
Greywater Systems vs Rainwater Harvesting Illustration
Greywater systems recycle lightly used water from sinks, showers, and laundry to irrigate gardens, reducing household water consumption and minimizing wastewater discharge. Rainwater harvesting collects and stores rain from roofs for various uses, including irrigation and household needs, promoting water independence especially in dry climates. Combining greywater recycling with rainwater harvesting enhances water efficiency and strengthens sustainable permaculture practices.
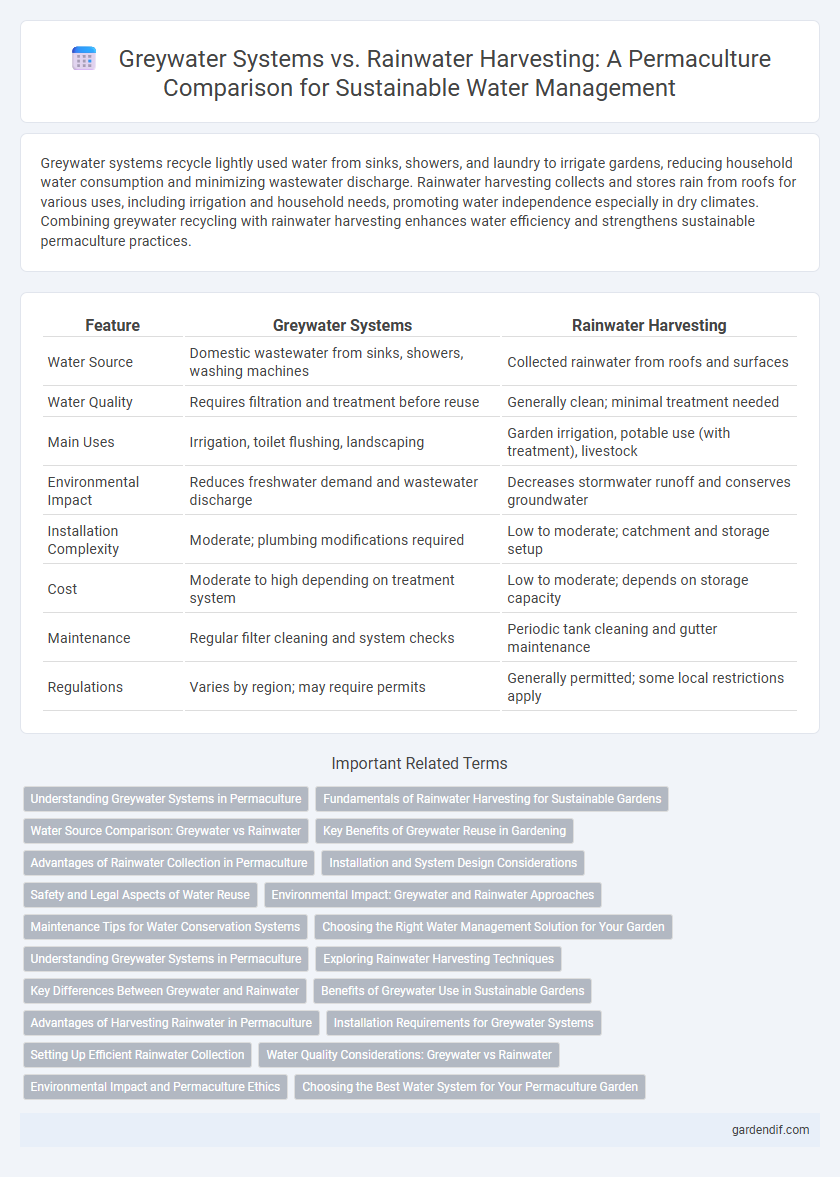
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Greywater Systems | Rainwater Harvesting |
|---|---|---|
| Water Source | Domestic wastewater from sinks, showers, washing machines | Collected rainwater from roofs and surfaces |
| Water Quality | Requires filtration and treatment before reuse | Generally clean; minimal treatment needed |
| Main Uses | Irrigation, toilet flushing, landscaping | Garden irrigation, potable use (with treatment), livestock |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces freshwater demand and wastewater discharge | Decreases stormwater runoff and conserves groundwater |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate; plumbing modifications required | Low to moderate; catchment and storage setup |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on treatment system | Low to moderate; depends on storage capacity |
| Maintenance | Regular filter cleaning and system checks | Periodic tank cleaning and gutter maintenance |
| Regulations | Varies by region; may require permits | Generally permitted; some local restrictions apply |
Understanding Greywater Systems in Permaculture
Greywater systems in permaculture efficiently recycle water from baths, sinks, and laundry to irrigate landscapes, reducing freshwater demand. These systems improve soil moisture levels and support plant growth by redirecting nutrient-rich water directly to gardens. Proper filtration and treatment are crucial to prevent contamination and maintain sustainable water cycles within permaculture designs.
Fundamentals of Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Gardens
Rainwater harvesting captures and stores rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces to irrigate gardens, reducing dependence on municipal water supplies and promoting sustainability. Essential components include catchment areas, gutters, filtration systems, and storage tanks designed to optimize water quality and availability. Integrating rainwater harvesting with permaculture principles enhances water conservation, soil health, and plant resilience by providing a reliable, natural irrigation source throughout the growing season.
Water Source Comparison: Greywater vs Rainwater
Greywater systems recycle household wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry, providing a consistent, nutrient-rich water source ideal for irrigating gardens in permaculture designs. Rainwater harvesting collects precipitation from rooftops and surfaces, offering a pure, chemical-free supply that depends on local rainfall patterns and seasonal variation. Choosing between greywater and rainwater systems depends on water availability, treatment needs, and specific permaculture goals such as sustainability and resource efficiency.
Key Benefits of Greywater Reuse in Gardening
Greywater reuse in gardening conserves freshwater by recycling household water from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation, reducing overall water consumption by up to 50%. This system lowers wastewater discharge and nutrient runoff, promoting soil health through the retention of beneficial organic matter and nutrients. Implementing greywater systems enhances plant growth and resilience while supporting sustainable permaculture practices by optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Advantages of Rainwater Collection in Permaculture
Rainwater collection in permaculture enhances water self-sufficiency by capturing cleaner water directly from rooftops, reducing reliance on municipal systems and minimizing greywater contamination risks. It supports plant health by providing naturally soft, chemical-free water rich in oxygen, which benefits soil microbiology and boosts crop yields. Moreover, rainwater harvesting offers scalable storage solutions that efficiently manage seasonal rainfall, promoting resilience during dry periods and conserving valuable groundwater resources.
Installation and System Design Considerations
Greywater systems require careful plumbing integration with household wastewater flows to separate and redirect gently used water, emphasizing filtration and safe dispersal methods to prevent contamination. Rainwater harvesting involves designing collection surfaces, gutters, and storage tanks optimized for local rainfall patterns, ensuring efficient capture and minimal debris entry into the system. Both systems demand site-specific planning to balance water quality needs, maintenance accessibility, and regulatory compliance for sustainable permaculture water management.
Safety and Legal Aspects of Water Reuse
Greywater systems must comply with local health regulations to ensure water does not pose a contamination risk, often requiring treatment or specific usage restrictions to protect human and environmental safety. Rainwater harvesting typically faces fewer legal constraints but must adhere to municipal codes regarding storage and usage to prevent mosquito breeding and contamination. Both systems demand careful management to balance sustainability goals with public health standards and legal compliance.
Environmental Impact: Greywater and Rainwater Approaches
Greywater systems reduce freshwater demand by recycling household wastewater for irrigation, lowering overall water consumption and decreasing strain on municipal water sources. Rainwater harvesting captures and stores precipitation, mitigating stormwater runoff and reducing erosion while providing a sustainable water supply during dry periods. Both methods enhance permaculture's environmental impact by promoting water conservation, reducing pollution, and improving soil health.
Maintenance Tips for Water Conservation Systems
Regular inspection and cleaning of filters in greywater systems prevent clogging and maintain efficient water flow, while rainwater harvesting requires routine gutter and tank cleaning to avoid debris buildup and mosquito breeding. Employing biodegradable soaps in greywater systems safeguards soil health and plant growth, whereas sealing rainwater tanks reduces contamination risks and water loss through evaporation. Scheduling seasonal checks for leaks or structural damage ensures long-term functionality and maximizes water conservation efficiency in both systems.
Choosing the Right Water Management Solution for Your Garden
Greywater systems recycle household wastewater from sinks and showers, providing a sustainable irrigation source that reduces freshwater consumption and supports soil health in permaculture gardens. Rainwater harvesting captures and stores rainfall from rooftops, offering a cost-effective, chemical-free water supply ideal for drought-prone areas and improving water resilience. Selecting the right system depends on garden size, local climate, water quality needs, and regulatory considerations, ensuring efficient water management aligned with permaculture principles.
Greywater Systems vs Rainwater Harvesting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com