
Support climbing vs bush varieties Illustration
Support climbing plants rely on structures such as trellises or fences to grow vertically, maximizing space and improving air circulation. Bush varieties grow independently as compact, self-supporting shrubs, making them ideal for smaller gardens or areas without support systems. Choosing between support climbing and bush varieties depends on available space, garden design, and maintenance preferences.
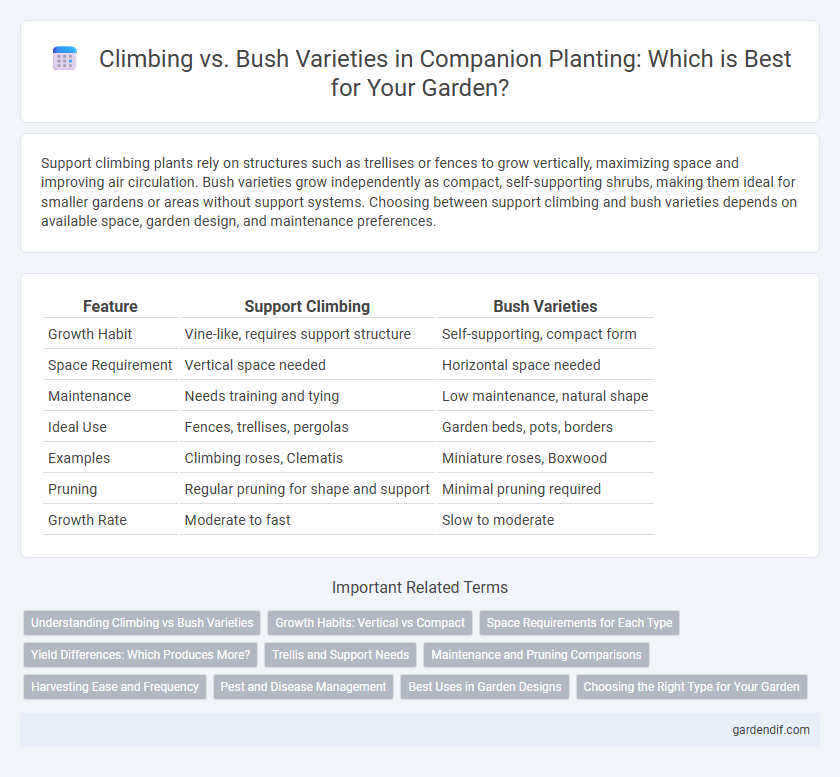
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Support Climbing | Bush Varieties |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Habit | Vine-like, requires support structure | Self-supporting, compact form |
| Space Requirement | Vertical space needed | Horizontal space needed |
| Maintenance | Needs training and tying | Low maintenance, natural shape |
| Ideal Use | Fences, trellises, pergolas | Garden beds, pots, borders |
| Examples | Climbing roses, Clematis | Miniature roses, Boxwood |
| Pruning | Regular pruning for shape and support | Minimal pruning required |
| Growth Rate | Moderate to fast | Slow to moderate |
Understanding Climbing vs Bush Varieties
Climbing companion plants grow vertically with the help of supports like trellises, making them ideal for maximizing small garden spaces by utilizing vertical height. Bush varieties, on the other hand, grow compactly without the need for support structures, providing dense foliage and easier maintenance. Choosing between climbing and bush companion plants depends on garden layout, available space, and the specific companion benefits such as pest control and soil enrichment.
Growth Habits: Vertical vs Compact
Support climbing companions exhibit vertical growth habits, rapidly extending upward with tendrils or twining stems that anchor onto structures, ideal for maximizing vertical space in gardens. In contrast, bush varieties display compact, dense growth forms that spread horizontally, providing fuller ground coverage and thriving without the need for external support. These differing growth habits influence planting strategies, with climbers suited for trellises and walls, while bush varieties enhance soil retention and biodiversity at ground level.
Space Requirements for Each Type
Support climbing companion plants, such as beans and peas, typically require vertical structures and careful spacing to prevent overcrowding, often needing at least 6 to 12 inches between plants to ensure optimal growth. Bush varieties like bush beans demand more horizontal space, generally around 12 to 18 inches apart, as they spread outward rather than upward, making them suitable for smaller garden areas without the need for trellises. Understanding these space requirements helps gardeners efficiently plan their companion planting, maximizing yield and health for both plant types.
Yield Differences: Which Produces More?
Support climbing plants, such as pole beans, typically produce higher yields per square foot compared to bush varieties due to their vertical growth habit, which optimizes space and sunlight exposure. Bush varieties offer the advantage of earlier harvests but generally yield less overall due to their limited growth height and shorter fruiting period. Yield differences also depend on factors like soil quality, pruning, and watering, with climbing types benefiting more from well-managed trellising systems.
Trellis and Support Needs
Support climbing companions require sturdy trellises to accommodate their vigorous growth and heavy foliage, ensuring proper air circulation and sunlight exposure. Bush varieties, being more compact and self-supporting, need minimal staking or low supports to maintain shape and prevent sprawling. Selecting the correct support type enhances plant health and optimizes garden space.
Maintenance and Pruning Comparisons
Support climbing plants require regular maintenance including training shoots along trellises and periodic pruning to promote airflow and prevent disease; pruning often involves cutting back to healthy buds to encourage vigorous growth. Bush varieties demand less frequent pruning but benefit from removing dead or overcrowded branches annually to maintain shape and vitality. Both types thrive with proper seasonal pruning schedules tailored to their growth habits, ensuring sustained health and productivity.
Harvesting Ease and Frequency
Support climbing companion plants typically offer easier harvesting due to their vertical growth, which reduces the risk of damage and allows for better air circulation around fruits. These varieties often produce multiple harvests throughout the season, enabling frequent picking and extended yield. In contrast, bush varieties tend to have denser foliage that can complicate harvest access, often resulting in fewer but larger harvest sessions.
Pest and Disease Management
Support climbing companions like beans and peas improve air circulation and sunlight exposure, reducing the risk of fungal diseases compared to bush varieties. Bush varieties tend to have denser foliage, creating a microclimate that favors pests such as aphids and spider mites. Selecting climbing companions with natural resistance and maintaining proper spacing enhances integrated pest and disease management in the garden.
Best Uses in Garden Designs
Support climbing plants thrive on trellises, fences, and arbors, providing vertical interest and maximizing garden space with vibrant flowers or lush foliage. Bush varieties excel as foundation plantings, borders, or mass plantings, offering structure, color, and wildlife habitat in compact areas. Selecting the right companion based on garden design needs enhances aesthetics and promotes healthy plant growth through complementary use of space and form.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Garden
Support climbing plants thrive when provided with sturdy trellises or frames, ideal for vertical growth in limited spaces, while bush varieties require more ground area and benefit from well-drained soil and ample sunlight. Choosing climbing types like clematis or honeysuckle enhances garden height and structure, whereas bush varieties such as hydrangeas or roses offer dense foliage and vibrant blooms at lower levels. Understanding your garden's space and light availability guides the selection between these growth habits, ensuring optimal plant health and aesthetic appeal.
Support climbing vs bush varieties Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com