conserving moisture, but hugelkultur is better suited for creating elevated planting sites while sheet mulching is ideal for ground-level soil building.
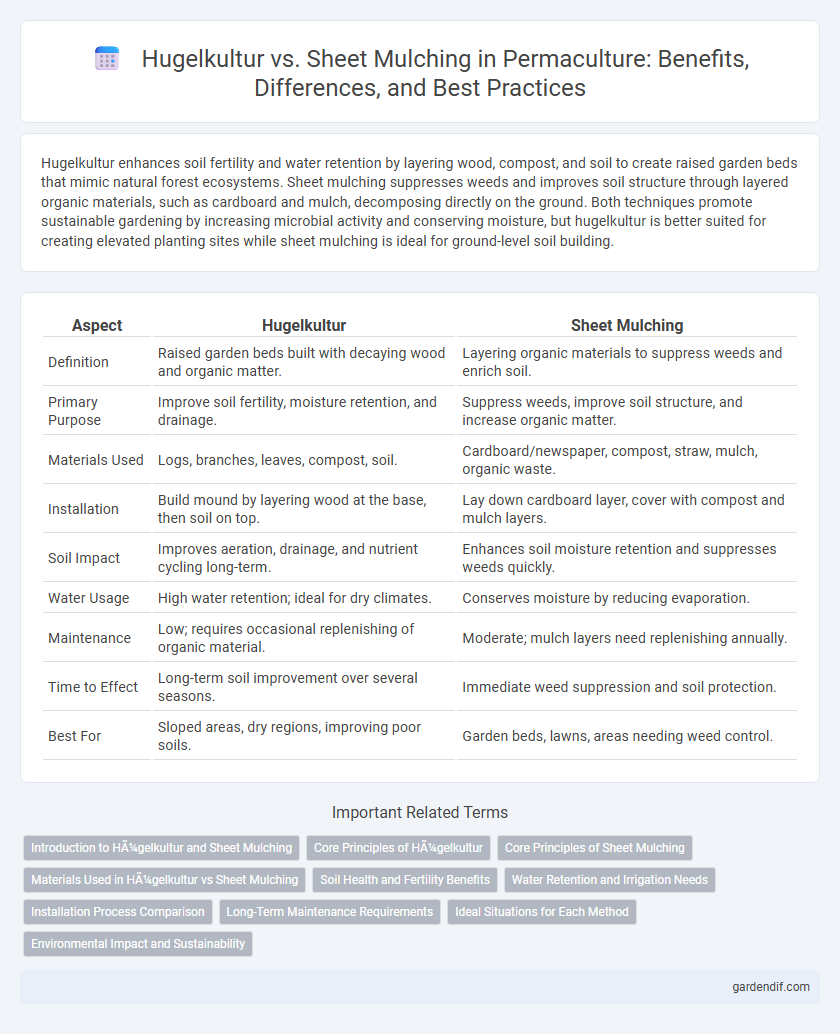
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hugelkultur | Sheet Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raised garden beds built with decaying wood and organic matter. | Layering organic materials to suppress weeds and enrich soil. |
| Primary Purpose | Improve soil fertility, moisture retention, and drainage. | Suppress weeds, improve soil structure, and increase organic matter. |
| Materials Used | Logs, branches, leaves, compost, soil. | Cardboard/newspaper, compost, straw, mulch, organic waste. |
| Installation | Build mound by layering wood at the base, then soil on top. | Lay down cardboard layer, cover with compost and mulch layers. |
| Soil Impact | Improves aeration, drainage, and nutrient cycling long-term. | Enhances soil moisture retention and suppresses weeds quickly. |
| Water Usage | High water retention; ideal for dry climates. | Conserves moisture by reducing evaporation. |
| Maintenance | Low; requires occasional replenishing of organic material. | Moderate; mulch layers need replenishing annually. |
| Time to Effect | Long-term soil improvement over several seasons. | Immediate weed suppression and soil protection. |
| Best For | Sloped areas, dry regions, improving poor soils. | Garden beds, lawns, areas needing weed control. |
Introduction to Hügelkultur and Sheet Mulching
Hugelkultur is a permaculture technique that involves creating raised garden beds using decaying wood and organic matter to improve soil fertility and moisture retention. Sheet mulching, also known as lasagna gardening, builds soil by layering organic materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on the ground to suppress weeds and enhance soil health. Both methods promote sustainable soil management, with Hugelkultur emphasizing vertical planting surfaces and decomposition, while sheet mulching focuses on improving flat soil layers through layered organic inputs.
Core Principles of Hügelkultur
Hugelkultur is a sustainable gardening method centered on creating raised beds by layering decomposing wood, organic matter, and soil, which enhances water retention and nutrient cycling. This technique mimics natural forest processes, promoting soil aeration, microbial activity, and long-term fertility through slow decomposition. In contrast to sheet mulching, Hugelkultur emphasizes building vertical soil profiles to improve drainage and create microclimates conducive to diverse plant growth.
Core Principles of Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching centers on building soil health by layering organic materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on the ground to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and promote microbial activity. This technique mimics natural decomposition processes, enriching soil fertility over time without disturbing the existing soil structure. Unlike Hugelkultur, which emphasizes raised beds with wood logs for nutrient cycling and moisture retention, sheet mulching prioritizes creating a biodegradable mulch barrier that enhances soil quality and plant growth through continuous organic matter breakdown.
Materials Used in Hügelkultur vs Sheet Mulching
Hugelkultur relies on decomposing wood, branches, and organic matter like leaf litter and grass clippings as base materials, creating a raised garden bed rich in nutrients and moisture retention. Sheet mulching uses layers of cardboard or newspaper topped with compost, straw, and mulch to suppress weeds and build soil fertility over time. Both methods integrate natural, biodegradable materials but differ fundamentally in their physical structure and decomposition dynamics within permaculture systems.
Soil Health and Fertility Benefits
Hugelkultur enhances soil health by creating raised beds with decomposing wood and organic matter that improve moisture retention, nutrient release, and microbial activity over time. Sheet mulching builds fertile soil through layering organic materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch, which suppress weeds, retain moisture, and boost microbial diversity. Both methods increase soil fertility and structure, but hugelkultur provides longer-term nutrient cycling while sheet mulching offers quicker soil conditioning and weed control.
Water Retention and Irrigation Needs
Hugelkultur enhances water retention by using decomposing wood and organic matter that slowly release moisture, reducing irrigation frequency. Sheet mulching improves soil moisture by creating a protective layer that minimizes evaporation and encourages microbial activity but typically requires more consistent watering. Both methods optimize water use in permaculture, with hugelkultur best suited for drier environments and sheet mulching beneficial for maintaining steady soil hydration levels.
Installation Process Comparison
Hugelkultur involves constructing raised garden beds by layering logs, branches, and organic matter, which requires significant initial labor and sourcing of woody debris. Sheet mulching, alternatively, consists of layering cardboard or newspaper over soil, topped with compost and mulch, making it quicker and easier to install with readily available materials. Both techniques improve soil fertility and moisture retention but differ greatly in their physical installation demands and materials used.
Long-Term Maintenance Requirements
Hugelkultur beds require minimal long-term maintenance as decomposing wood gradually enriches the soil, reducing the need for frequent watering and fertilization. Sheet mulching demands periodic replenishment of organic layers to sustain soil health and suppress weeds effectively. Both methods improve soil fertility, but hugelkultur offers a low-maintenance solution suited for long-term permaculture systems.
Ideal Situations for Each Method
Hugelkultur is ideal for areas with poor soil drainage or low fertility, as it creates raised beds that improve aeration and nutrient retention through decomposing woody material. Sheet mulching suits flat or gently sloped sites with existing vegetation, effectively suppressing weeds and enriching soil by layering organic matter directly on the ground. Both methods enhance soil health but align best with different terrain and moisture conditions in permaculture design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hugelkultur enhances soil moisture retention and promotes carbon sequestration through decomposing woody materials, fostering long-term soil fertility and biodiversity. Sheet mulching reduces waste by repurposing organic matter into layers that suppress weeds and improve soil structure with minimal disturbance. Both practices support sustainable gardening, but Hugelkultur's deeper biomass integration offers greater potential for carbon storage and resilience in drought-prone environments.
Hügelkultur vs Sheet Mulching Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com