
Strip harvesting vs selective picking Illustration
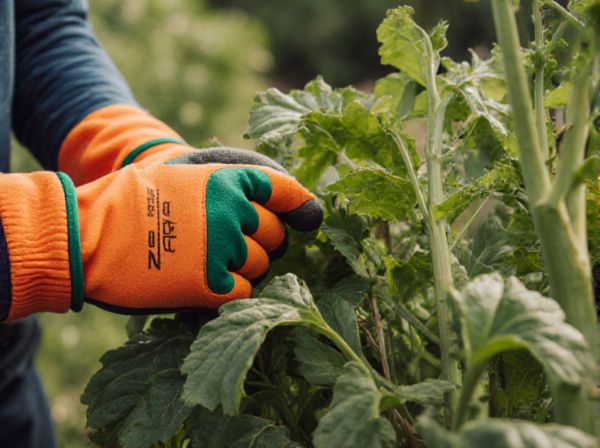
Strip harvesting involves collecting all crops from a designated area at once, maximizing efficiency and speed but often leading to greater waste and reduced quality. Selective picking targets only ripe or high-quality produce, enhancing product consistency and minimizing damage yet requiring more labor and time. Balancing these methods depends on crop type, market demands, and resource availability to optimize yield and profitability.
Table of Comparison
| Harvest Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strip Harvesting | Removing all crops or fruit from a defined strip or section at once. | Faster, efficient for large-scale production, reduces labor costs. | Can damage plants, lower fruit quality, less selective yield. | Uniform crops requiring quick extraction, e.g., grains or some fruits. |
| Selective Picking | Harvesting only ripe or mature produce selectively by hand or tool. | Higher fruit quality, extends harvest season, minimal plant damage. | Labor-intensive, slower process, higher costs. | High-value crops needing quality control, e.g., coffee, tea, specialty fruits. |
Understanding Strip Harvesting in Gardening
Strip harvesting in gardening involves removing entire rows or sections of crops at once, maximizing efficiency for plants like lettuce or kale that grow in dense clusters. This method reduces labor time and allows for rapid replanting, making it ideal for commercial gardens aiming for fast turnover. While selective picking targets only mature fruits or vegetables to encourage continuous growth, strip harvesting prioritizes speed and uniformity in crop extraction.
What is Selective Picking?
Selective picking is a harvesting method where only ripe or mature fruits, vegetables, or crops are handpicked, ensuring quality and minimizing waste. This technique contrasts with strip harvesting, which involves cutting or collecting the entire crop regardless of ripeness. Selective picking enhances crop quality, reduces damage, and allows for multiple harvests from the same field.
Key Differences Between Strip Harvesting and Selective Picking
Strip harvesting involves removing all crops or fruits from a designated area in a single pass, ensuring maximum yield efficiency but potentially affecting soil structure and future crop cycles. Selective picking targets only ripe or mature produce, promoting higher quality harvests and sustaining plant health, yet it requires more labor and time. The primary differences lie in the trade-offs between speed and crop preservation, impact on soil, and labor intensity.
Pros and Cons of Strip Harvesting
Strip harvesting enables rapid collection of crops by removing entire rows or sections at once, significantly increasing efficiency for large-scale operations. However, this method can lead to uneven crop ripeness and increased waste due to harvesting immature or overripe produce. It also disturbs soil structure and biodiversity, making it less sustainable compared to selective picking.
Advantages of Selective Picking Techniques
Selective picking techniques in harvest maximize fruit quality by allowing only ripe produce to be collected, reducing waste and enhancing market value. This method supports sustainable agriculture by minimizing damage to plants and enabling multiple harvests throughout the growing season. Farmers benefit from improved yield consistency and better resource management compared to strip harvesting.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Strip harvesting maximizes efficiency by removing entire crop sections simultaneously, often resulting in higher overall yield but with a risk of including less mature or lower-quality produce. Selective picking targets only ripe or premium-quality crops, enhancing product quality and market value but typically yielding lower quantities due to selective exclusion. Crop type, market demands, and timing heavily influence the balance between yield and quality in these harvesting methods.
Labor and Time Considerations for Each Method
Strip harvesting demands less labor and significantly reduces time due to the mechanized removal of entire crop sections, making it efficient for large-scale operations. Selective picking requires a skilled workforce and more time as workers carefully harvest only mature produce, ensuring higher quality but increasing labor costs. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing labor availability, time constraints, and desired crop quality outcomes.
Effect on Plant Health and Future Harvests
Strip harvesting removes entire crop rows at once, causing significant stress to plants and reducing the root system's ability to regenerate, which can negatively impact future harvests. Selective picking preserves plant structure by harvesting only mature fruits, allowing continuous growth and enhancing long-term plant health. This method promotes sustainable yields by minimizing damage and supporting robust regrowth cycles for subsequent harvests.
Best Crops for Strip Harvesting vs Selective Picking
Strip harvesting is highly effective for uniform, fast-maturing crops such as wheat, barley, and corn, allowing large-scale, mechanized collection with minimal labor. Selective picking suits delicate, high-value crops like strawberries, grapes, and coffee cherries, where hand-harvesting ensures quality and minimizes damage. Optimal crop choice depends on balancing harvest speed, labor cost, and the crop's sensitivity to damage.
Choosing the Right Harvesting Method for Your Garden
Strip harvesting involves removing all crops in a specific area at once, maximizing efficiency for uniform plants like grains or root vegetables. Selective picking targets only ripe fruits or vegetables, preserving the rest for continued growth, ideal for gardens with varied maturity stages. Choosing the right harvesting method depends on crop type, garden size, and desired yield timing to optimize both productivity and quality.
Strip harvesting vs selective picking Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com