
Plastic Glazing vs Glass Glazing Illustration
Plastic glazing offers superior impact resistance and better insulation properties compared to glass glazing, making it an energy-efficient choice for greenhouse construction. It is lighter and easier to install, reducing structural support requirements and overall costs. However, glass glazing provides enhanced durability and clarity, allowing maximum light transmission critical for plant growth.
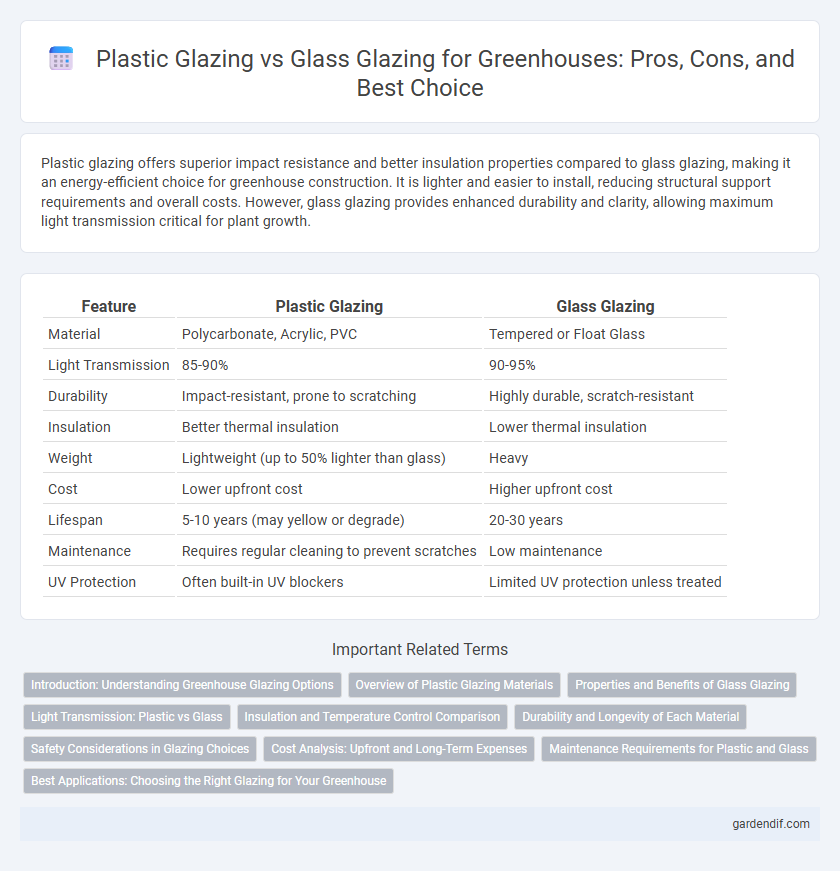
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Glazing | Glass Glazing |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polycarbonate, Acrylic, PVC | Tempered or Float Glass |
| Light Transmission | 85-90% | 90-95% |
| Durability | Impact-resistant, prone to scratching | Highly durable, scratch-resistant |
| Insulation | Better thermal insulation | Lower thermal insulation |
| Weight | Lightweight (up to 50% lighter than glass) | Heavy |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Lifespan | 5-10 years (may yellow or degrade) | 20-30 years |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning to prevent scratches | Low maintenance |
| UV Protection | Often built-in UV blockers | Limited UV protection unless treated |
Introduction: Understanding Greenhouse Glazing Options
Plastic glazing offers lightweight, impact-resistant qualities and superior insulation for greenhouse applications, reducing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency. Glass glazing provides excellent clarity and durability, supporting optimal light transmission essential for plant growth. Selecting between plastic and glass glazing depends on factors like climate, budget, and desired longevity.
Overview of Plastic Glazing Materials
Plastic glazing materials in greenhouses, such as polycarbonate, acrylic, and polyethylene, offer lightweight, impact-resistant alternatives to traditional glass glazing. These plastics provide excellent thermal insulation, UV protection, and flexibility, enhancing energy efficiency and plant growth conditions. Compared to glass, plastic glazing reduces installation costs and breakage risk, making it a durable choice for various greenhouse applications.
Properties and Benefits of Glass Glazing
Glass glazing in greenhouses offers superior thermal insulation and durability compared to plastic glazing, enabling better temperature regulation and longer lifespan. Its high light transmittance supports optimal photosynthesis, promoting healthier plant growth and increased yields. Glass is also more resistant to scratches and weathering, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring consistent performance over time.
Light Transmission: Plastic vs Glass
Plastic glazing transmits more light than glass glazing, typically allowing around 90-95% of sunlight to pass through, enhancing plant growth in greenhouses. Glass glazing generally permits 80-90% light transmission but offers superior clarity and durability. The higher light transmission of plastic materials like polycarbonate or acrylic can improve photosynthesis efficiency, making them preferred for maximizing light exposure in controlled environments.
Insulation and Temperature Control Comparison
Plastic glazing in greenhouses offers superior insulation properties compared to glass glazing, significantly reducing heat loss during colder months. Materials like polycarbonate and polyethylene provide better temperature control by effectively trapping heat while allowing adequate light transmission for plant growth. Glass glazing, although durable and offering clearer visibility, tends to have higher thermal conductivity, resulting in faster heat dissipation and less stable internal temperatures.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Plastic glazing in greenhouses, typically made from polycarbonate or acrylic, offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it less prone to cracking or shattering compared to glass glazing. Glass glazing, especially tempered or laminated variants, provides excellent clarity and a longer service life, often lasting 20 to 30 years with minimal degradation under UV exposure. While plastic glazing generally lasts around 10 to 15 years before yellowing or becoming brittle, its durability under impact and lightweight nature can enhance structural longevity in harsh weather conditions.
Safety Considerations in Glazing Choices
Plastic glazing in greenhouses offers enhanced impact resistance and shatterproof properties, significantly reducing the risk of injury from broken panels compared to traditional glass glazing. Glass glazing, while providing superior clarity and UV stability, poses greater hazards due to its brittleness and potential for sharp shards upon breakage. Safety considerations prioritize plastic glazing for environments where accidental impacts are frequent or safety regulations demand reduced injury risks.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Plastic glazing in greenhouses offers lower upfront costs compared to glass glazing, making it an economical choice for budget-sensitive projects. However, plastic materials such as polycarbonate or polyethylene often require more frequent replacement and maintenance, leading to higher long-term expenses. Glass glazing, though initially more expensive, provides greater durability, energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs, resulting in better value over time.
Maintenance Requirements for Plastic and Glass
Plastic glazing in greenhouses requires less frequent cleaning and is more resistant to breakage, reducing maintenance efforts and costs compared to glass. Glass glazing demands regular cleaning to maintain transparency and is prone to cracking or shattering, necessitating more careful handling and potential replacement. The durability and lightweight nature of plastic glazing make it a lower-maintenance option for greenhouse structures.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Glazing for Your Greenhouse
Plastic glazing offers lightweight durability and superior impact resistance, making it ideal for small to medium-sized greenhouses or mobile setups. Glass glazing provides excellent light transmission and longevity, best suited for permanent structures requiring maximum clarity and aesthetic appeal. Selecting the right glazing depends on factors like climate, budget, and the desired greenhouse lifespan.
Plastic Glazing vs Glass Glazing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com