
Organic mulching vs Synthetic mulching Illustration
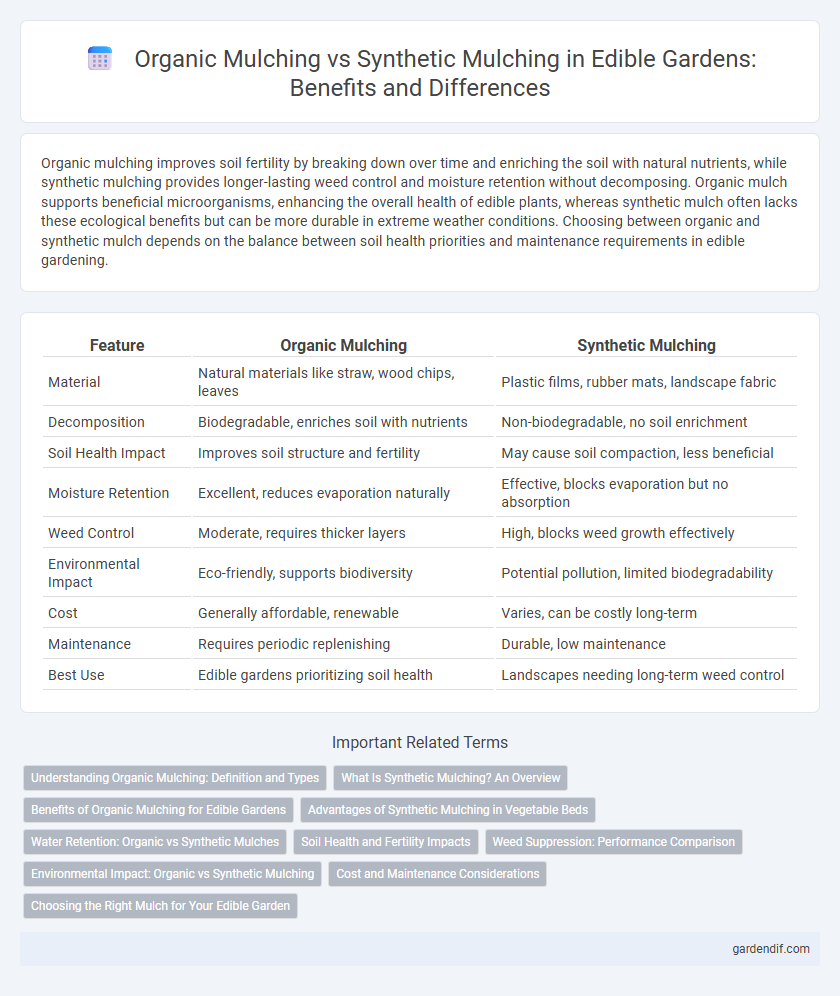
Organic mulching improves soil fertility by breaking down over time and enriching the soil with natural nutrients, while synthetic mulching provides longer-lasting weed control and moisture retention without decomposing. Organic mulch supports beneficial microorganisms, enhancing the overall health of edible plants, whereas synthetic mulch often lacks these ecological benefits but can be more durable in extreme weather conditions. Choosing between organic and synthetic mulch depends on the balance between soil health priorities and maintenance requirements in edible gardening.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Organic Mulching | Synthetic Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural materials like straw, wood chips, leaves | Plastic films, rubber mats, landscape fabric |
| Decomposition | Biodegradable, enriches soil with nutrients | Non-biodegradable, no soil enrichment |
| Soil Health Impact | Improves soil structure and fertility | May cause soil compaction, less beneficial |
| Moisture Retention | Excellent, reduces evaporation naturally | Effective, blocks evaporation but no absorption |
| Weed Control | Moderate, requires thicker layers | High, blocks weed growth effectively |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, supports biodiversity | Potential pollution, limited biodegradability |
| Cost | Generally affordable, renewable | Varies, can be costly long-term |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic replenishing | Durable, low maintenance |
| Best Use | Edible gardens prioritizing soil health | Landscapes needing long-term weed control |
Understanding Organic Mulching: Definition and Types
Organic mulching involves using natural materials such as straw, wood chips, leaves, and compost to cover the soil surface, enhancing moisture retention and soil fertility. Common types include straw mulch, bark mulch, leaf mold, and compost mulch, each contributing to improved microbial activity and nutrient cycling. This method promotes sustainable gardening by gradually decomposing and enriching the soil, unlike synthetic mulches which do not provide these ecological benefits.
What Is Synthetic Mulching? An Overview
Synthetic mulching involves the use of man-made materials such as plastic films, landscape fabrics, and geotextiles to cover soil surfaces, helping to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. These materials are designed to be durable and resistant to environmental degradation, providing long-lasting benefits compared to organic mulches. Common synthetic mulching options include black polyethylene sheets, woven polypropylene fabric, and rubber mulch, which are widely used in commercial agriculture and home gardening for their efficiency and low maintenance.
Benefits of Organic Mulching for Edible Gardens
Organic mulching enhances soil fertility by gradually decomposing and releasing essential nutrients, promoting healthier plant growth in edible gardens. It improves moisture retention, reducing water needs, and supports beneficial soil organisms that boost plant resilience. Unlike synthetic mulches, organic options such as straw, wood chips, or compost minimize environmental impact and contribute to sustainable gardening practices.
Advantages of Synthetic Mulching in Vegetable Beds
Synthetic mulching offers superior weed suppression and moisture retention in vegetable beds, promoting healthier plant growth and higher yields. Its durability reduces the need for frequent replacement, saving time and labor compared to organic mulches that decompose quickly. Furthermore, synthetic mulches create a stable soil temperature, enhancing root development and extending the growing season for various vegetables.
Water Retention: Organic vs Synthetic Mulches
Organic mulches such as straw, wood chips, and compost improve water retention by absorbing moisture and releasing it slowly into the soil, enhancing soil structure and promoting healthy root growth. Synthetic mulches like plastic films create a barrier that reduces evaporation but do not improve soil quality or moisture absorption capacity. Choosing organic mulch benefits long-term soil hydration and plant health, while synthetic mulch offers immediate water conservation but may require additional soil amendments.
Soil Health and Fertility Impacts
Organic mulching enhances soil health by improving microbial activity and increasing nutrient availability through natural decomposition, leading to better fertility and soil structure. Synthetic mulches, while effective at moisture retention and weed control, do not contribute organic matter, potentially limiting long-term soil fertility and microbial diversity. Choosing organic mulches such as straw, compost, or wood chips supports sustainable soil ecosystems and nutrient cycling essential for productive edible gardens.
Weed Suppression: Performance Comparison
Organic mulching, such as straw, wood chips, or compost, excels in weed suppression by creating a thick, natural barrier that blocks sunlight and inhibits weed seed germination while enriching soil health through nutrient release. Synthetic mulches, including plastic films, provide an effective physical barrier that suppresses weeds by completely blocking light but do not contribute to soil fertility or microbial activity. Studies indicate that organic mulching offers sustainable weed control benefits with added soil improvement, whereas synthetic mulching offers immediate and longer-lasting weed suppression but requires careful disposal and environmental consideration.
Environmental Impact: Organic vs Synthetic Mulching
Organic mulching, composed of natural materials like straw, wood chips, and compost, enhances soil health by enriching microbial activity and improving water retention while decomposing harmlessly. Synthetic mulching, often made from plastic or polymer sheets, can reduce water evaporation but contributes to long-term environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential microplastic contamination. Choosing organic mulches supports sustainable agricultural practices by promoting soil biodiversity and reducing landfill waste compared to synthetic alternatives.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Organic mulching involves higher initial investment due to materials like straw or wood chips but offers long-term soil health benefits that can reduce maintenance costs over time. Synthetic mulches, such as plastic or rubber, generally have lower upfront costs and require less frequent replacement but may increase expenses related to environmental disposal and soil degradation management. Choosing between organic and synthetic mulching depends on balancing immediate budget constraints with ongoing care and ecological impacts.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Edible Garden
Organic mulching, such as straw, wood chips, or compost, improves soil fertility by breaking down and enriching the soil, promoting healthier growth for vegetables and herbs. Synthetic mulches, like plastic or landscape fabric, offer superior weed control and moisture retention but do not contribute nutrients to the soil. Selecting the right mulch for your edible garden depends on crop type, climate, and maintenance preferences, balancing soil health benefits with practical weed and moisture management.
Organic mulching vs Synthetic mulching Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com