
Landscape fabric vs Mulch Illustration
Landscape fabric and mulch serve different purposes in garden maintenance; landscape fabric acts as a barrier to prevent weed growth while allowing water and air to reach the soil, whereas mulch enriches the soil, retains moisture, and regulates temperature. Using landscape fabric under mulch can enhance weed control by blocking sunlight but may limit the natural decomposition process that benefits soil health. Mulch alone offers organic matter that breaks down over time, improving soil structure and fertility, which landscape fabric does not provide.
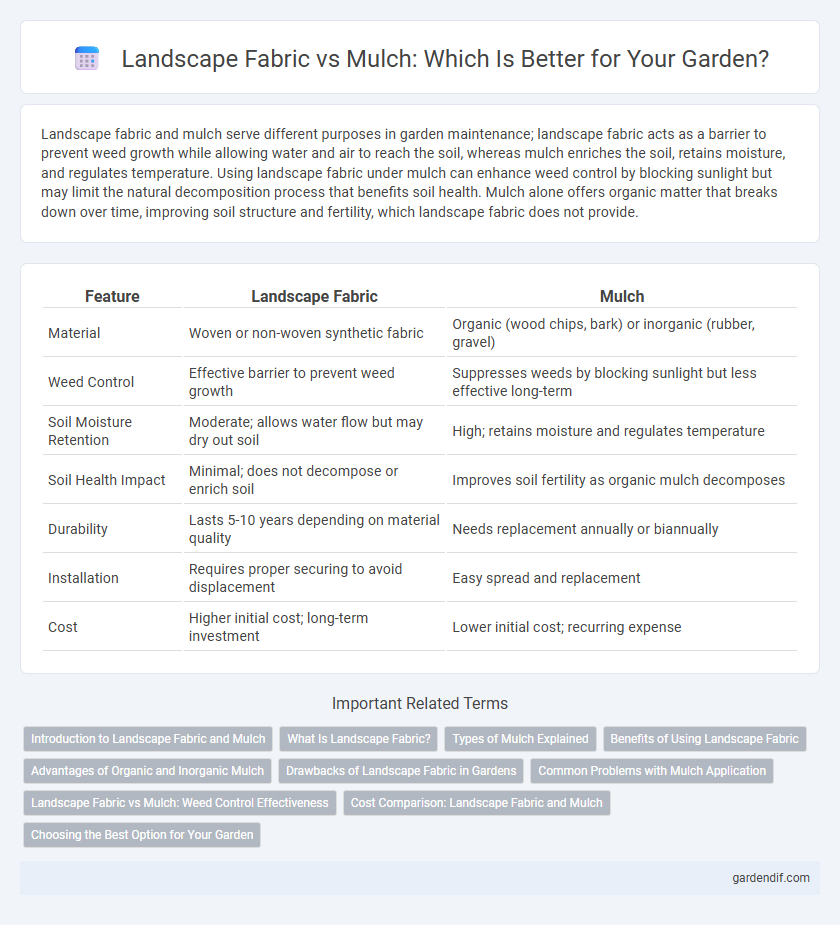
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Landscape Fabric | Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Woven or non-woven synthetic fabric | Organic (wood chips, bark) or inorganic (rubber, gravel) |
| Weed Control | Effective barrier to prevent weed growth | Suppresses weeds by blocking sunlight but less effective long-term |
| Soil Moisture Retention | Moderate; allows water flow but may dry out soil | High; retains moisture and regulates temperature |
| Soil Health Impact | Minimal; does not decompose or enrich soil | Improves soil fertility as organic mulch decomposes |
| Durability | Lasts 5-10 years depending on material quality | Needs replacement annually or biannually |
| Installation | Requires proper securing to avoid displacement | Easy spread and replacement |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; long-term investment | Lower initial cost; recurring expense |
Introduction to Landscape Fabric and Mulch
Landscape fabric is a permeable material designed to suppress weed growth while allowing water and nutrients to pass through to plants. Mulch, composed of organic materials such as bark, wood chips, or leaves, provides soil moisture retention, temperature regulation, and organic matter enrichment as it decomposes. Both landscape fabric and mulch play crucial roles in garden maintenance, with landscape fabric serving as a durable weed barrier and mulch enhancing soil health and aesthetics.
What Is Landscape Fabric?
Landscape fabric is a geotextile material designed to suppress weed growth while allowing water and air to penetrate the soil. It is commonly made from woven polypropylene or polyester fibers, creating a durable barrier that helps maintain soil moisture and prevent erosion. Unlike organic mulch, landscape fabric does not decompose, making it a long-lasting option for garden beds and pathways.
Types of Mulch Explained
Organic mulches, such as wood chips, bark, straw, and compost, improve soil fertility while suppressing weeds and retaining moisture. Inorganic mulches, including landscape fabric, black plastic, and gravel, provide long-lasting weed control and moisture retention but do not enrich the soil. Landscape fabric, a popular synthetic option, functions as a physical barrier to weeds while allowing water and air to penetrate; however, it can sometimes impede organic matter from reaching the soil and may degrade over time.
Benefits of Using Landscape Fabric
Landscape fabric improves weed control by creating a durable barrier that prevents weed growth while allowing water and nutrients to penetrate the soil. It reduces soil erosion and helps maintain consistent moisture levels, promoting healthier plant growth in garden beds. Unlike organic mulch, landscape fabric is long-lasting and minimizes the need for frequent replacement, making it a cost-effective solution for landscape maintenance.
Advantages of Organic and Inorganic Mulch
Organic mulch, such as wood chips and bark, improves soil fertility by decomposing and adding essential nutrients, while enhancing moisture retention and temperature regulation. Inorganic mulch, including rubber and landscape fabric, offers long-lasting weed suppression and durability without breaking down, making it ideal for low-maintenance areas. Both types of mulch contribute to soil erosion prevention and aesthetic appeal, with organic mulch supporting healthier plant growth and inorganic mulch providing consistent protection.
Drawbacks of Landscape Fabric in Gardens
Landscape fabric can hinder water and nutrient absorption, restricting root growth and plant health in gardens. It often leads to soil compaction and reduced organic matter, negatively impacting soil fertility over time. Additionally, fabric layers can become clogged with debris, limiting air circulation and creating a barrier that suppresses beneficial soil organisms.
Common Problems with Mulch Application
Mulch often faces issues such as excessive moisture retention leading to root rot, and improper application can attract pests like termites and rodents. Landscape fabric provides a barrier that reduces weed growth but may cause water drainage problems and soil compaction over time. Both methods require careful management to balance moisture control, soil health, and weed suppression for optimal landscape performance.
Landscape Fabric vs Mulch: Weed Control Effectiveness
Landscape fabric offers superior initial weed control by forming a physical barrier that prevents sunlight from reaching weed seeds, reducing germination rates. Mulch, while less effective at completely blocking weed growth, improves soil moisture retention and organic matter content, leading to long-term weed suppression. Combining landscape fabric with a layer of mulch maximizes weed control benefits by providing both physical obstruction and enhanced soil health.
Cost Comparison: Landscape Fabric and Mulch
Landscape fabric typically costs between $0.10 to $0.50 per square foot, making it more expensive upfront than mulch, which averages around $15 to $75 per cubic yard depending on the type. While landscape fabric is a one-time investment that can last several years, mulch often requires replenishment annually or biannually, affecting long-term expenses. Choosing between the two depends on budget considerations, maintenance willingness, and the specific landscaping needs of the property.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Garden
Landscape fabric offers long-lasting weed control by blocking sunlight while allowing water and air to penetrate soil, making it ideal for preventing perennial weed growth. Mulch improves soil fertility and moisture retention by decomposing over time and enriching the soil with organic matter, supporting plant health and growth. Selecting between landscape fabric and mulch depends on garden goals: fabric suits low-maintenance weed suppression, whereas mulch enhances soil quality and provides a natural aesthetic.
Landscape fabric vs Mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com