
Seed priming vs Soaking Illustration
Seed priming enhances germination by partially hydrating seeds to activate metabolic processes without allowing radicle emergence, leading to faster and more uniform sprouting compared to soaking. Soaking involves immersing seeds in water for a period, which initiates germination but can cause oxygen deprivation or seed damage if overdone. Seed priming offers controlled moisture uptake, improving stress tolerance and seedling vigor more effectively than simple soaking methods.
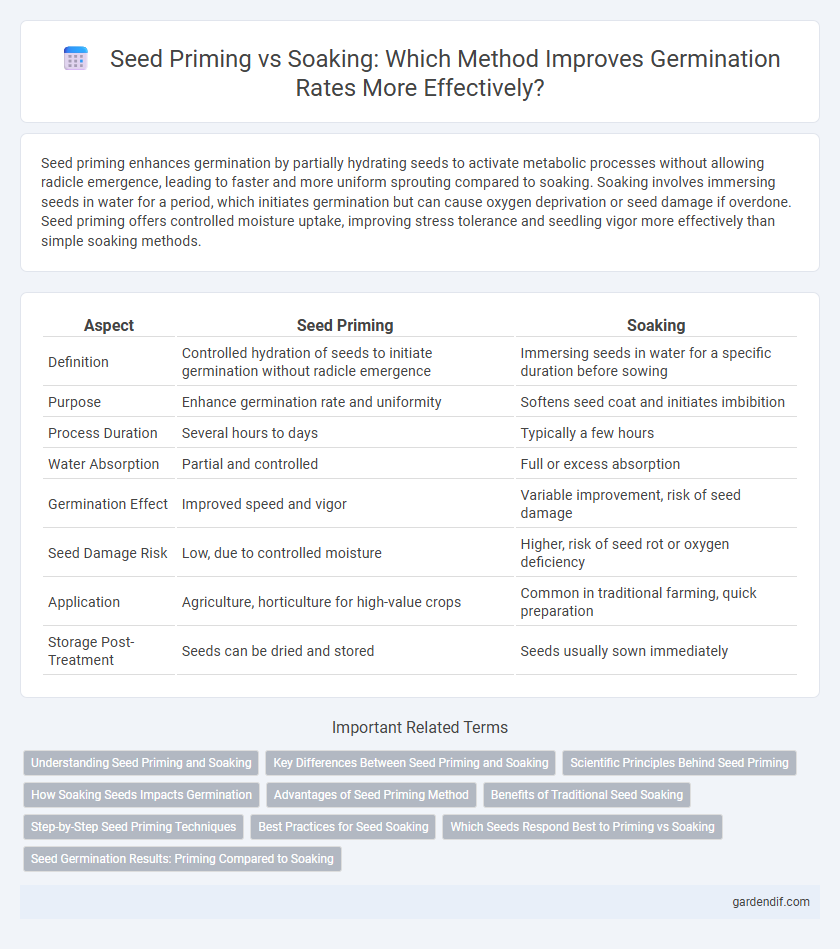
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Seed Priming | Soaking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled hydration of seeds to initiate germination without radicle emergence | Immersing seeds in water for a specific duration before sowing |
| Purpose | Enhance germination rate and uniformity | Softens seed coat and initiates imbibition |
| Process Duration | Several hours to days | Typically a few hours |
| Water Absorption | Partial and controlled | Full or excess absorption |
| Germination Effect | Improved speed and vigor | Variable improvement, risk of seed damage |
| Seed Damage Risk | Low, due to controlled moisture | Higher, risk of seed rot or oxygen deficiency |
| Application | Agriculture, horticulture for high-value crops | Common in traditional farming, quick preparation |
| Storage Post-Treatment | Seeds can be dried and stored | Seeds usually sown immediately |
Understanding Seed Priming and Soaking
Seed priming enhances germination by partially hydrating seeds to activate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, improving uniformity and speed of germination. Soaking involves immersing seeds in water for a set period to initiate hydration, but excessive soaking can lead to oxygen deprivation and seed damage. Seed priming techniques, including hydropriming, osmopriming, and biopriming, optimize water uptake and enzymatic activity, while soaking is a simpler, less controlled method that may affect seed vigor.
Key Differences Between Seed Priming and Soaking
Seed priming involves controlled hydration to initiate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, enhancing uniform germination rates and seedling vigor, while soaking simply involves immersing seeds in water to fully hydrate them before planting. Priming techniques optimize water uptake and oxygen availability, reducing germination time and improving stress tolerance, whereas soaking may lead to seed damage or reduced viability if prolonged. Seed priming integrates physiological and biochemical changes that promote faster germination, contrasting with soaking's passive hydration approach.
Scientific Principles Behind Seed Priming
Seed priming enhances germination by regulating water uptake through controlled hydration, activating metabolic processes without allowing radicle protrusion. This pre-germination treatment optimizes enzyme activity and repair mechanisms, improving seed vigor and uniformity compared to simple soaking, which often leads to uncontrolled imbibition and potential seed damage. Scientific principles emphasize osmoregulation and metabolic activation during priming, crucial for improving germination rates and stress tolerance.
How Soaking Seeds Impacts Germination
Soaking seeds accelerates germination by hydrating the seed coat, which activates enzyme processes essential for embryo development. This method enhances water uptake, breaking seed dormancy and promoting faster sprout emergence compared to dry seeds. Prolonged soaking, however, can reduce oxygen availability, increasing the risk of seed decay and inhibiting germination.
Advantages of Seed Priming Method
Seed priming improves germination rates by enhancing seed metabolism before planting, leading to faster and more uniform seedling emergence compared to soaking. This method reduces the risk of seed damage and fungal infections by controlling water uptake, unlike soaking which can cause overhydration. Seed priming also enhances drought tolerance and seedling vigor, resulting in better crop establishment and higher yields.
Benefits of Traditional Seed Soaking
Traditional seed soaking enhances germination by hydrating seeds uniformly, which activates metabolic processes necessary for sprouting. This method reduces seed dormancy and improves enzyme activity, leading to faster and more consistent seedling emergence. Soaking also leaches out inhibitors and toxins, increasing overall seed vigor and crop yield potential.
Step-by-Step Seed Priming Techniques
Seed priming involves controlled hydration techniques that initiate metabolic processes before sowing, enhancing germination rates and uniformity. Step-by-step seed priming typically includes selecting high-quality seeds, soaking them in water or nutrient solutions for specific durations, followed by surface drying to restore original moisture content before planting. This method contrasts with simple soaking, which lacks the drying phase and may cause seed damage or uneven germination.
Best Practices for Seed Soaking
Seed soaking involves immersing seeds in water for a specific duration to enhance germination speed and uniformity, with optimal soaking times varying by species to prevent oxygen deprivation and seed rot. Best practices include using clean, aerated water at controlled temperatures between 20-25degC and limiting soaking periods generally to 6-12 hours, depending on seed hardness and size. Proper drainage and immediate sowing after soaking maximize seed viability, while avoiding prolonged soaking prevents leaching of vital nutrients and susceptibility to fungal infections.
Which Seeds Respond Best to Priming vs Soaking
Seeds with hard coats or physiological dormancy, such as legumes and certain cereals, respond best to priming as it enhances uniform germination and stress tolerance. Soaking is more effective for seeds with less rigid seed coats like cucumbers and melons, where rapid water imbibition accelerates germination. Priming optimizes metabolic readiness without risking seed damage, whereas soaking can sometimes cause seed deterioration if prolonged.
Seed Germination Results: Priming Compared to Soaking
Seed priming significantly enhances germination rates compared to soaking by initiating metabolic processes without allowing radicle protrusion, resulting in faster and more uniform seedling emergence. Soaking merely hydrates seeds and may lead to oxygen depletion or seed damage if prolonged, reducing germination efficiency. Empirical studies reveal primed seeds often achieve 20-30% higher germination percentages and earlier germination onset than soaked counterparts.
Seed priming vs Soaking Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com