
Aeroponic propagation vs Hydroponic cloning Illustration
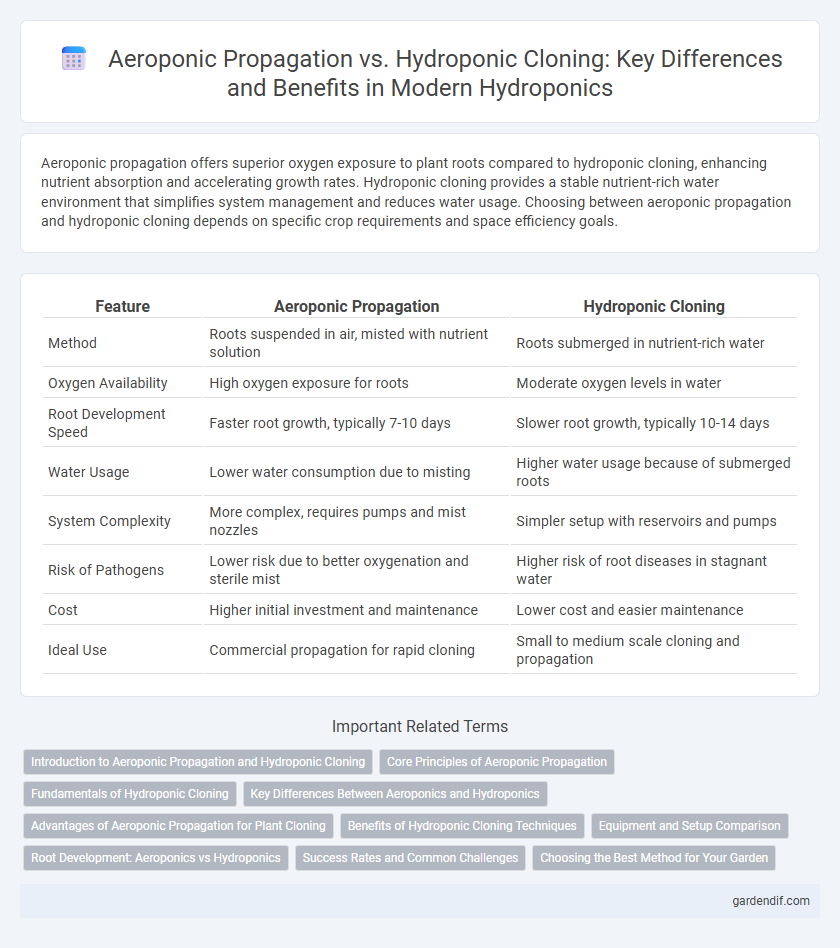
Aeroponic propagation offers superior oxygen exposure to plant roots compared to hydroponic cloning, enhancing nutrient absorption and accelerating growth rates. Hydroponic cloning provides a stable nutrient-rich water environment that simplifies system management and reduces water usage. Choosing between aeroponic propagation and hydroponic cloning depends on specific crop requirements and space efficiency goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aeroponic Propagation | Hydroponic Cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Roots suspended in air, misted with nutrient solution | Roots submerged in nutrient-rich water |
| Oxygen Availability | High oxygen exposure for roots | Moderate oxygen levels in water |
| Root Development Speed | Faster root growth, typically 7-10 days | Slower root growth, typically 10-14 days |
| Water Usage | Lower water consumption due to misting | Higher water usage because of submerged roots |
| System Complexity | More complex, requires pumps and mist nozzles | Simpler setup with reservoirs and pumps |
| Risk of Pathogens | Lower risk due to better oxygenation and sterile mist | Higher risk of root diseases in stagnant water |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance | Lower cost and easier maintenance |
| Ideal Use | Commercial propagation for rapid cloning | Small to medium scale cloning and propagation |
Introduction to Aeroponic Propagation and Hydroponic Cloning
Aeroponic propagation involves suspending plant cuttings in air while misting roots with nutrient-rich water, promoting faster root development and higher oxygen exposure compared to hydroponic cloning, where cuttings are placed in a nutrient solution or inert medium. This method enhances root aeration and nutrient uptake, leading to increased cloning success rates and reduced water usage. Hydroponic cloning, widely used for its simplicity and scalability, provides stable moisture levels essential for rooting but may result in slower root growth due to less oxygen availability around the roots.
Core Principles of Aeroponic Propagation
Aeroponic propagation relies on suspending plant cuttings in an air environment where nutrient-rich mist delivers oxygen and moisture directly to the roots, enhancing oxygenation and promoting rapid root growth. This soil-free method maximizes nutrient absorption efficiency and reduces water usage compared to traditional hydroponic cloning, where roots are submerged in a nutrient solution. The core principle of aeroponic propagation is maintaining optimal root exposure to air and precise misting intervals to stimulate vigorous root development and healthier plant clones.
Fundamentals of Hydroponic Cloning
Hydroponic cloning relies on nutrient-rich water solutions to stimulate root development in plant cuttings, ensuring rapid propagation and high success rates. Unlike aeroponic propagation, which suspends cuttings in air with misted nutrients, hydroponic cloning offers consistent moisture and controlled oxygen levels to optimize root growth. Mastery of pH balance, temperature control, and nutrient concentration is fundamental for maximizing the efficiency of hydroponic cloning systems.
Key Differences Between Aeroponics and Hydroponics
Aeroponic propagation suspends plant roots in air and delivers nutrient-rich mist directly, ensuring higher oxygen availability and faster growth compared to hydroponic cloning, where roots are submerged in nutrient solution. Aeroponics typically uses less water and nutrients due to its precise misting system, making it more resource-efficient than hydroponics, which relies on constant water circulation. The aeroponic environment also reduces root diseases by maintaining drier root surfaces, whereas hydroponics requires careful monitoring of water conditions to prevent pathogen proliferation.
Advantages of Aeroponic Propagation for Plant Cloning
Aeroponic propagation offers superior oxygenation to roots compared to hydroponic cloning, promoting faster growth and higher rooting success rates. This soil-free method reduces the risk of disease and root rot by delivering nutrients through a fine mist, enhancing nutrient absorption efficiency. Aeroponics also uses less water and space, making it an environmentally sustainable and cost-effective solution for large-scale plant cloning operations.
Benefits of Hydroponic Cloning Techniques
Hydroponic cloning techniques offer precise nutrient control and faster root development compared to aeroponic propagation, enhancing plant uniformity and stability. These systems reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional soil methods and minimize disease risk through a sterile growing environment. High success rates in cloning and consistent crop yields make hydroponic cloning highly efficient for commercial cultivation of crops like lettuce, herbs, and cannabis.
Equipment and Setup Comparison
Aeroponic propagation systems require specialized misting nozzles and high-pressure pumps to deliver nutrient-rich aerosols directly to plant roots in a suspended environment, while hydroponic cloning setups utilize trays or net pots submerged in nutrient solutions or supported by inert media such as rock wool or coconut coir. Aeroponics demands precise environmental controls including humidifiers and timers to maintain optimal mist intervals, contrasting with hydroponic systems that prioritize constant nutrient circulation through reservoirs and pumps. The complexity and maintenance of aeroponic equipment often result in higher initial investment and calibration needs compared to the relatively straightforward hydroponic cloning rigs designed for scalability and ease of use.
Root Development: Aeroponics vs Hydroponics
Aeroponic propagation promotes faster and more robust root development by suspending plant cuttings in air and delivering a fine mist of nutrient-rich solution, enhancing oxygen availability to roots. Hydroponic cloning immerses cuttings in nutrient solutions, resulting in steady root growth but with less oxygen exposure compared to aeroponics. Increased oxygenation in aeroponics accelerates root hair formation and improves nutrient uptake, leading to healthier and more vigorous clones.
Success Rates and Common Challenges
Aeroponic propagation achieves success rates exceeding 90% due to its superior oxygenation and nutrient absorption, promoting faster root development compared to hydroponic cloning, which typically ranges between 70-85% success. Common challenges in aeroponics include maintaining consistent misting cycles and preventing nozzle clogging, while hydroponic cloning often struggles with waterborne pathogen management and root rot. Both systems require precise environmental control, but aeroponics demands higher technical maintenance to sustain optimal propagation conditions.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Garden
Aeroponic propagation uses mist to deliver nutrients directly to plant roots suspended in air, promoting faster root growth and reducing water usage compared to traditional hydroponic cloning, which submerges roots in nutrient-rich water. Hydroponic cloning is simpler to set up and maintain, making it ideal for beginners or small-scale gardens seeking consistency and ease of monitoring. Gardeners should choose aeroponic systems for accelerated growth and efficiency or hydroponic cloning for cost-effectiveness and straightforward scalability.
Aeroponic propagation vs Hydroponic cloning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com