
Heritage Beans vs Commercial Beans Illustration
Heritage beans offer unique flavors and textures that reflect traditional farming practices and regional biodiversity, making them ideal for artisanal and gourmet dishes. Commercial beans are typically bred for uniformity, yield, and shelf life, favoring mass production and consistent quality for everyday consumption. Choosing heritage beans supports agricultural diversity and preserves heirloom varieties often lost in commercial cultivation.
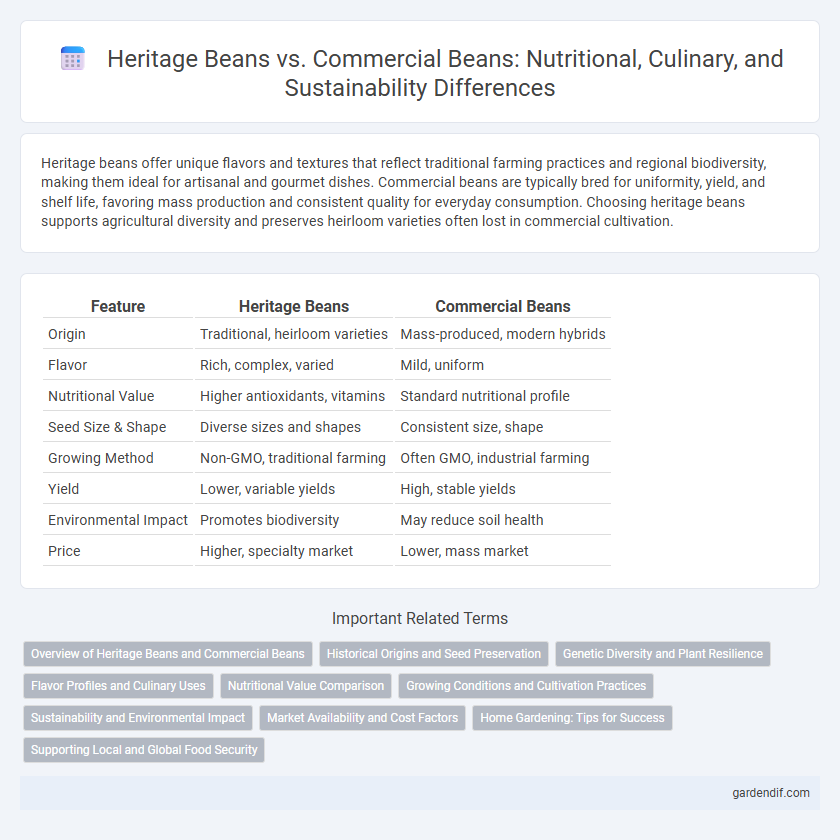
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heritage Beans | Commercial Beans |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Traditional, heirloom varieties | Mass-produced, modern hybrids |
| Flavor | Rich, complex, varied | Mild, uniform |
| Nutritional Value | Higher antioxidants, vitamins | Standard nutritional profile |
| Seed Size & Shape | Diverse sizes and shapes | Consistent size, shape |
| Growing Method | Non-GMO, traditional farming | Often GMO, industrial farming |
| Yield | Lower, variable yields | High, stable yields |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes biodiversity | May reduce soil health |
| Price | Higher, specialty market | Lower, mass market |
Overview of Heritage Beans and Commercial Beans
Heritage beans, often heirloom varieties, are prized for their unique flavors, diverse colors, and historical cultivation methods, preserving genetic diversity and local agricultural traditions. Commercial beans prioritize high yield, uniformity, and disease resistance, supporting large-scale production and consistent market supply. Both types offer distinct benefits, with heritage beans favored for culinary quality and sustainability, while commercial beans cater to industrial efficiency and volume.
Historical Origins and Seed Preservation
Heritage beans trace their historical origins to indigenous agriculture, preserved through generations by heirloom seed-saving practices that maintain genetic diversity and cultural heritage. Commercial beans, in contrast, typically derive from modern breeding programs prioritizing yield, uniformity, and disease resistance, often resulting in a narrower genetic base. Seed preservation efforts for heritage beans safeguard rare varieties against extinction, supporting biodiversity and traditional food systems.
Genetic Diversity and Plant Resilience
Heritage beans exhibit greater genetic diversity compared to commercial beans, providing a richer pool of traits that enhance plant resilience against pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. This genetic variability allows heritage beans to adapt more effectively to changing conditions, ensuring sustainability and food security. In contrast, commercial beans often prioritize uniformity and high yield, which can reduce resilience and increase vulnerability to crop failures.
Flavor Profiles and Culinary Uses
Heritage beans offer complex, rich flavor profiles with earthy, nutty, and sometimes sweet undertones that enhance traditional recipes, while commercial beans tend to have milder, more uniform tastes suited for mass production. Culinary uses for heritage beans often include slow-cooked dishes like stews and soups, highlighting their robust texture and depth, whereas commercial beans are favored for quick cooking and versatile applications such as salads or purees. The distinctive flavors of heritage beans contribute to authentic regional cuisines, making them prized in gourmet and farm-to-table cooking.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Heritage beans typically contain higher levels of protein, fiber, and essential micronutrients such as iron and magnesium compared to commercial beans, which are often bred for yield and uniformity rather than nutrient density. The diverse genetic profiles of heritage beans contribute to their richer antioxidant content and complex amino acid profiles, supporting better nutritional benefits. In contrast, commercial beans may lack this nutritional variety due to selective breeding and extensive processing.
Growing Conditions and Cultivation Practices
Heritage beans thrive in diverse microclimates and often require traditional cultivation practices that emphasize soil health and crop rotation, enhancing flavor complexity and resilience. Commercial beans are typically grown under standardized conditions with intensive use of fertilizers and pesticides to maximize yield and uniformity. These distinct growing conditions result in heritage beans having unique taste profiles and nutritional benefits compared to the more uniform commercial varieties.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Heritage beans, often cultivated through traditional farming methods, support biodiversity and promote soil health by enhancing nitrogen fixation and reducing chemical dependency. Commercial beans typically rely on monoculture practices and synthetic fertilizers, which can lead to soil degradation, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and water pollution. Choosing heritage beans contributes to sustainable agriculture by preserving genetic diversity and minimizing environmental impact compared to conventional commercial bean production.
Market Availability and Cost Factors
Heritage beans, often heirloom varieties, are less commonly found in mainstream supermarkets and usually available through specialty or farmers' markets, which can limit their market availability compared to widely distributed commercial beans. The cost of heritage beans tends to be higher due to smaller-scale production, traditional farming methods, and limited supply chains. Commercial beans benefit from mass production and standardized farming practices, making them more affordable and easily accessible in larger retail outlets.
Home Gardening: Tips for Success
Heritage beans offer unique flavors and genetic diversity, making them ideal for home gardeners seeking resilience and taste. To maximize success, plant heritage beans in well-drained soil with consistent moisture and provide adequate support for climbing varieties. Commercial beans generally require less maintenance but may lack the disease resistance found in heirloom varieties, making heritage beans a rewarding choice for sustainable home gardening.
Supporting Local and Global Food Security
Heritage beans, rich in genetic diversity and adapted to local climates, play a crucial role in supporting both local and global food security by preserving resilient crop varieties. Unlike commercial beans, which often prioritize uniformity and high yield, heritage beans contribute to sustainable agriculture by enhancing soil health and reducing dependency on chemical inputs. Promoting heritage bean cultivation helps maintain biodiversity, supports small-scale farmers, and strengthens food systems against climate change challenges worldwide.
Heritage Beans vs Commercial Beans Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com