
Native Plant Landscaping vs Exotic Plant Landscaping Illustration
Native plant landscaping enhances biodiversity by supporting local wildlife and requiring less water and maintenance due to plants' adaptation to the regional climate. Exotic plant landscaping introduces unique textures and colors, but these species may demand more resources and have the potential to disrupt ecosystems. Choosing native plants fosters environmental sustainability while exotic varieties offer aesthetic diversity and personalization in landscape design.
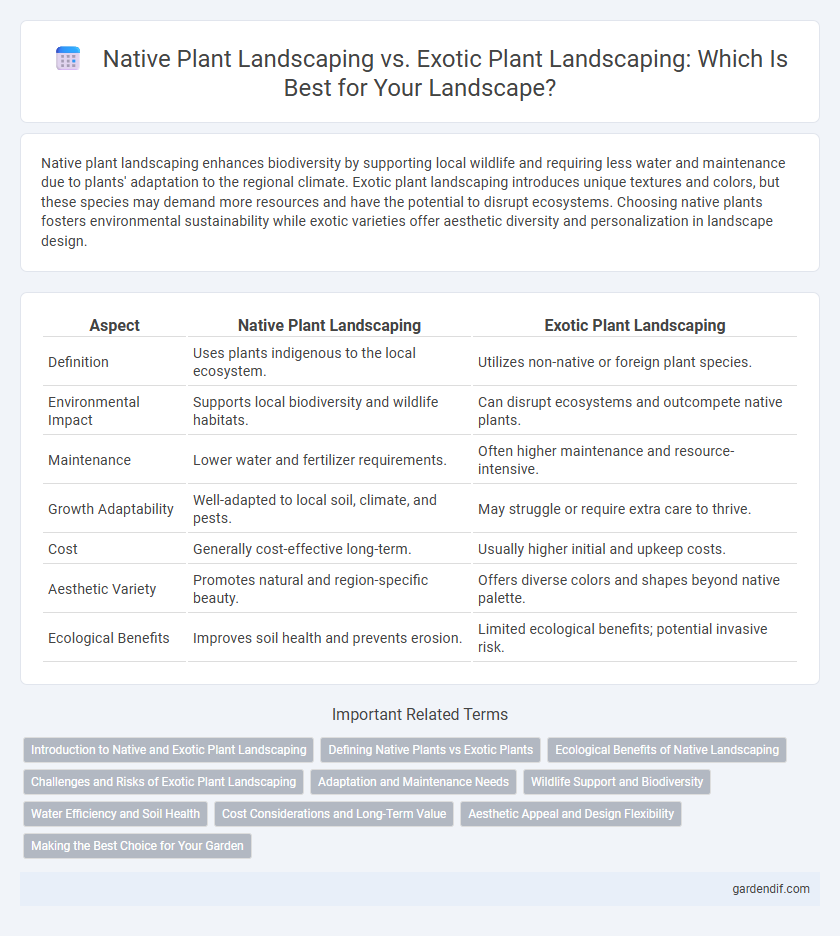
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Native Plant Landscaping | Exotic Plant Landscaping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses plants indigenous to the local ecosystem. | Utilizes non-native or foreign plant species. |
| Environmental Impact | Supports local biodiversity and wildlife habitats. | Can disrupt ecosystems and outcompete native plants. |
| Maintenance | Lower water and fertilizer requirements. | Often higher maintenance and resource-intensive. |
| Growth Adaptability | Well-adapted to local soil, climate, and pests. | May struggle or require extra care to thrive. |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective long-term. | Usually higher initial and upkeep costs. |
| Aesthetic Variety | Promotes natural and region-specific beauty. | Offers diverse colors and shapes beyond native palette. |
| Ecological Benefits | Improves soil health and prevents erosion. | Limited ecological benefits; potential invasive risk. |
Introduction to Native and Exotic Plant Landscaping
Native plant landscaping utilizes species naturally adapted to local climate, soil, and ecosystem conditions, promoting biodiversity, reducing water usage, and supporting native wildlife. Exotic plant landscaping incorporates non-native species that may offer unique aesthetics or growth habits but can require more maintenance and risk ecological imbalance. Understanding the ecological impact and resource needs of native versus exotic plants is essential for sustainable landscape design.
Defining Native Plants vs Exotic Plants
Native plants are species indigenous to a specific region, having evolved naturally in the local ecosystem, while exotic plants are introduced species from different geographic areas. Native plants support local wildlife, promote biodiversity, and require less water and maintenance due to their adaptation to regional climate and soil conditions. Exotic plants may offer unique aesthetics but often demand more resources and can disrupt native habitats by outcompeting local flora.
Ecological Benefits of Native Landscaping
Native plant landscaping enhances local biodiversity by supporting indigenous wildlife, including pollinators and birds, which rely on these plants for food and habitat. Native plants require less water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing environmental pollution and conserving natural resources. Their deep root systems improve soil structure and prevent erosion, promoting long-term ecosystem stability.
Challenges and Risks of Exotic Plant Landscaping
Exotic plant landscaping often introduces challenges such as invasive species that outcompete native flora, leading to reduced biodiversity and disrupted ecosystems. These plants may require excessive water, fertilizers, and pesticides, increasing environmental strain and maintenance costs. The risk of spreading diseases and pests unfamiliar to local environments further complicates the sustainable management of exotic landscapes.
Adaptation and Maintenance Needs
Native plant landscaping offers superior adaptation to local soil, climate, and pest conditions, significantly reducing water and fertilizer requirements. Exotic plant landscaping often demands intensive maintenance, including frequent watering, soil amendments, and pest control to thrive outside their natural environment. Choosing native species enhances ecosystem resilience and lowers labor costs associated with upkeep.
Wildlife Support and Biodiversity
Native plant landscaping enhances local biodiversity by providing essential habitats and food sources tailored to native wildlife species, promoting ecological balance and supporting pollinators. In contrast, exotic plant landscaping often disrupts local ecosystems by outcompeting native flora, reducing habitat quality and limiting resources for indigenous fauna. Prioritizing native plants fosters resilient landscapes that sustain diverse wildlife populations and maintain regional ecological integrity.
Water Efficiency and Soil Health
Native plant landscaping promotes superior water efficiency by adapting to local rainfall patterns, reducing irrigation needs, and enhancing soil health through symbiotic relationships with indigenous microorganisms. Exotic plant landscaping often demands increased water consumption and chemical inputs that can disrupt soil microbial balance, leading to diminished soil fertility over time. Prioritizing native species supports sustainable landscaping by improving drought resilience and maintaining nutrient-rich, well-structured soil ecosystems.
Cost Considerations and Long-Term Value
Native plant landscaping often requires lower initial investment and reduced maintenance costs due to its adaptation to local soil and climate, minimizing water, fertilizer, and pesticide usage. Exotic plant landscaping can involve higher upfront expenses and ongoing care to manage non-native species' specific needs and potential invasiveness. Long-term value favors native plants by enhancing biodiversity, improving soil health, and providing sustainable ecosystem services that exotic plants may lack.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Native plant landscaping enhances aesthetic appeal by showcasing local flora that naturally harmonizes with the surrounding environment, creating a cohesive and authentic visual experience. Exotic plant landscaping offers greater design flexibility through a wider variety of colors, textures, and growth habits, allowing for unique and personalized garden styles. Native plants typically require less maintenance and adapt well to local climate conditions, while exotic plants may demand more care but provide distinct visual contrasts that can elevate landscape creativity.
Making the Best Choice for Your Garden
Native plant landscaping enhances local biodiversity by supporting pollinators and requiring less water, making it an eco-friendly and sustainable choice for your garden. Exotic plant landscaping introduces unique textures and colors but often demands more maintenance and can disrupt local ecosystems. Choosing the best approach depends on balancing aesthetic goals with environmental impact and long-term garden health.
Native Plant Landscaping vs Exotic Plant Landscaping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com