
Companion Planting vs Mono-planting Illustration
Companion planting enhances ornamental gardens by promoting natural pest control and improving soil health through synergistic plant relationships. This method increases biodiversity and aesthetic appeal, contrasting with mono-planting, which often leads to soil depletion and higher vulnerability to pests and diseases. Choosing companion plants strategically supports sustainable growth and vibrant, resilient garden landscapes.
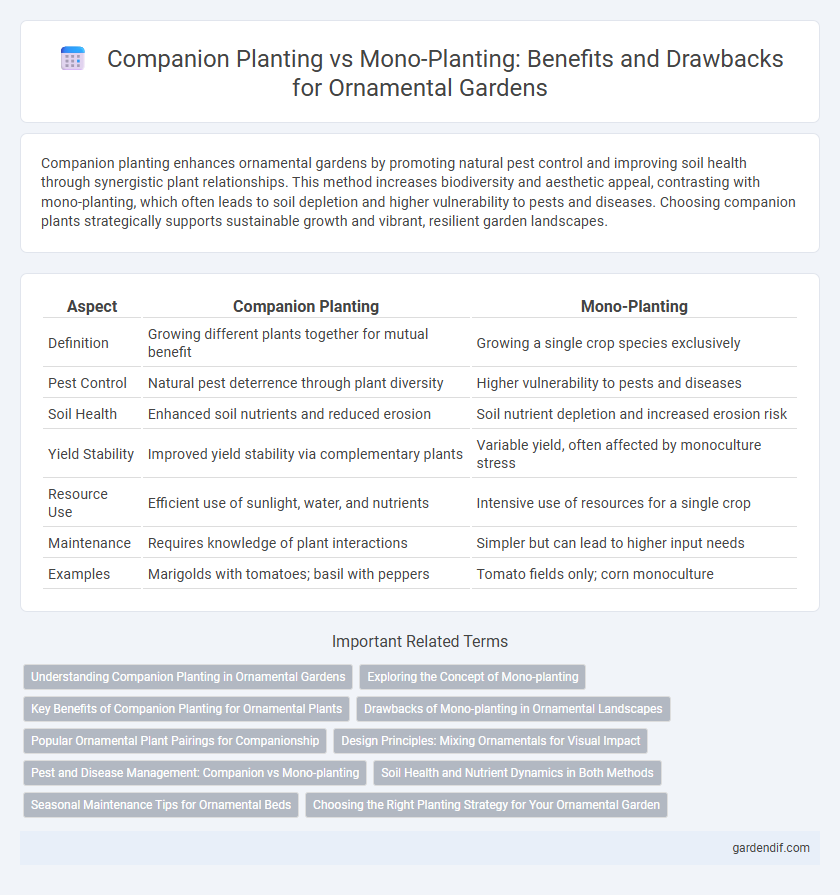
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Companion Planting | Mono-Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing different plants together for mutual benefit | Growing a single crop species exclusively |
| Pest Control | Natural pest deterrence through plant diversity | Higher vulnerability to pests and diseases |
| Soil Health | Enhanced soil nutrients and reduced erosion | Soil nutrient depletion and increased erosion risk |
| Yield Stability | Improved yield stability via complementary plants | Variable yield, often affected by monoculture stress |
| Resource Use | Efficient use of sunlight, water, and nutrients | Intensive use of resources for a single crop |
| Maintenance | Requires knowledge of plant interactions | Simpler but can lead to higher input needs |
| Examples | Marigolds with tomatoes; basil with peppers | Tomato fields only; corn monoculture |
Understanding Companion Planting in Ornamental Gardens
Companion planting in ornamental gardens enhances plant health and visual appeal by strategically pairing species that support each other's growth and deter pests. This method promotes biodiversity, reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, and improves soil fertility compared to mono-planting, which often leads to nutrient depletion and increased vulnerability to diseases. Integrating companion plants like marigolds, lavender, and nasturtiums nurtures a resilient and thriving ornamental ecosystem.
Exploring the Concept of Mono-planting
Mono-planting, the practice of cultivating a single plant species in a specific area, contrasts sharply with the diversity found in ornamental companion planting. This method simplifies maintenance and pest management but can increase vulnerability to diseases and nutrient depletion due to the lack of plant variety. Research in ornamental horticulture highlights that while mono-planting allows for uniform aesthetics, it often reduces ecological benefits such as pest control and soil health provided by companion plants.
Key Benefits of Companion Planting for Ornamental Plants
Companion planting enhances ornamental plants by promoting natural pest control, improving pollination, and increasing overall plant health through beneficial interactions. Diverse plant pairings reduce the risk of disease spread compared to mono-planting, creating a resilient garden ecosystem. Companion plants like marigolds and petunias can repel pests and attract pollinators, boosting flower quality and garden aesthetics.
Drawbacks of Mono-planting in Ornamental Landscapes
Mono-planting in ornamental landscapes often leads to reduced biodiversity, making plants more susceptible to pests and diseases due to the lack of natural predators and genetic variation. This practice can result in soil nutrient depletion, as the same species repeatedly consume specific nutrients without rotation or replenishment. Consequently, monoculture landscapes may require increased pesticide and fertilizer use, elevating maintenance costs and environmental impact.
Popular Ornamental Plant Pairings for Companionship
Companion planting enhances ornamental garden health by pairing species like marigolds with petunias, which deter pests and boost growth simultaneously. Strategic combinations such as lavender with roses improve fragrance and bloom longevity while minimizing disease risk. Mono-planting lacks these synergistic benefits, often leading to increased vulnerability and less vibrant displays.
Design Principles: Mixing Ornamentals for Visual Impact
Companion planting in ornamental gardens enhances visual impact by combining diverse textures, colors, and heights to create dynamic and harmonious displays. Strategic groupings of plants with complementary bloom times and foliage contrast maximize aesthetic appeal and seasonal interest. Mono-planting, while uniform, often lacks the layered complexity achieved through thoughtful companion design principles emphasizing balance and rhythm.
Pest and Disease Management: Companion vs Mono-planting
Companion planting enhances pest and disease management by introducing plant diversity that naturally repels harmful insects and attracts beneficial predators, reducing the need for chemical interventions. Mono-planting creates a uniform environment that often leads to rapid pest infestations and increased vulnerability to diseases due to the lack of natural barriers and biological controls. Integrating specific companion plants like marigolds or basil around ornamental species can significantly lower pest populations and improve overall plant health.
Soil Health and Nutrient Dynamics in Both Methods
Companion planting enhances soil health by promoting biodiversity, which supports nutrient cycling and improves soil structure through varied root systems and microbial activity. Mono-planting depletes specific nutrients rapidly due to repetitive cropping of the same species, often leading to soil degradation and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. Integrating diverse plants in ornamental gardens optimizes nutrient uptake, reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, and maintains balanced soil fertility over time.
Seasonal Maintenance Tips for Ornamental Beds
Companion planting in ornamental beds promotes biodiversity, reducing pest infestations and improving soil health during seasonal maintenance, unlike mono-planting which can deplete nutrients and increase vulnerability to diseases. Integrating compatible flowers such as marigolds, lavender, or nasturtiums alongside primary ornamental plants enhances natural pest control and supports pollinator activity throughout the growing season. Regular pruning, mulching, and targeted fertilization tailored to mixed plant beds ensure robust growth and vibrant seasonal displays without relying on chemical interventions.
Choosing the Right Planting Strategy for Your Ornamental Garden
Companion planting enhances ornamental gardens by promoting plant health, improving pest resistance, and increasing biodiversity, leading to more vibrant and resilient landscapes. Mono-planting simplifies maintenance and creates uniform visual appeal but often risks pest outbreaks and soil depletion without crop rotation. Selecting the right strategy depends on garden size, plant species compatibility, and desired aesthetic outcomes to ensure sustainable growth and ornamental beauty.
Companion Planting vs Mono-planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com