
Clipping vs Shearing Illustration
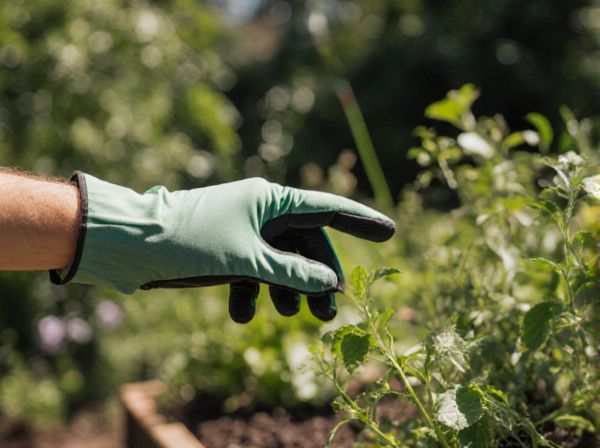
Clipping involves selectively trimming the edges and fine details of ornamental plants to maintain shape and encourage dense growth. Shearing, on the other hand, is a more uniform cut that quickly shapes larger areas, often creating a smooth, manicured appearance. Both techniques enhance the aesthetic appeal but differ in precision and the texture they produce on hedges and topiaries.
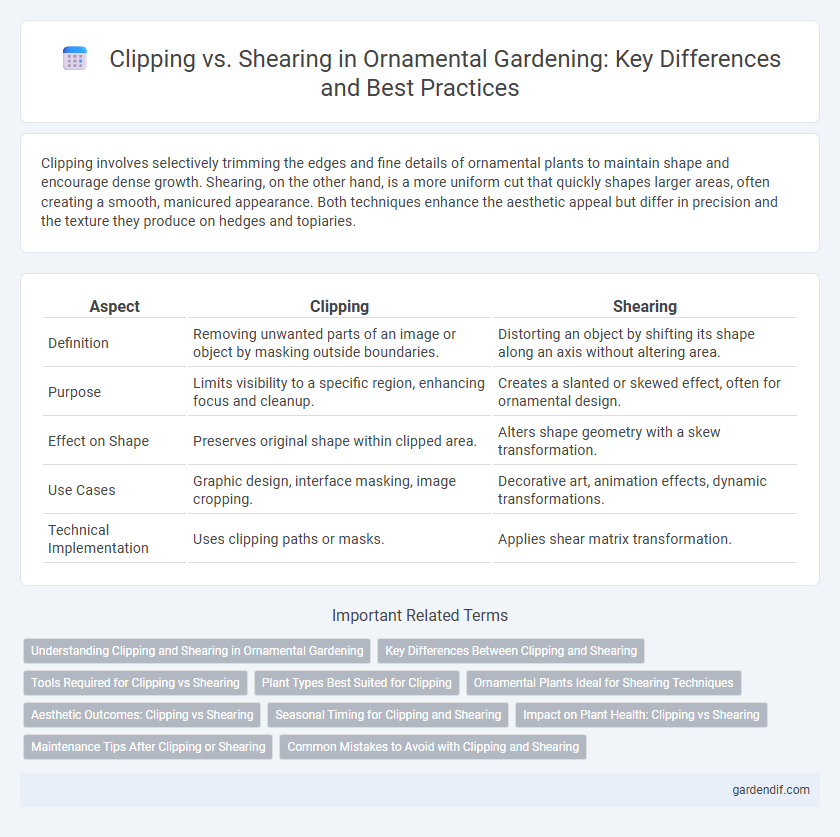
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Clipping | Shearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removing unwanted parts of an image or object by masking outside boundaries. | Distorting an object by shifting its shape along an axis without altering area. |
| Purpose | Limits visibility to a specific region, enhancing focus and cleanup. | Creates a slanted or skewed effect, often for ornamental design. |
| Effect on Shape | Preserves original shape within clipped area. | Alters shape geometry with a skew transformation. |
| Use Cases | Graphic design, interface masking, image cropping. | Decorative art, animation effects, dynamic transformations. |
| Technical Implementation | Uses clipping paths or masks. | Applies shear matrix transformation. |
Understanding Clipping and Shearing in Ornamental Gardening
Clipping in ornamental gardening involves selectively trimming the outer edges of plants to maintain shape and promote dense growth, often used for hedges and topiaries. Shearing, on the other hand, removes larger portions of foliage or branches, providing a more uniform and controlled aesthetic, especially for formal garden designs. Understanding the differences between clipping and shearing ensures precise maintenance techniques that enhance plant health and visual appeal in ornamental landscapes.
Key Differences Between Clipping and Shearing
Clipping in ornamental design involves restricting the visual area by cutting parts of an image or shape to fit within a defined boundary, preserving the original dimensions outside the clipping path. Shearing transforms the shape itself by slanting or skewing it, altering the geometry to create an angular distortion effect. Key differences include that clipping masks hide external content without changing its structure, while shearing modifies the object's form, impacting its alignment and proportions within ornamental patterns.
Tools Required for Clipping vs Shearing
Clipping requires precise hand tools such as pruning shears, secateurs, and manual clippers, ideal for detailed shaping of ornamental plants. Shearing, on the other hand, utilizes larger equipment like hedge trimmers, powered shears, or electric clippers designed for mass trimming and uniform shaping of hedges. The choice between clipping and shearing tools significantly affects the maintenance efficiency and aesthetic precision in ornamental gardening.
Plant Types Best Suited for Clipping
Clipping is best suited for dense, slow-growing plants with small leaves such as boxwood, yew, and privet, which respond well to precise shaping and formal topiary styles. These plants tolerate frequent cuts and maintain their form without excessive stress, making them ideal for creating hedges, patterns, and intricate designs. Ornamental plants with woody stems and tight foliage benefit most from clipping as it encourages lush, compact growth.
Ornamental Plants Ideal for Shearing Techniques
Ornamental plants ideal for shearing techniques include boxwood, privet, yew, and holly, prized for their dense foliage and ability to maintain sharp, clean edges. Shearing enhances the formal appearance of topiaries, hedges, and sculpted garden designs by promoting uniform growth and a polished finish. Regular shearing encourages healthy, bushy development in these species, making them perfect for intricate ornamental shapes.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Clipping vs Shearing
Clipping creates precise, clean lines that enhance the symmetry and formal aesthetic of ornamental plants, making it ideal for topiary and hedges. Shearing produces a natural, softer texture by trimming the outer foliage without distinct shaping, preserving the plant's volume and organic form. Both techniques influence the plant's visual appeal, with clipping emphasizing structure and shearing maintaining a relaxed, lush appearance.
Seasonal Timing for Clipping and Shearing
Clipping is best performed during the active growing season, typically in late spring to early summer, to maintain plant shape and encourage dense growth without causing stress. Shearing, on the other hand, is ideally done in late winter or early spring before new growth begins, allowing for major shaping or size reduction while minimizing damage. Timing these techniques appropriately enhances ornamental plant health and appearance throughout the year.
Impact on Plant Health: Clipping vs Shearing
Clipping precisely removes select plant parts, minimizing stress and promoting healthy regrowth by allowing natural airflow and sunlight penetration. Shearing, often done with hedge trimmers, can cause uniform cuts that may lead to dense foliage, increasing the risk of fungal diseases and reducing overall plant vigor. Optimal plant health depends on using clipping techniques for delicate shaping and reserving shearing for routine maintenance to avoid excessive damage.
Maintenance Tips After Clipping or Shearing
Maintain ornamental plants after clipping or shearing by regularly inspecting for signs of stress or disease to ensure healthy regrowth. Water deeply and consistently, especially after trimming, to support root vitality and reduce shock. Apply a balanced fertilizer tailored for ornamental species to promote lush foliage and vibrant blooms.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Clipping and Shearing
Common mistakes to avoid with clipping and shearing in ornamental gardening include cutting too deeply, which can damage the plant's growth points, and using dull or inappropriate tools that cause uneven cuts or tearing. Over-clipping can stress plants like boxwoods and hedges, leading to weak regrowth or disease susceptibility. Ensuring proper timing during the growth cycle and maintaining sharp shears or clippers enhances plant health and aesthetic form.
Clipping vs Shearing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com