
Hydroponic lettuce vs Soil-grown lettuce Illustration
Hydroponic lettuce grows faster and often yields higher nutrient content compared to soil-grown lettuce due to controlled environment conditions enhancing nutrient absorption. Soil-grown lettuce benefits from natural soil microbes that can improve flavor complexity and texture, offering a more traditional taste experience. Both methods impact water usage differently, with hydroponic systems typically using less water, making them a sustainable option for urban farming.
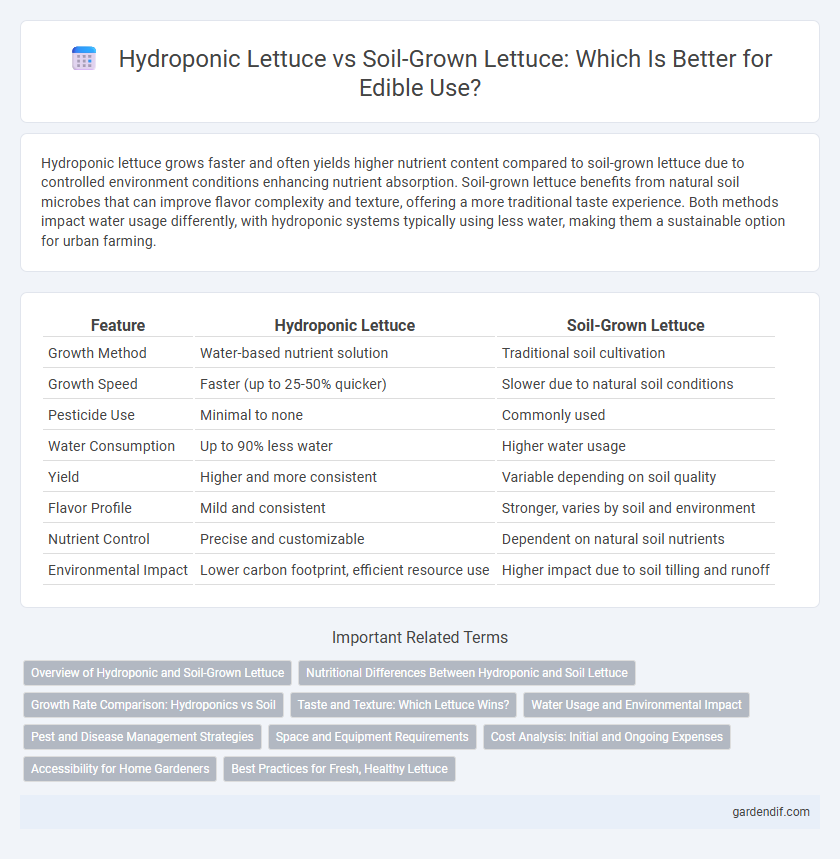
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroponic Lettuce | Soil-Grown Lettuce |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Method | Water-based nutrient solution | Traditional soil cultivation |
| Growth Speed | Faster (up to 25-50% quicker) | Slower due to natural soil conditions |
| Pesticide Use | Minimal to none | Commonly used |
| Water Consumption | Up to 90% less water | Higher water usage |
| Yield | Higher and more consistent | Variable depending on soil quality |
| Flavor Profile | Mild and consistent | Stronger, varies by soil and environment |
| Nutrient Control | Precise and customizable | Dependent on natural soil nutrients |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, efficient resource use | Higher impact due to soil tilling and runoff |
Overview of Hydroponic and Soil-Grown Lettuce
Hydroponic lettuce is cultivated in a controlled nutrient-rich water solution, offering faster growth rates and higher yields compared to soil-grown lettuce, which relies on soil quality and natural environmental conditions. Hydroponic systems reduce water usage by up to 90% and minimize pesticide use, making them an eco-friendly alternative to traditional soil farming. Soil-grown lettuce, while dependent on soil fertility and weather variability, often develops stronger root systems and distinct flavor profiles due to natural mineral absorption.
Nutritional Differences Between Hydroponic and Soil Lettuce
Hydroponic lettuce often contains higher levels of essential nutrients such as vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants compared to soil-grown lettuce due to controlled nutrient delivery. Soil-grown lettuce typically exhibits greater variability in mineral content influenced by soil quality and environmental factors. Studies indicate hydroponic cultivation can enhance nutrient density while reducing pesticide residues, offering a nutritionally consistent product.
Growth Rate Comparison: Hydroponics vs Soil
Hydroponic lettuce demonstrates a significantly faster growth rate compared to soil-grown lettuce, often reaching harvest readiness in 30 days versus 45 days in traditional soil methods. This accelerated growth results from optimal nutrient delivery and controlled environmental conditions inherent to hydroponic systems. Increased photosynthesis efficiency and consistent moisture levels further enhance hydroponic lettuce development, making it a preferred choice for rapid crop cycles.
Taste and Texture: Which Lettuce Wins?
Hydroponic lettuce often delivers a crisper texture and cleaner taste due to controlled nutrient delivery and absence of soil contaminants, making it favored in hydroponic farming systems. Soil-grown lettuce tends to have a richer, earthier flavor profile and a slightly softer texture influenced by natural soil minerals and microbial activity. Taste preferences vary, but hydroponic lettuce excels in consistency whereas soil-grown lettuce offers more complex flavor nuances.
Water Usage and Environmental Impact
Hydroponic lettuce requires up to 90% less water than soil-grown lettuce by recycling nutrient-rich water in a controlled environment, significantly reducing water waste. This method also minimizes soil erosion and pesticide runoff, lowering the environmental footprint of cultivation. Soil-grown lettuce depends heavily on irrigation, leading to higher water consumption and potential groundwater contamination.
Pest and Disease Management Strategies
Hydroponic lettuce benefits from a controlled environment that significantly reduces pest infestations and the spread of soil-borne diseases, unlike soil-grown lettuce, which is more vulnerable to nematodes, fungal infections, and insect pests. Integrated pest management (IPM) in hydroponics often includes biological controls like beneficial insects, while soil-grown systems rely heavily on crop rotation, soil fumigation, and chemical pesticides to mitigate pest pressure. Disease management in hydroponics emphasizes nutrient solution sterilization and monitoring, whereas soil-based methods focus on soil health maintenance and pathogen-resistant cultivars.
Space and Equipment Requirements
Hydroponic lettuce cultivation requires less physical space than soil-grown methods, making it ideal for urban farming and indoor gardening. Equipment for hydroponics includes nutrient delivery systems, water pumps, and grow lights, which optimize plant growth without the need for soil. In contrast, soil-grown lettuce needs larger plots of arable land and traditional farming tools but less specialized technology.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Ongoing Expenses
Hydroponic lettuce systems require higher initial investments due to specialized equipment such as grow trays, pumps, and nutrient delivery systems, whereas soil-grown lettuce primarily incurs costs in land preparation and traditional farming tools. Ongoing expenses for hydroponics include nutrient solutions, electricity for lighting and water circulation, and system maintenance, while soil cultivation demands expenditures on fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation. Despite higher startup costs, hydroponic lettuce can offer reduced labor and water usage, potentially lowering long-term operational expenses compared to soil-grown lettuce.
Accessibility for Home Gardeners
Hydroponic lettuce offers home gardeners a space-efficient and soil-free cultivation method, allowing for year-round growing indoors or in limited outdoor spaces. Soil-grown lettuce requires traditional garden space and may face challenges such as soil-borne diseases and pests, making it less accessible for urban gardeners. Hydroponic systems often come in compact kits that simplify setup and maintenance, making fresh lettuce production more approachable for beginners.
Best Practices for Fresh, Healthy Lettuce
Hydroponic lettuce offers precise nutrient control and reduced pesticide use, resulting in consistently fresh and healthy leaves. Soil-grown lettuce benefits from natural microbial activity that enhances flavor complexity and nutrient density. Best practices include maintaining optimal water pH (5.5-6.5) for hydroponics and ensuring well-drained, organic-rich soil for soil-grown lettuce to maximize growth and taste quality.
Hydroponic lettuce vs Soil-grown lettuce Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com