
Manual Shading vs Automated Shading Illustration
Manual shading in greenhouses relies on human intervention to adjust covers, which can lead to inconsistent light control and increased labor costs. Automated shading systems use sensors and motorized mechanisms to optimize light levels precisely, enhancing plant growth and energy efficiency. Investing in automation improves climate regulation while reducing manual workload and errors.
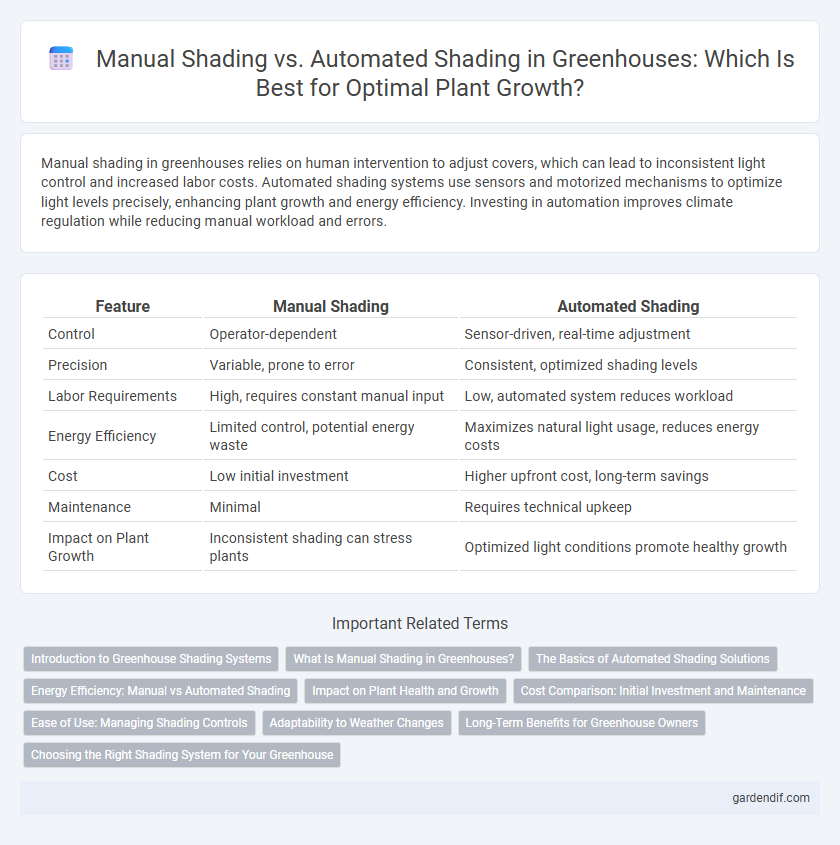
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Shading | Automated Shading |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Operator-dependent | Sensor-driven, real-time adjustment |
| Precision | Variable, prone to error | Consistent, optimized shading levels |
| Labor Requirements | High, requires constant manual input | Low, automated system reduces workload |
| Energy Efficiency | Limited control, potential energy waste | Maximizes natural light usage, reduces energy costs |
| Cost | Low initial investment | Higher upfront cost, long-term savings |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Requires technical upkeep |
| Impact on Plant Growth | Inconsistent shading can stress plants | Optimized light conditions promote healthy growth |
Introduction to Greenhouse Shading Systems
Greenhouse shading systems play a critical role in controlling temperature, light intensity, and plant growth conditions. Manual shading involves the physical adjustment of shade cloths by hand, offering simplicity but requiring labor and consistent attention. Automated shading systems utilize sensors and motorized controls to optimize shading dynamically, enhancing energy efficiency and maintaining ideal microclimates for crop productivity.
What Is Manual Shading in Greenhouses?
Manual shading in greenhouses involves physically adjusting shading materials like shade cloths or blinds to control sunlight exposure and temperature. This process requires human intervention to open, close, or reposition shading elements based on weather conditions and crop needs. Manual shading offers precise control but can be labor-intensive and less responsive compared to automated shading systems.
The Basics of Automated Shading Solutions
Automated shading solutions in greenhouses utilize sensors and motorized systems to adjust shading materials based on real-time sunlight intensity, optimizing plant growth by maintaining ideal light conditions. These systems reduce labor costs and improve energy efficiency by minimizing overheating and controlling light exposure precisely. Integration with climate control systems enhances overall environmental management, resulting in consistent crop yields and better resource use.
Energy Efficiency: Manual vs Automated Shading
Automated shading systems in greenhouses optimize energy efficiency by dynamically adjusting to sunlight intensity and temperature changes, reducing the need for supplemental heating and cooling. Manual shading relies on human intervention, which often leads to inconsistent application and potential energy waste. Energy savings with automated shading can reach up to 30%, significantly lowering operational costs and enhancing sustainable greenhouse management.
Impact on Plant Health and Growth
Manual shading in greenhouses allows for targeted control but often leads to inconsistent light exposure, which can stress plants and inhibit optimal growth. Automated shading systems provide precise regulation of sunlight intensity and duration, promoting uniform photosynthesis and reducing heat stress, thus enhancing overall plant health and development. Consistent shading adjustments help maintain ideal microclimates, directly supporting faster growth rates and improved crop yields.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Manual shading systems in greenhouses require lower initial investment costs but often incur higher ongoing maintenance expenses due to labor intensity and frequent adjustments. Automated shading solutions involve a significant upfront cost for installation and advanced technology integration but typically reduce long-term maintenance and operational expenses through precise, programmable controls. Cost efficiency depends on greenhouse size, labor availability, and desired climate control precision, with automated shading favored for large-scale or high-tech environments.
Ease of Use: Managing Shading Controls
Manual shading in greenhouses requires direct human intervention to adjust shading screens, often demanding more time and labor for precise control, which can lead to inconsistencies. Automated shading systems use sensors and programmable controls to adjust shading dynamically based on real-time environmental data, significantly reducing the need for manual labor. This technology enhances ease of use by allowing consistent light management without continuous human attention, optimizing plant growth conditions efficiently.
Adaptability to Weather Changes
Manual shading systems rely on human intervention to adjust coverings based on weather conditions, which may lead to delayed responses during sudden changes. Automated shading incorporates sensors and control algorithms that continuously monitor temperature, light intensity, and humidity to dynamically optimize shading in real time. This adaptability enhances plant growth by maintaining stable microclimate conditions despite fluctuating external weather.
Long-Term Benefits for Greenhouse Owners
Manual shading requires consistent labor and time, limiting efficiency and scalability for greenhouse owners. Automated shading systems optimize light control, improve crop yields, and reduce energy costs by adjusting shading based on real-time environmental data. Long-term benefits include enhanced plant growth, lower operational expenses, and increased profitability through precise climate management.
Choosing the Right Shading System for Your Greenhouse
Manual shading systems in greenhouses offer cost-effective control but require constant monitoring and physical adjustment, making them less practical for large or commercial setups. Automated shading systems use sensors and timers to optimize temperature and sunlight exposure, enhancing plant growth efficiency while reducing labor costs. Selecting the right shading system depends on greenhouse size, budget, and desired precision in environmental control.
Manual Shading vs Automated Shading Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com