
Trap cropping vs repellent planting Illustration
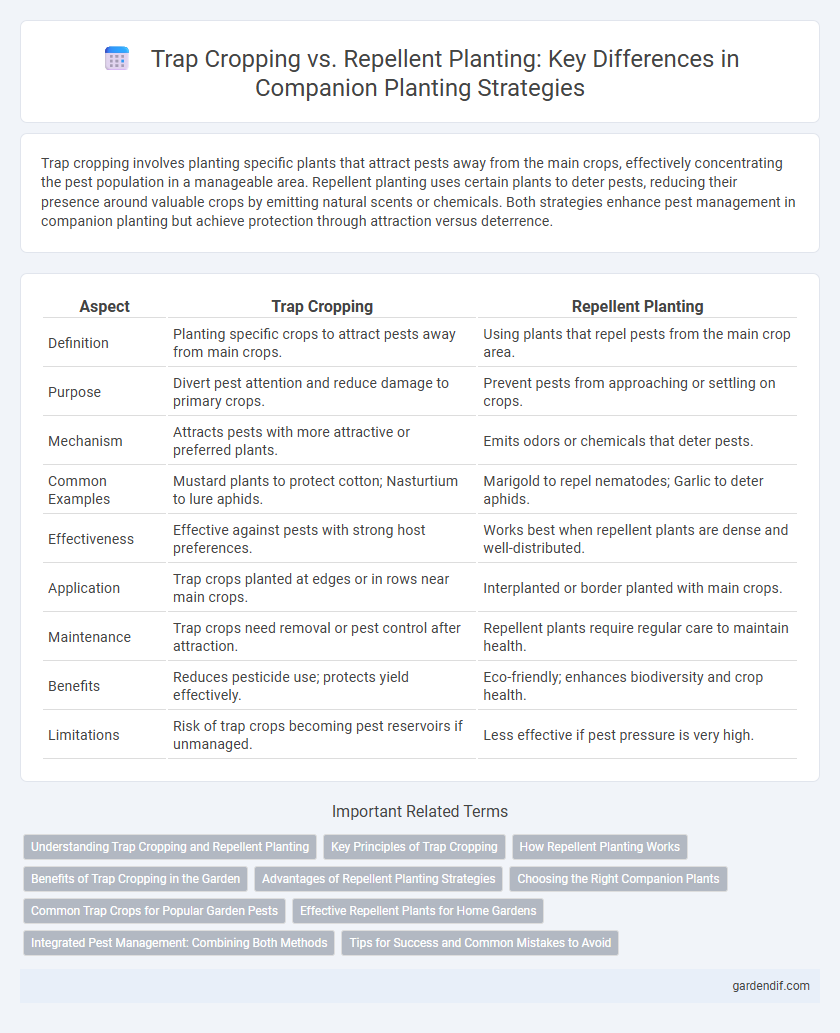
Trap cropping involves planting specific plants that attract pests away from the main crops, effectively concentrating the pest population in a manageable area. Repellent planting uses certain plants to deter pests, reducing their presence around valuable crops by emitting natural scents or chemicals. Both strategies enhance pest management in companion planting but achieve protection through attraction versus deterrence.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Trap Cropping | Repellent Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planting specific crops to attract pests away from main crops. | Using plants that repel pests from the main crop area. |
| Purpose | Divert pest attention and reduce damage to primary crops. | Prevent pests from approaching or settling on crops. |
| Mechanism | Attracts pests with more attractive or preferred plants. | Emits odors or chemicals that deter pests. |
| Common Examples | Mustard plants to protect cotton; Nasturtium to lure aphids. | Marigold to repel nematodes; Garlic to deter aphids. |
| Effectiveness | Effective against pests with strong host preferences. | Works best when repellent plants are dense and well-distributed. |
| Application | Trap crops planted at edges or in rows near main crops. | Interplanted or border planted with main crops. |
| Maintenance | Trap crops need removal or pest control after attraction. | Repellent plants require regular care to maintain health. |
| Benefits | Reduces pesticide use; protects yield effectively. | Eco-friendly; enhances biodiversity and crop health. |
| Limitations | Risk of trap crops becoming pest reservoirs if unmanaged. | Less effective if pest pressure is very high. |
Understanding Trap Cropping and Repellent Planting
Trap cropping involves planting specific plants that attract pests away from the main crop, effectively reducing pest damage by concentrating pests on a less valuable or sacrificial crop. Repellent planting uses barrier or companion plants that emit odors or chemicals deterring pests, minimizing their presence near the primary crop. Understanding the distinct mechanisms of trap cropping and repellent planting is crucial for optimizing integrated pest management strategies in sustainable agriculture.
Key Principles of Trap Cropping
Trap cropping involves planting a specific crop near the main crop to lure pests away, effectively reducing pest damage to valuable plants. Key principles include selecting a highly attractive trap crop, strategically placing it to intercept pest movement, and timing its growth to coincide with the pest's lifecycle. This method enhances pest management by concentrating pests in manageable areas, minimizing pesticide use and promoting sustainable agriculture.
How Repellent Planting Works
Repellent planting works by using specific plants that emit odors or chemical compounds deterring pests from targeting nearby crops, effectively reducing pest pressure without chemical pesticides. These plants create a protective zone by masking the scent of the main crop or by directly repelling insects that cause damage. This method promotes sustainable pest management in companion planting systems by naturally discouraging harmful pests and encouraging beneficial insects.
Benefits of Trap Cropping in the Garden
Trap cropping strategically attracts pests to specific plants, reducing damage to valuable crops and enhancing overall garden productivity. By concentrating pest populations on sacrificial trap plants, gardeners minimize the need for chemical interventions, promoting a healthier ecosystem. This method supports biodiversity, improves pest management, and leads to higher yields in companion planting systems.
Advantages of Repellent Planting Strategies
Repellent planting strategies offer targeted pest management by emitting natural chemical cues that deter harmful insects without harming beneficial species, promoting ecological balance. These methods reduce reliance on synthetic pesticides, contributing to sustainable agriculture and lower environmental impact. Enhanced crop yields and improved plant health result from minimized pest damage, making repellent planting a cost-effective and eco-friendly companion planting approach.
Choosing the Right Companion Plants
Choosing the right companion plants involves evaluating the effectiveness of trap cropping versus repellent planting based on target pests and crop compatibility. Trap cropping attracts and confines pests to sacrificial plants, reducing damage to main crops, while repellent planting uses species that deter pests through natural odors or chemicals. Selecting companion plants requires understanding local pest behavior, plant growth habits, and ecological balance to optimize pest control and crop yield.
Common Trap Crops for Popular Garden Pests
Common trap crops like mustard, nasturtium, and marigold effectively lure aphids, whiteflies, and flea beetles away from main plants, reducing pest damage in vegetable gardens. Repellent plants such as garlic or basil emit odors that deter pests but do not attract them, offering a less targeted pest management strategy. Selecting trap crops tailored to specific pests provides a more focused and efficient companion planting technique for integrated pest control.
Effective Repellent Plants for Home Gardens
Effective repellent plants for home gardens include marigolds, basil, and garlic, which deter pests like aphids, whiteflies, and nematodes by emitting strong odors that insects avoid. These plants serve as natural protectors by creating a barrier that reduces pest colonization and decreases the need for chemical pesticides. Strategic placement of repellent plants near susceptible crops enhances garden health and promotes sustainable pest management.
Integrated Pest Management: Combining Both Methods
Trap cropping and repellent planting play crucial roles in Integrated Pest Management by targeting pest behavior through attraction and deterrence. Using trap crops, pest insects are lured away from main crops, minimizing damage, while repellent plants discourage pests with natural compounds, reducing infestation risks. Combining these strategies enhances pest control effectiveness, promoting sustainable agriculture and lowering chemical pesticide reliance.
Tips for Success and Common Mistakes to Avoid
Effective trap cropping requires selecting highly attractive plants to draw pests away from the main crop and timely removal of these trap plants before pests migrate back. Repellent planting demands choosing strong-scented or pest-deterring species planted consistently around the primary crop to ensure maximum efficacy. Common mistakes include mixing incompatible plants, neglecting proper spacing, and failing to monitor pest activity, which can reduce the protective benefits of both methods.
Trap cropping vs repellent planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com