
Herbaceous companions vs woody companions Illustration
Herbaceous companions enhance garden diversity with their soft stems and seasonal growth, providing vibrant colors and attracting beneficial insects. Woody companions offer structural support and long-term stability through their durable trunks and perennial nature, often improving soil quality and microclimate. Combining both types creates a balanced ecosystem that promotes plant health and maximizes space.
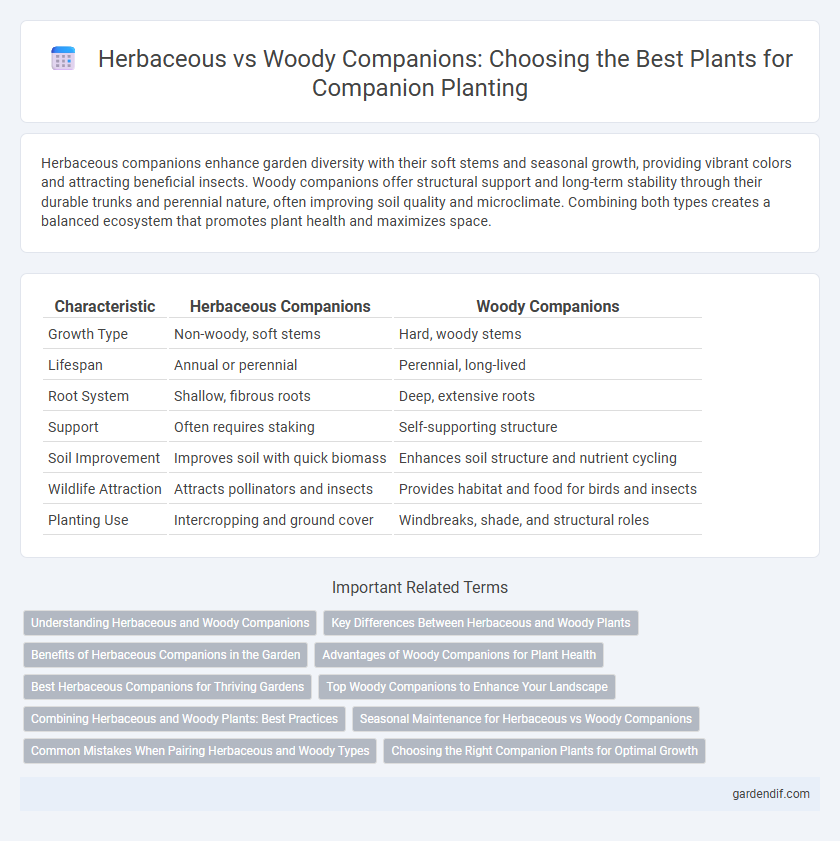
Table of Comparison
| Characteristic | Herbaceous Companions | Woody Companions |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Type | Non-woody, soft stems | Hard, woody stems |
| Lifespan | Annual or perennial | Perennial, long-lived |
| Root System | Shallow, fibrous roots | Deep, extensive roots |
| Support | Often requires staking | Self-supporting structure |
| Soil Improvement | Improves soil with quick biomass | Enhances soil structure and nutrient cycling |
| Wildlife Attraction | Attracts pollinators and insects | Provides habitat and food for birds and insects |
| Planting Use | Intercropping and ground cover | Windbreaks, shade, and structural roles |
Understanding Herbaceous and Woody Companions
Herbaceous companions consist of soft-stemmed plants that complete their life cycle within a single growing season, making them ideal for quick growth and seasonal diversity in companion planting. Woody companions, such as shrubs and trees, provide structural support, long-term stability, and enhanced nutrient cycling through deep root systems and persistent biomass. Understanding the complementary roles of herbaceous and woody companions enables gardeners to optimize plant health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services in sustainable planting designs.
Key Differences Between Herbaceous and Woody Plants
Herbaceous companions have soft, non-woody stems that die back seasonally, while woody companions develop hard, lignified stems that persist year-round. Herbaceous plants often grow faster and require less maintenance, making them ideal for annual or short-term garden integration, whereas woody plants provide structural support and long-term habitat stability. The root systems of woody companions tend to be deeper and more extensive compared to the shallow roots of herbaceous companions, affecting soil health and moisture retention.
Benefits of Herbaceous Companions in the Garden
Herbaceous companions in the garden enhance soil health through improved aeration and organic matter contribution, promoting nutrient availability for surrounding plants. Their rapid growth cycles enable effective weed suppression and attract beneficial insects that aid in pest control. These companions also increase biodiversity, fostering a balanced ecosystem that supports plant resilience and productivity.
Advantages of Woody Companions for Plant Health
Woody companions enhance plant health by providing durable support structures that improve air circulation and reduce pest infestations. Their deep root systems promote soil stability and nutrient uptake, fostering a resilient growing environment. These companions also contribute to microclimate regulation, protecting vulnerable plants from extreme weather conditions.
Best Herbaceous Companions for Thriving Gardens
Herbaceous companions such as basil, marigold, and chives create optimal conditions for thriving gardens by enhancing soil nutrients and deterring pests naturally. These plants improve pollination rates and support beneficial insect populations, promoting healthier growth in surrounding vegetables and flowers. Integrating herbaceous companions into garden beds increases biodiversity, leading to more resilient and productive garden ecosystems.
Top Woody Companions to Enhance Your Landscape
Top woody companions such as dogwood, viburnum, and holly trees provide structure, year-round interest, and habitat benefits that enhance landscape aesthetics and biodiversity. These woody plants offer height variation and seasonal texture, making them ideal for framing garden designs and creating natural privacy screens. Integrating woody companions with herbaceous plants increases resilience against pests and environmental stress, promoting a balanced and thriving ecosystem.
Combining Herbaceous and Woody Plants: Best Practices
Combining herbaceous and woody plants enhances garden biodiversity by providing varied structural layers and seasonal interest. Integrate deep-rooted woody shrubs with shallow-rooted herbaceous plants to optimize soil nutrient use and prevent competition. Selecting complementary species based on light, moisture, and growth habits promotes healthy coexistence and sustained garden productivity.
Seasonal Maintenance for Herbaceous vs Woody Companions
Herbaceous companions require more frequent seasonal maintenance such as regular pruning, deadheading, and cutting back to promote new growth and prevent disease. Woody companions need less frequent but more intensive seasonal care including structural pruning in late winter or early spring to maintain shape and encourage healthy branching. Proper seasonal maintenance tailored to each type ensures optimal growth, flowering, and overall plant health throughout the year.
Common Mistakes When Pairing Herbaceous and Woody Types
Herbaceous companions often suffer from overshadowing when paired with woody types due to differing light and root space requirements, leading to stunted growth or poor health. A common mistake involves failing to consider the water needs and soil preferences of both, as woody plants typically demand deeper, less frequent watering while herbaceous plants prefer consistent moisture. Neglecting these fundamental differences results in competition for resources, making balanced pairings critical for successful garden design.
Choosing the Right Companion Plants for Optimal Growth
Herbaceous companions, such as basil and marigold, enhance soil nutrients and attract beneficial insects, promoting optimal growth for neighboring plants. Woody companions like nitrogen-fixing trees provide long-term structural support and improve soil fertility through deep root systems. Selecting the right balance between herbaceous and woody companions maximizes nutrient cycling, pest control, and plant health in diverse garden ecosystems.
Herbaceous companions vs woody companions Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com