
Biodynamic Compost vs Organic Compost Illustration
Biodynamic compost distinguishes itself from organic compost by incorporating specific preparations based on anthroposophical principles, enhancing soil vitality and microbial activity. While both compost types promote natural nutrient cycling and improve soil health, biodynamic methods emphasize the integration of cosmic rhythms and holistic farm management. This approach results in enriched compost that supports plant resilience and sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
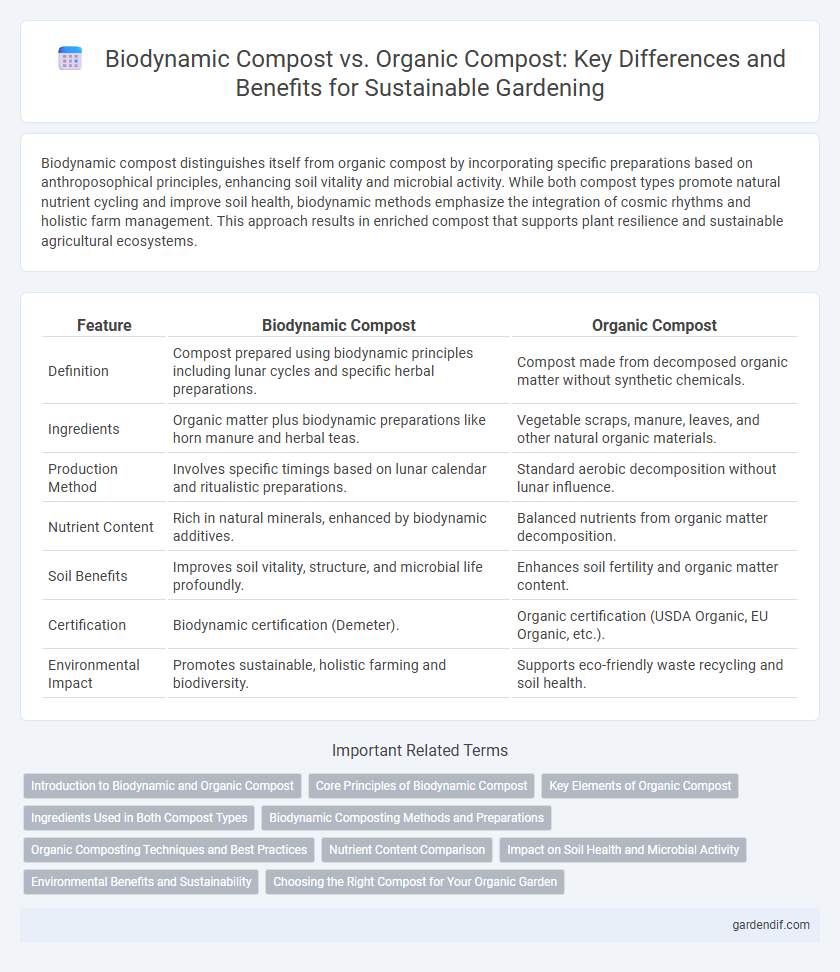
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biodynamic Compost | Organic Compost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compost prepared using biodynamic principles including lunar cycles and specific herbal preparations. | Compost made from decomposed organic matter without synthetic chemicals. |
| Ingredients | Organic matter plus biodynamic preparations like horn manure and herbal teas. | Vegetable scraps, manure, leaves, and other natural organic materials. |
| Production Method | Involves specific timings based on lunar calendar and ritualistic preparations. | Standard aerobic decomposition without lunar influence. |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in natural minerals, enhanced by biodynamic additives. | Balanced nutrients from organic matter decomposition. |
| Soil Benefits | Improves soil vitality, structure, and microbial life profoundly. | Enhances soil fertility and organic matter content. |
| Certification | Biodynamic certification (Demeter). | Organic certification (USDA Organic, EU Organic, etc.). |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainable, holistic farming and biodiversity. | Supports eco-friendly waste recycling and soil health. |
Introduction to Biodynamic and Organic Compost
Biodynamic compost integrates principles from biodynamic agriculture, emphasizing lunar cycles and specific herbal preparations to enhance soil vitality and microbial activity. Organic compost relies on decomposed plant and animal matter, promoting nutrient-rich soil without synthetic chemicals or pesticides. Both methods improve soil health, but biodynamic compost incorporates unique spiritual and ecological approaches for sustainable farming.
Core Principles of Biodynamic Compost
Biodynamic compost emphasizes holistic soil health by integrating specific herbal preparations, animal manures, and astronomical planting calendars to enhance microbial activity and nutrient availability. Its core principles include fostering a self-sustaining ecosystem and using biodynamic preparations like horn manure (500) and horn silica (501) to revitalize soil vitality. Unlike organic compost, biodynamic compost aligns soil fertility with cosmic rhythms, aiming for a dynamic interaction between earth, plants, and celestial forces.
Key Elements of Organic Compost
Key elements of organic compost include decomposed plant material, microbial activity, and balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratios essential for soil enrichment. Biodynamic compost, while organic, incorporates specific preparations like herbal additives and lunar cycle considerations to enhance nutrient cycling and soil vitality. Organic compost primarily emphasizes natural decomposition processes to improve soil structure, moisture retention, and microbe diversity.
Ingredients Used in Both Compost Types
Biodynamic compost incorporates ingredients such as herbal preparations, rock dust, and specific compost preparations like horn manure, enhancing soil vitality through natural mineral and microbial activity. Organic compost relies primarily on decomposed plant matter, food scraps, manure, and green waste, focusing on nutrient-rich organic materials without synthetic additives. Both compost types aim to improve soil health, but biodynamic compost emphasizes holistic ecosystem balance through unique natural amendments.
Biodynamic Composting Methods and Preparations
Biodynamic composting methods incorporate specific herbal preparations such as yarrow, chamomile, and nettle to enhance microbial activity and soil vitality, distinguishing it from standard organic composting. This approach emphasizes lunar and cosmic rhythms to time compost turning and application, accelerating nutrient cycling and fostering holistic ecosystem health. Biodynamic preparations, numbered 500 to 508, are integral to enriching compost piles, stimulating beneficial soil organisms, and improving plant growth outcomes beyond typical organic compost benefits.
Organic Composting Techniques and Best Practices
Organic composting techniques emphasize the use of natural materials like kitchen scraps, yard waste, and manure to create nutrient-rich soil amendments without synthetic additives. Best practices include maintaining a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, proper aeration through regular turning, and moisture control to optimize microbial activity and decomposition. Unlike biodynamic compost, organic composting focuses solely on ecological cycling and soil health, avoiding esoteric preparations or lunar planting calendars.
Nutrient Content Comparison
Biodynamic compost typically contains higher concentrations of key nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium due to its preparation methods that incorporate specific herbal preparations and lunar cycle timings. Organic compost, while rich in essential macronutrients, often exhibits more variability in nutrient content because it relies primarily on natural decomposition without added biodynamic influences. Studies indicate that biodynamic compost enhances soil nutrient bioavailability more effectively, promoting improved plant growth and soil health in sustainable agriculture.
Impact on Soil Health and Microbial Activity
Biodynamic compost enhances soil health by integrating specific herbal preparations that stimulate microbial diversity and activity, leading to improved nutrient cycling and soil structure. Organic compost enriches soil with decomposed organic matter, promoting microbial populations but lacks the targeted stimulants present in biodynamic methods. Studies reveal biodynamic compost supports higher microbial biomass and enzymatic activity, crucial for sustainable soil fertility and plant growth.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
Biodynamic compost enhances soil health by integrating herbal preparations and lunar cycles, promoting microbial diversity and improving nutrient retention more effectively than standard organic compost. Organic compost primarily recycles plant-based waste, reducing landfill impact and greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing soil fertility and structure. Both methods support sustainable agriculture, but biodynamic compost emphasizes ecological balance and long-term ecosystem resilience through holistic soil management practices.
Choosing the Right Compost for Your Organic Garden
Biodynamic compost enhances soil health by integrating fermented herbal preparations and lunar cycle timing, promoting a balanced ecosystem that supports robust plant growth. Organic compost, created from decomposed plant and animal matter, supplies essential nutrients that improve soil structure and microbial activity without synthetic chemicals. Choosing between biodynamic and organic compost depends on your garden's specific needs, with biodynamic offering advanced holistic benefits and organic providing reliable nutrient enrichment for sustainable organic gardening.
Biodynamic Compost vs Organic Compost Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com