
Cold Frame vs Greenhouse Illustration
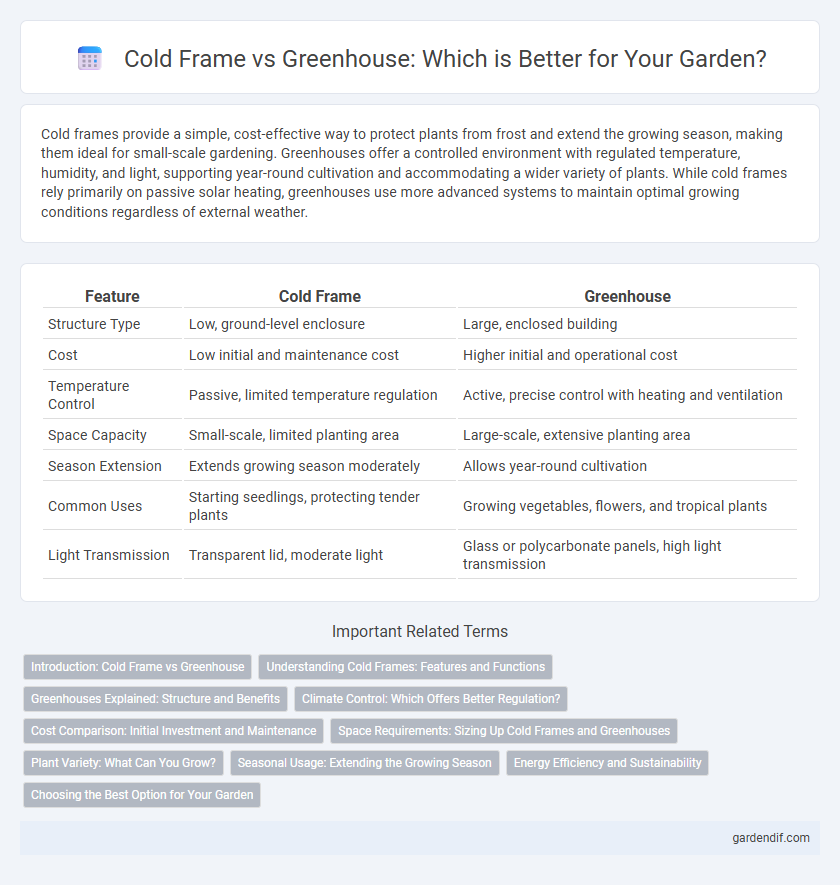
Cold frames provide a simple, cost-effective way to protect plants from frost and extend the growing season, making them ideal for small-scale gardening. Greenhouses offer a controlled environment with regulated temperature, humidity, and light, supporting year-round cultivation and accommodating a wider variety of plants. While cold frames rely primarily on passive solar heating, greenhouses use more advanced systems to maintain optimal growing conditions regardless of external weather.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Frame | Greenhouse |
|---|---|---|
| Structure Type | Low, ground-level enclosure | Large, enclosed building |
| Cost | Low initial and maintenance cost | Higher initial and operational cost |
| Temperature Control | Passive, limited temperature regulation | Active, precise control with heating and ventilation |
| Space Capacity | Small-scale, limited planting area | Large-scale, extensive planting area |
| Season Extension | Extends growing season moderately | Allows year-round cultivation |
| Common Uses | Starting seedlings, protecting tender plants | Growing vegetables, flowers, and tropical plants |
| Light Transmission | Transparent lid, moderate light | Glass or polycarbonate panels, high light transmission |
Introduction: Cold Frame vs Greenhouse
Cold frames and greenhouses are essential structures for extending growing seasons and protecting plants from adverse weather conditions. Cold frames are low, unheated boxes that trap solar heat, ideal for hardening off seedlings and starting early crops in small spaces, while greenhouses offer larger, climate-controlled environments suitable for year-round cultivation of a diverse range of plants. Choosing between cold frame and greenhouse depends on factors such as available space, budget, temperature regulation needs, and the specific plants being grown.
Understanding Cold Frames: Features and Functions
Cold frames are low-profile, unheated structures with transparent tops designed to protect plants from frost and extend the growing season. They utilize passive solar energy, trapping sunlight to create a warmer microenvironment ideal for seed starting, hardening off seedlings, and overwintering delicate plants. Typically made from wood or metal frames with glass or plastic covers, cold frames require minimal maintenance and are a cost-effective alternative to full-sized greenhouses.
Greenhouses Explained: Structure and Benefits
Greenhouses are enclosed structures designed to create a controlled environment for plant growth, utilizing transparent materials like glass or polycarbonate to maximize sunlight exposure while retaining warmth. Unlike cold frames, greenhouses offer more space, better ventilation, and temperature regulation, enabling cultivation of diverse crops year-round regardless of outdoor weather conditions. Their structural design supports advanced systems like heating, cooling, and automated irrigation, significantly enhancing plant productivity and extending growing seasons.
Climate Control: Which Offers Better Regulation?
Cold frames provide basic climate control by trapping solar heat and shielding plants from frost, making them ideal for early-season growing and seed starting. Greenhouses offer advanced regulation with temperature, humidity, and ventilation systems that maintain optimal conditions year-round for diverse crops. The superior climate control capabilities of greenhouses ensure consistent plant growth and higher yields compared to cold frames.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Cold frames require a significantly lower initial investment, often costing between $50 to $200, whereas greenhouses typically range from $1,000 to over $10,000 depending on size and materials. Maintenance costs for cold frames remain minimal, primarily involving occasional repairs and seasonal adjustments, while greenhouses demand higher ongoing expenses including ventilation systems, heating, and structural upkeep. Investing in a greenhouse offers greater climate control and extended growing seasons, but cold frames present a more budget-friendly option for amateur gardeners.
Space Requirements: Sizing Up Cold Frames and Greenhouses
Cold frames generally require less space than greenhouses, making them ideal for gardeners with limited outdoor areas or small balconies. While cold frames are compact and easily placed on patios or garden beds, greenhouses demand more substantial space to accommodate their larger structures and growing capacity. Optimizing garden layout involves assessing the available area and balancing the advantages of cold frames' space efficiency against greenhouses' expanded growing zones.
Plant Variety: What Can You Grow?
Cold frames are ideal for starting hardy vegetables and herbs such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, providing a controlled environment for early seedling growth. Greenhouses offer a broader range of plant variety options, supporting tropical plants, fruiting vegetables like tomatoes and peppers, and delicate flowers by maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels. The extended growing season in greenhouses allows for cultivation of both warm- and cool-weather crops, surpassing the limited scope of cold frames.
Seasonal Usage: Extending the Growing Season
Cold frames provide a cost-effective solution for extending the growing season by protecting plants from frost during early spring and late fall. Greenhouses offer a more controlled environment with temperature regulation and light management, allowing year-round cultivation of a wider variety of crops. While cold frames are ideal for short-term seasonal protection, greenhouses support continuous growth and higher yields through all seasons.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Cold frames offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional greenhouses by utilizing passive solar heating and natural insulation, reducing the need for supplemental energy. Greenhouses, while providing extended growing seasons and climate control, often require substantial energy inputs for heating and ventilation, impacting sustainability. Integrating cold frames with greenhouse systems can optimize energy use and promote environmentally sustainable horticulture practices.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Garden
Cold frames offer a cost-effective and space-saving solution for extending the growing season by protecting plants from frost and cold temperatures. Greenhouses provide a controlled environment with better temperature regulation, humidity control, and protection against pests, ideal for year-round gardening and growing a wider variety of plants. Choosing between a cold frame and a greenhouse depends on your budget, available space, and desired level of climate control for optimal plant growth.
Cold Frame vs Greenhouse Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com