
Chives vs aphids Illustration
Chives act as a natural deterrent against aphids due to their strong aroma, which masks the scent of nearby plants and repels these pests. Planting chives near susceptible vegetables and flowers can significantly reduce aphid infestations without the need for chemical pesticides. Their presence supports a healthier garden ecosystem by promoting pest control and enhancing plant growth.
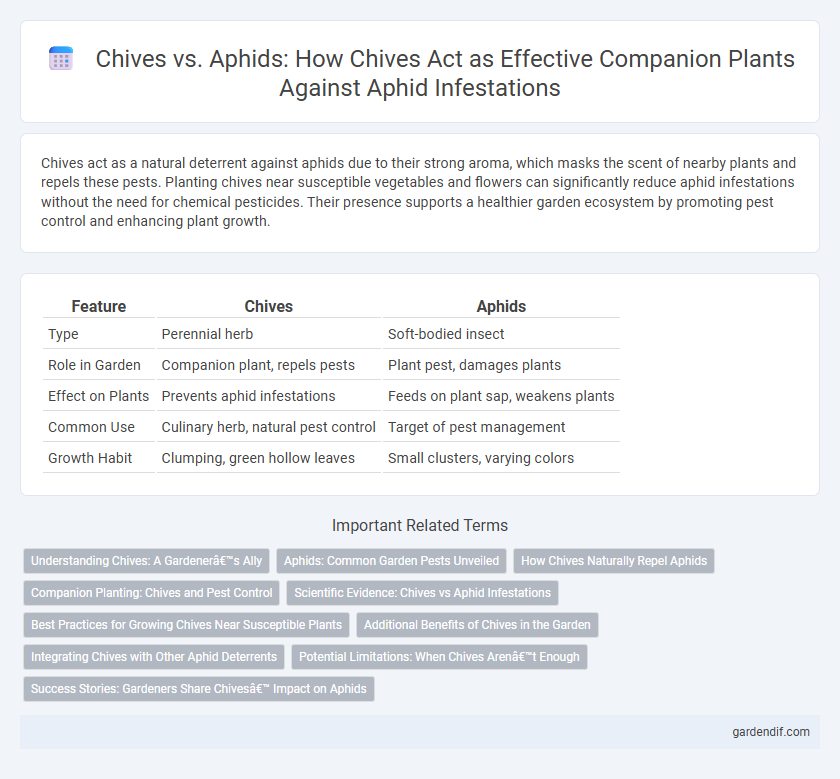
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chives | Aphids |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Perennial herb | Soft-bodied insect |
| Role in Garden | Companion plant, repels pests | Plant pest, damages plants |
| Effect on Plants | Prevents aphid infestations | Feeds on plant sap, weakens plants |
| Common Use | Culinary herb, natural pest control | Target of pest management |
| Growth Habit | Clumping, green hollow leaves | Small clusters, varying colors |
Understanding Chives: A Gardener’s Ally
Chives serve as a natural pest deterrent against aphids by releasing sulfur compounds that repel these insects, protecting nearby plants from infestation. Their dense, tubular leaves create a physical barrier, reducing aphid access and minimizing damage to companion crops. Integrating chives into vegetable gardens enhances plant health and promotes a balanced ecosystem without relying on chemical pesticides.
Aphids: Common Garden Pests Unveiled
Aphids, notorious garden pests, feed on plant sap, weakening chives by causing yellowing leaves and stunted growth. These small, soft-bodied insects reproduce rapidly, making early detection and control essential to preserve chive health. Natural predators like ladybugs and organic insecticidal soaps offer effective aphid management without harming companion plants.
How Chives Naturally Repel Aphids
Chives contain sulfur compounds and a strong onion-like scent that naturally repel aphids by disrupting their sensory receptors. These aromatic properties act as an effective deterrent, reducing aphid infestations without harmful chemicals. Incorporating chives in gardens promotes healthy plant growth and protects nearby crops from aphid damage.
Companion Planting: Chives and Pest Control
Chives serve as an effective companion plant by naturally repelling aphids through their strong sulfur compounds, which disrupt aphid feeding and reproduction. Planting chives near susceptible crops like roses, tomatoes, or lettuce reduces aphid infestations, promoting healthier plant growth without chemical pesticides. This natural pest control method enhances garden biodiversity and supports sustainable gardening practices.
Scientific Evidence: Chives vs Aphid Infestations
Scientific studies highlight chives (Allium schoenoprasum) as an effective natural deterrent against aphid infestations due to their strong sulfur-containing compounds, which disrupt aphid feeding behavior. Research published in agricultural entomology journals demonstrates a significant reduction in aphid populations on plants grown near chives, confirming their role as a companion plant in integrated pest management. These findings support the practical use of chives to minimize reliance on chemical pesticides while enhancing garden biodiversity.
Best Practices for Growing Chives Near Susceptible Plants
Plant chives near susceptible plants to naturally repel aphids, as their strong aroma deters these pests without harmful chemicals. Regularly inspect chives for aphid presence, removing any clusters by spraying with water or applying insecticidal soap if infestation appears. Employing companion planting techniques, such as interspersing chives with roses or tomatoes, enhances plant health and reduces aphid damage effectively.
Additional Benefits of Chives in the Garden
Chives act as a natural aphid repellent, reducing pest populations without harmful chemicals and promoting a healthier garden ecosystem. Their sulfur compounds not only deter aphids but also improve soil health and enhance the growth of neighboring plants. Incorporating chives into garden beds supports biodiversity by attracting beneficial insects like pollinators and predatory bugs that control aphid infestations.
Integrating Chives with Other Aphid Deterrents
Chives act as a natural aphid deterrent by emitting sulfur compounds that repel these pests, making them an effective companion plant in vegetable gardens. Integrating chives with other aphid deterrents such as marigolds, garlic, and nasturtiums enhances pest control through complementary chemical defenses and diversified plant structures. Combining these plants creates a synergistic environment that reduces aphid populations while promoting overall garden health.
Potential Limitations: When Chives Aren’t Enough
Chives can help repel aphids by emitting sulfur compounds that disrupt their feeding, but their effectiveness is often limited in large infestations or severe aphid outbreaks. Aphids can quickly multiply and overwhelm chives' natural deterrent capabilities, especially without additional biological controls or physical removal methods. Relying solely on chives as a companion plant might not provide sufficient protection, necessitating integrated pest management for optimal aphid control.
Success Stories: Gardeners Share Chives’ Impact on Aphids
Gardeners consistently report that planting chives near vulnerable plants significantly reduces aphid infestations, highlighting chives' natural insect-repellent properties. The strong sulfur compounds in chives disrupt aphids' feeding patterns, effectively decreasing their population without harmful pesticides. These success stories emphasize chives as an eco-friendly, low-maintenance solution for managing aphids in home gardens.
Chives vs aphids Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com