
Light Requirement vs Darkness Requirement Illustration
Certain seeds require light to trigger germination, as exposure to specific wavelengths stimulates biochemical processes essential for growth. Conversely, some seeds necessitate darkness, relying on the absence of light to initiate enzyme activity that breaks dormancy. Understanding these light and darkness requirements is crucial for optimizing seed germination and ensuring successful plant development.
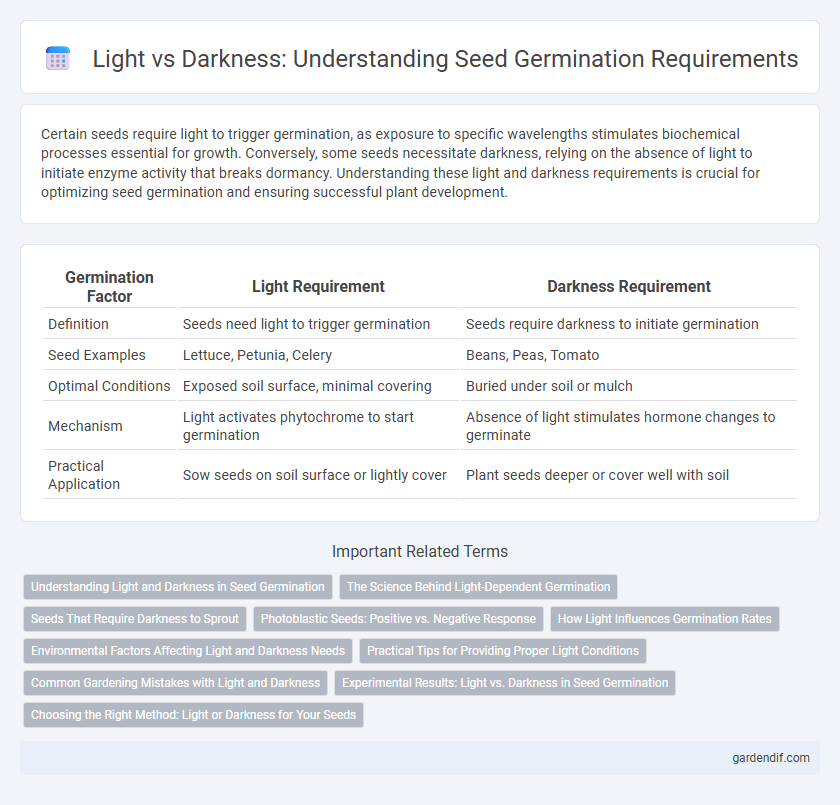
Table of Comparison
| Germination Factor | Light Requirement | Darkness Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seeds need light to trigger germination | Seeds require darkness to initiate germination |
| Seed Examples | Lettuce, Petunia, Celery | Beans, Peas, Tomato |
| Optimal Conditions | Exposed soil surface, minimal covering | Buried under soil or mulch |
| Mechanism | Light activates phytochrome to start germination | Absence of light stimulates hormone changes to germinate |
| Practical Application | Sow seeds on soil surface or lightly cover | Plant seeds deeper or cover well with soil |
Understanding Light and Darkness in Seed Germination
Seed germination often depends on species-specific light and darkness requirements that influence the activation of phytochrome pigments regulating growth hormones. Photoblastic seeds, such as lettuce, require exposure to light to trigger germination, while others like peony need darkness to initiate the process. Understanding the role of light and darkness optimizes seed germination rates by manipulating environmental conditions to suit specific seed types.
The Science Behind Light-Dependent Germination
Light-dependent germination occurs when specific seeds require exposure to light to initiate the biochemical processes triggering sprouting, primarily involving phytochrome photoreceptors that detect red and far-red light wavelengths. These photoreceptors regulate gene expression and hormonal pathways, such as the synthesis of gibberellins, which promote seed germination by breaking dormancy and stimulating embryo growth. In contrast, seeds with darkness requirements often rely on different molecular mechanisms, emphasizing the critical role of light quality and duration in seed germination ecology and agriculture.
Seeds That Require Darkness to Sprout
Seeds that require darkness to sprout include lettuce, pansy, and impatiens, which need to be buried beneath the soil to block light exposure. These seeds rely on the absence of light to trigger hormonal changes that promote germination, ensuring successful seedling development. Proper depth and soil coverage are crucial for darkness-dependent seeds to achieve optimal germination rates.
Photoblastic Seeds: Positive vs. Negative Response
Photoblastic seeds exhibit distinct germination responses based on light exposure, categorized as positive or negative photoblastism. Positive photoblastic seeds require light to trigger germination, as seen in lettuce (Lactuca sativa), where red light activates phytochrome receptors promoting seedling growth. Negative photoblastic seeds germinate in darkness, such as tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), where light inhibits phytochrome-mediated processes, delaying germination until buried under soil or leaf litter.
How Light Influences Germination Rates
Light significantly influences germination rates, with certain seeds requiring exposure to specific wavelengths to trigger enzyme activation and hormonal changes essential for sprouting. Photoreceptors such as phytochromes detect light quality and duration, promoting germination in light-dependent seeds like lettuce and petunia. Conversely, some seeds rely on darkness to maintain dormancy, where absence of light prevents premature germination until optimal conditions arise.
Environmental Factors Affecting Light and Darkness Needs
Seed germination is influenced by specific light and darkness requirements that vary by species, driven largely by environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and soil composition. Photoreceptors like phytochromes regulate responses to light quality and duration, affecting germination rates under light or dark conditions. Variations in seed coat thickness and chemical inhibitors also interact with light exposure, determining the optimal balance of light and darkness needed for successful germination.
Practical Tips for Providing Proper Light Conditions
Providing proper light conditions for seed germination involves understanding species-specific requirements, as some seeds demand light exposure while others need darkness to sprout effectively. Use transparent covers or place trays in well-lit areas for light-dependent seeds, ensuring indirect sunlight to avoid overheating. For darkness-requiring seeds, cover trays with opaque materials like black plastic or keep them in shaded environments to simulate natural underground conditions.
Common Gardening Mistakes with Light and Darkness
Many gardeners mistakenly expose seeds to excessive light or complete darkness, ignoring species-specific germination requirements; some seeds like lettuce need light to trigger sprouting, while others such as beans require darkness to initiate growth. Failing to mimic natural conditions by either covering light-demanding seeds or exposing darkness-reliant seeds to light results in poor germination rates and weak seedlings. Understanding the precise light or darkness requirements for each seed type optimizes sprouting success and prevents common cultivation failures in home gardening.
Experimental Results: Light vs. Darkness in Seed Germination
Experimental results reveal that seed germination rates vary significantly between light and darkness conditions, with photoblastic seeds showing distinct preferences based on species-specific light requirements. Positive photoblastic seeds demonstrate higher germination percentages under light exposure, while negative photoblastic seeds germinate more efficiently in darkness. Studies indicate that light quality, intensity, and duration critically influence the activation of germination-related physiological pathways, affecting hormone regulation such as gibberellin and abscisic acid balance.
Choosing the Right Method: Light or Darkness for Your Seeds
Selecting the appropriate germination method depends on the seed species' light sensitivity, as some seeds require light exposure to trigger sprouting while others need darkness to initiate growth. Understanding photoblastic responses--positive photoblastic seeds germinate in light, and negative photoblastic seeds germinate in darkness--ensures optimal germination rates. Monitoring seed packet instructions and experimenting with controlled light or dark conditions enhances successful seedling development.
Light Requirement vs Darkness Requirement Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com