
Heirloom Tomatoes vs Hybrid Tomatoes Illustration
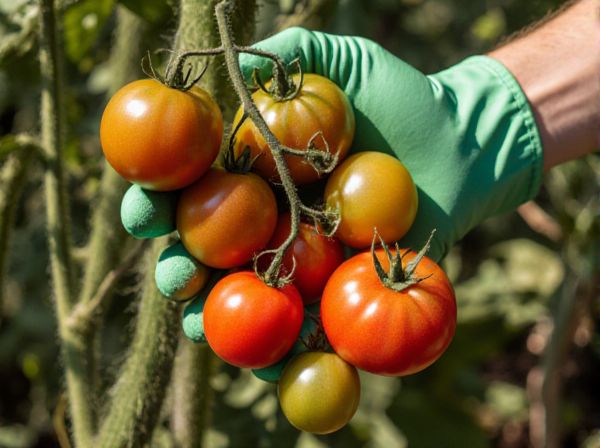
Heirloom tomatoes offer rich, complex flavors and unique colors due to their open-pollinated heritage, preserving genetic diversity. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for consistency, higher yield, and disease resistance, often resulting in more uniform appearance but milder taste. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid tomatoes depends on whether flavor and variety or durability and productivity are prioritized.
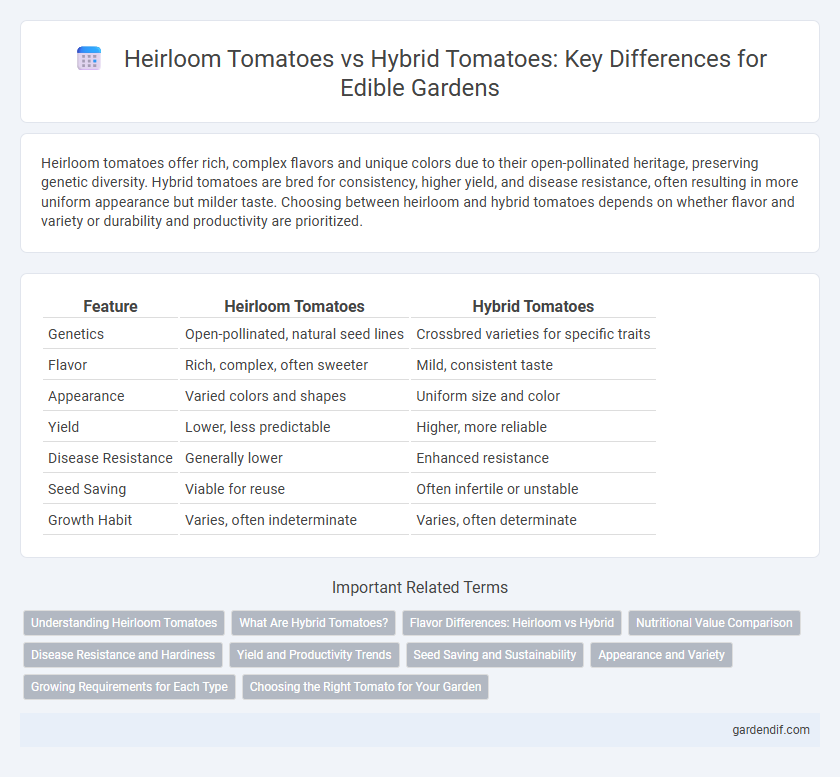
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heirloom Tomatoes | Hybrid Tomatoes |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Open-pollinated, natural seed lines | Crossbred varieties for specific traits |
| Flavor | Rich, complex, often sweeter | Mild, consistent taste |
| Appearance | Varied colors and shapes | Uniform size and color |
| Yield | Lower, less predictable | Higher, more reliable |
| Disease Resistance | Generally lower | Enhanced resistance |
| Seed Saving | Viable for reuse | Often infertile or unstable |
| Growth Habit | Varies, often indeterminate | Varies, often determinate |
Understanding Heirloom Tomatoes
Heirloom tomatoes are open-pollinated varieties that have been passed down through generations, prized for their unique flavors, colors, and shapes. Unlike hybrid tomatoes, which are bred for uniformity and durability, heirlooms often emphasize taste and heritage, making them popular among home gardeners and gourmet chefs. These tomatoes generally thrive best in specific climates and require careful cultivation to preserve their genetic diversity.
What Are Hybrid Tomatoes?
Hybrid tomatoes are cultivated varieties created by cross-breeding two different tomato plants to combine desirable traits like disease resistance, higher yield, and uniform appearance. These tomatoes often have enhanced shelf life and improved adaptability to various growing conditions compared to heirloom varieties. Hybrid tomatoes are widely favored in commercial agriculture for consistent quality and productivity.
Flavor Differences: Heirloom vs Hybrid
Heirloom tomatoes are prized for their rich, complex flavors and diverse taste profiles, often ranging from sweet and tangy to earthy and robust, due to their open-pollinated heritage. Hybrid tomatoes typically offer a milder, more uniform flavor designed for durability and higher yields, which can sometimes result in less intensity compared to heirlooms. The distinctive, vibrant taste of heirloom tomatoes makes them a favorite for fresh consumption, while hybrids are valued for consistent production and shelf-life.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Heirloom tomatoes are often prized for their rich flavor and higher antioxidant levels, including lycopene and vitamin C, compared to many hybrid varieties. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for durability and yield, sometimes resulting in lower concentrations of certain phytonutrients. Studies indicate heirlooms may offer superior nutritional benefits due to their varied genetic profiles and minimal selective breeding.
Disease Resistance and Hardiness
Heirloom tomatoes often have rich flavors but tend to be less resistant to diseases and environmental stress compared to hybrid tomatoes. Hybrid tomatoes are specifically bred for enhanced disease resistance and greater hardiness, making them more reliable in diverse growing conditions. Choosing between heirloom and hybrid varieties depends on prioritizing flavor diversity or plant resilience and productivity.
Yield and Productivity Trends
Heirloom tomatoes typically yield lower harvests per plant compared to hybrid tomatoes, reflecting their focus on flavor and genetic diversity rather than productivity. Hybrid tomatoes are bred for higher yield and disease resistance, resulting in more consistent and abundant crops, making them popular among commercial growers. Over recent productivity trends, hybrids continue to dominate due to optimized growth traits, while heirlooms maintain niche appeal for gourmet and local markets.
Seed Saving and Sustainability
Heirloom tomatoes preserve genetic diversity by allowing gardeners to save seeds year after year, fostering sustainability in home gardens and small farms. Hybrid tomatoes, while offering higher yields and disease resistance, produce seeds that often fail to breed true, requiring new purchases each season and limiting long-term seed saving. Choosing heirloom varieties supports biodiversity and a resilient food system by promoting seed sovereignty and reducing reliance on commercial seed suppliers.
Appearance and Variety
Heirloom tomatoes showcase diverse shapes, vibrant colors, and unique patterns, including stripes and multicolored hues, making them visually striking compared to hybrid tomatoes. Hybrids tend to have a more uniform appearance, with consistent size, shape, and bright red or pink coloration suited for commercial markets. The variety in heirlooms spans dozens of rare cultivars, whereas hybrids prioritize disease resistance and yield with a narrower aesthetic range.
Growing Requirements for Each Type
Heirloom tomatoes require consistent watering, well-drained soil rich in organic matter, and full sun exposure for at least 6-8 hours daily to thrive. Hybrid tomatoes often have enhanced disease resistance and may tolerate a wider range of soil types while still needing ample sunlight and regular irrigation. Proper staking or caging is essential for both types to support growth and maximize fruit production.
Choosing the Right Tomato for Your Garden
Heirloom tomatoes offer rich, diverse flavors and unique shapes that appeal to gardeners valuing taste and genetic variety, while hybrid tomatoes provide disease resistance and higher yields ideal for reliable production. When choosing the right tomato for your garden, consider your local climate, disease pressures, and whether flavor or productivity is your priority. Selecting cultivars like Brandywine or Cherokee Purple for heirlooms, versus Roma or Better Boy for hybrids, optimizes garden success based on these factors.
Heirloom Tomatoes vs Hybrid Tomatoes Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com