
Xeriscaping vs Water Gardening Illustration
Xeriscaping emphasizes drought-tolerant plants and efficient water use, creating sustainable landscapes with minimal irrigation. Water gardening incorporates aquatic plants and features like ponds or fountains, enhancing ornamental appeal with vibrant, water-based elements. Choosing between xeriscaping and water gardening depends on climate, water availability, and desired garden aesthetics.
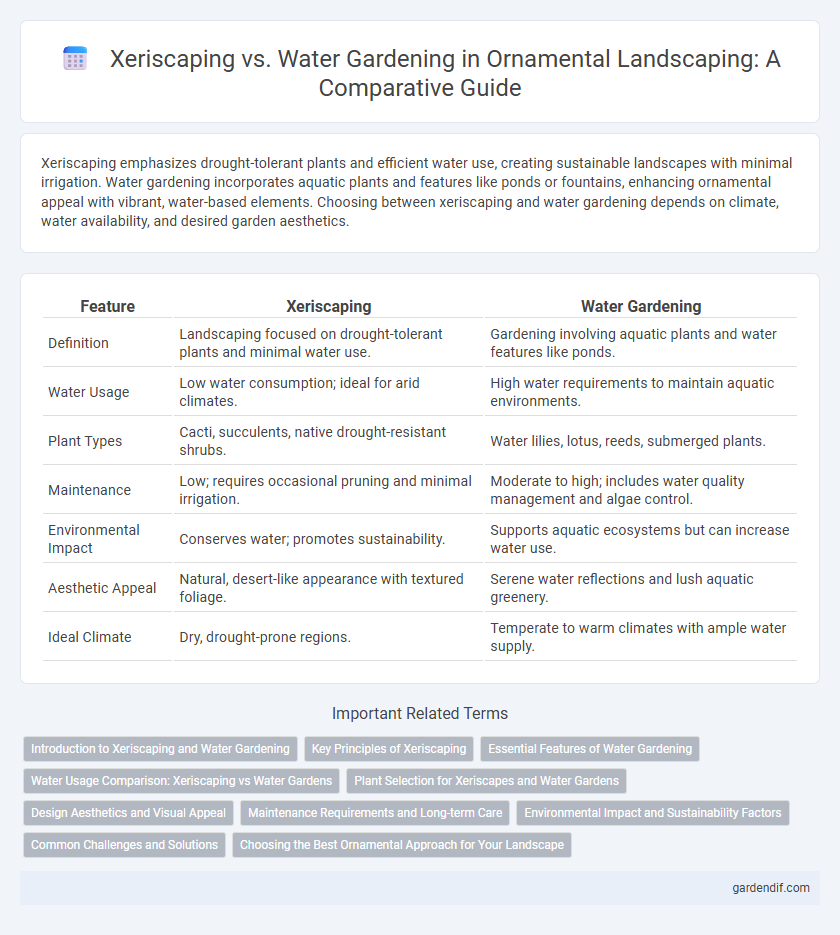
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Xeriscaping | Water Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Landscaping focused on drought-tolerant plants and minimal water use. | Gardening involving aquatic plants and water features like ponds. |
| Water Usage | Low water consumption; ideal for arid climates. | High water requirements to maintain aquatic environments. |
| Plant Types | Cacti, succulents, native drought-resistant shrubs. | Water lilies, lotus, reeds, submerged plants. |
| Maintenance | Low; requires occasional pruning and minimal irrigation. | Moderate to high; includes water quality management and algae control. |
| Environmental Impact | Conserves water; promotes sustainability. | Supports aquatic ecosystems but can increase water use. |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Natural, desert-like appearance with textured foliage. | Serene water reflections and lush aquatic greenery. |
| Ideal Climate | Dry, drought-prone regions. | Temperate to warm climates with ample water supply. |
Introduction to Xeriscaping and Water Gardening
Xeriscaping is a landscaping method focused on water conservation by using drought-tolerant plants, native species, and efficient irrigation techniques, ideal for arid regions. Water gardening involves creating aquatic gardens with features like ponds, water lilies, and fish, emphasizing aesthetics and ecosystem balance in wetter environments. Both practices enhance ornamental landscapes while addressing environmental and resource considerations.
Key Principles of Xeriscaping
Xeriscaping emphasizes water conservation through strategic plant selection, soil improvement, and efficient irrigation methods tailored for ornamental landscapes. Key principles include using drought-tolerant native plants, mulching to retain soil moisture, and designing landscapes with grouped plants based on water needs to minimize waste. This approach contrasts with water gardening, which often involves higher water usage and aquatic features, making xeriscaping ideal for sustainable, low-maintenance ornamental gardening.
Essential Features of Water Gardening
Water gardening emphasizes aquatic plants, fish habitats, and decorative water features like ponds and fountains that enhance aesthetic appeal while supporting local ecosystems. Essential features include proper water filtration, aeration systems, and carefully selected plant species such as water lilies and lotuses to maintain water quality and biodiversity. This approach requires regular maintenance to balance water chemistry and prevent algae growth, distinguishing it from the drought-resistant, low-irrigation principles of xeriscaping.
Water Usage Comparison: Xeriscaping vs Water Gardens
Xeriscaping significantly reduces water consumption by utilizing drought-tolerant plants and efficient irrigation techniques, resulting in up to 50-75% less water usage compared to traditional landscaping. Water gardens, while visually appealing and beneficial for local ecosystems, demand continuous water replenishment to maintain water levels, leading to higher overall water consumption. Choosing xeriscaping is an environmentally sustainable option for regions facing water scarcity, whereas water gardens require careful water management to balance aesthetic and conservation goals.
Plant Selection for Xeriscapes and Water Gardens
Xeriscaping relies on drought-tolerant plants such as succulents, native grasses, and hardy perennials like lavender and agave, which require minimal irrigation and thrive in arid conditions. Water gardening emphasizes aquatic plants like water lilies, lotus, and cattails that grow in or near water bodies, enhancing pond ecosystems while supporting wildlife. Choosing plants based on environmental compatibility ensures sustainable, low-maintenance ornamental landscapes tailored to either dry or aquatic settings.
Design Aesthetics and Visual Appeal
Xeriscaping emphasizes drought-resistant plants and minimalist layouts, creating a clean, structured aesthetic that highlights natural textures and muted color palettes. Water gardening incorporates ponds, fountains, and aquatic plants to develop dynamic, reflective surfaces and lush greenery, offering vibrant color contrasts and movement. Both design approaches enhance outdoor spaces, with xeriscaping delivering sustainability-driven elegance and water gardening providing a tranquil, visually rich environment.
Maintenance Requirements and Long-term Care
Xeriscaping requires minimal maintenance with drought-tolerant plants that reduce watering frequency and soil erosion, making it ideal for sustainable landscapes. Water gardening involves regular care such as pond cleaning, water quality monitoring, and aquatic plant pruning to prevent algae overgrowth and maintain ecosystem balance. Long-term care for xeriscaping focuses on soil health and occasional plant replacement, while water gardening demands consistent attention to filtration systems and aquatic life management.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Xeriscaping significantly reduces water consumption by utilizing drought-tolerant plants, native species, and efficient irrigation techniques, promoting soil health and minimizing chemical runoff. Water gardening, while aesthetically pleasing, often requires substantial water use and maintenance, potentially disrupting local ecosystems through altered water chemistry and invasive species introduction. Sustainable landscaping prioritizes xeriscaping for its lower environmental footprint, enhanced biodiversity, and long-term resource conservation over traditional water-intensive ornamental gardens.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Xeriscaping faces challenges such as soil erosion, plant selection, and initial establishment costs, which can be mitigated by using drought-tolerant native plants and efficient drip irrigation systems. Water gardening often struggles with algae growth, mosquito breeding, and maintaining water quality, addressed through aeration devices, introducing aquatic predators, and regular filtration. Both approaches require tailored maintenance strategies to optimize water usage and ensure healthy, ornamental landscapes.
Choosing the Best Ornamental Approach for Your Landscape
Xeriscaping emphasizes drought-tolerant plants and water-efficient landscaping techniques, making it ideal for arid regions or areas with water restrictions. Water gardening incorporates aquatic plants and water features, enhancing biodiversity and creating a tranquil, decorative focal point in the landscape. Selecting the best ornamental approach depends on regional climate, available water resources, and desired aesthetic effects to balance sustainability with visual appeal.
Xeriscaping vs Water Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com