
Flood Table vs Vertical Hydroponics Illustration
Flood table systems provide a stable, nutrient-rich environment by periodically flooding plant roots, promoting even nutrient absorption and aeration. Vertical hydroponics optimize space by growing plants in stacked layers, making them ideal for urban settings or areas with limited floor space. Both methods enhance water efficiency and crop yield but differ in spatial arrangement and maintenance complexity.
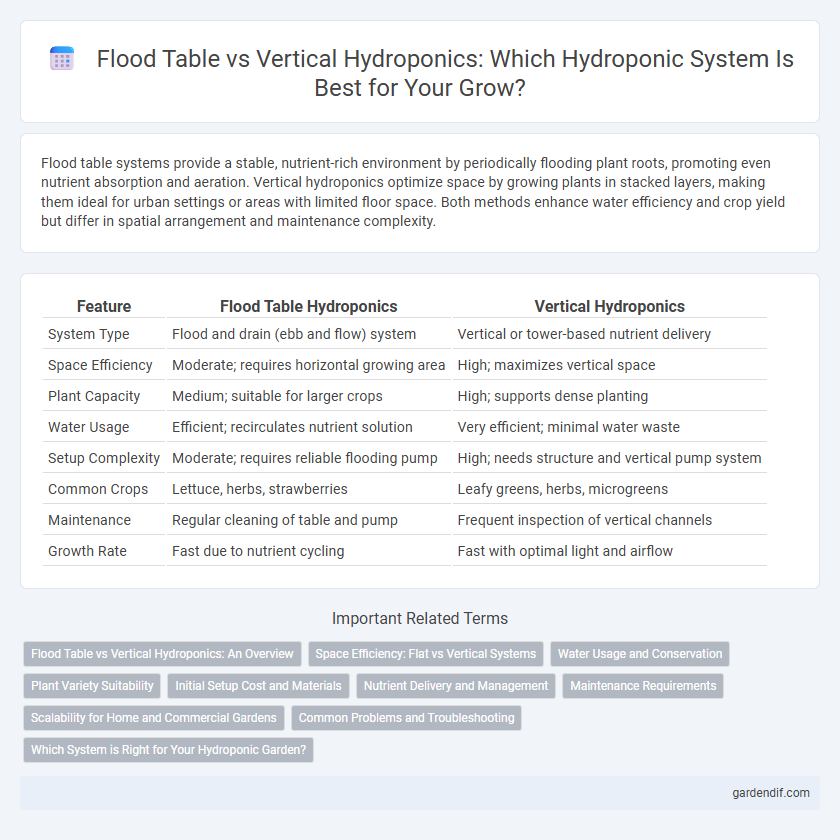
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flood Table Hydroponics | Vertical Hydroponics |
|---|---|---|
| System Type | Flood and drain (ebb and flow) system | Vertical or tower-based nutrient delivery |
| Space Efficiency | Moderate; requires horizontal growing area | High; maximizes vertical space |
| Plant Capacity | Medium; suitable for larger crops | High; supports dense planting |
| Water Usage | Efficient; recirculates nutrient solution | Very efficient; minimal water waste |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate; requires reliable flooding pump | High; needs structure and vertical pump system |
| Common Crops | Lettuce, herbs, strawberries | Leafy greens, herbs, microgreens |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning of table and pump | Frequent inspection of vertical channels |
| Growth Rate | Fast due to nutrient cycling | Fast with optimal light and airflow |
Flood Table vs Vertical Hydroponics: An Overview
Flood table hydroponics delivers nutrient-rich water through periodic flooding of a flat growing surface, promoting uniform root exposure and efficient oxygenation. Vertical hydroponics maximizes space by stacking multiple growing layers, ideal for urban environments and increasing crop density per square foot. Both systems vary in setup complexity and suitability depending on crop type, space availability, and desired yield outcomes.
Space Efficiency: Flat vs Vertical Systems
Flood table hydroponics utilizes a flat growing surface that maximizes horizontal space, making it suitable for larger areas where expansion is possible. Vertical hydroponic systems stack growing channels upwards, significantly increasing plant density per square foot and optimizing limited floor space in urban or indoor environments. The vertical arrangement also enhances light exposure and airflow, resulting in higher yields within compact spaces.
Water Usage and Conservation
Flood table hydroponics uses a shallow, water-filled reservoir that floods and drains to supply nutrients, optimizing water recycling and minimizing waste through a contained system. Vertical hydroponics stacks plants vertically, significantly reducing water usage by recirculating nutrient solution in a closed-loop system, which enhances water conservation in limited spaces. Both methods excel in efficient water use compared to traditional soil farming, but vertical hydroponics offers superior water savings by maximizing surface area and minimizing evaporation.
Plant Variety Suitability
Flood Table hydroponics supports a wide range of plant varieties including leafy greens, herbs, and larger fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers due to its spacious, horizontal layout and efficient nutrient delivery. Vertical hydroponics excels with smaller, fast-growing plants such as lettuce, strawberries, and herbs, optimizing vertical space and light exposure but may limit root expansion for larger crops. Choosing between the two depends on crop size, growth habits, and production goals within controlled environment agriculture systems.
Initial Setup Cost and Materials
Flood table hydroponics typically requires a larger initial investment for durable materials such as waterproof trays, pumps, and nutrient reservoirs, making it costlier upfront compared to vertical hydroponics. Vertical hydroponic systems use space-efficient towers or vertical channels, often constructed from lightweight PVC or plastic, reducing both material costs and installation complexity. Choosing between these systems depends on budget constraints and available space, with vertical setups generally offering a more affordable and compact solution for beginners.
Nutrient Delivery and Management
Flood table systems provide uniform nutrient delivery by periodically flooding the grow tray, ensuring roots receive consistent access to oxygen and nutrients while allowing excess solution to drain away. Vertical hydroponics maximize space efficiency through stacked layers, but require precise nutrient management and flow control to prevent uneven distribution and nutrient depletion in upper or lower layers. Effective nutrient monitoring and recirculation technology are critical in both systems to maintain optimal pH, EC levels, and prevent nutrient imbalances that impact plant growth.
Maintenance Requirements
Flood table hydroponics requires regular monitoring of water levels, filtration systems, and pump functionality to prevent nutrient imbalances and algae growth. Vertical hydroponics often demands more frequent inspection of individual plant sites and structural components to ensure even nutrient distribution and avoid clogs. Maintenance intensity varies with system complexity, but vertical setups typically need more hands-on attention due to their multi-level design.
Scalability for Home and Commercial Gardens
Flood Table systems offer scalability by accommodating large surface areas ideal for commercial gardens, enabling simultaneous cultivation of diverse crops with automated water delivery and drainage. Vertical Hydroponics maximizes space efficiency, making it perfect for home gardens and urban settings where vertical stacking significantly increases yield per square foot. Both systems support scalable growth, but Flood Tables excel in wide-area expansion while Vertical Hydroponics is optimal for high-density, small-footprint environments.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
Flood table systems often face water stagnation and root rot due to inadequate drainage and inconsistent flooding cycles, requiring regular monitoring of water flow rates and cleaning of channels to prevent blockage. Vertical hydroponics commonly encounter uneven nutrient distribution and light exposure, leading to variable plant growth; optimizing pump pressure and rotating plant positions helps maintain uniformity. Both systems benefit from consistent pH and EC level checks to troubleshoot nutrient deficiencies and ensure optimal plant health.
Which System is Right for Your Hydroponic Garden?
Flood table hydroponic systems excel in large-scale, nutrient film delivery with excellent root oxygenation, ideal for leafy greens and herbs in spacious setups. Vertical hydroponics maximize space efficiency and crop density by stacking multiple growing channels, suited for urban gardens or limited areas. Choosing the right system depends on available space, crop type, and scalability requirements.
Flood Table vs Vertical Hydroponics Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com