
Facilitation vs competition Illustration
Companions foster facilitation by encouraging collaboration, mutual support, and shared goals, which enhance personal growth and collective success. In contrast, competition emphasizes outperforming others, often leading to rivalry and stress that can hinder teamwork and positive relationships. Prioritizing facilitation over competition cultivates a more inclusive and supportive environment where individuals thrive together.
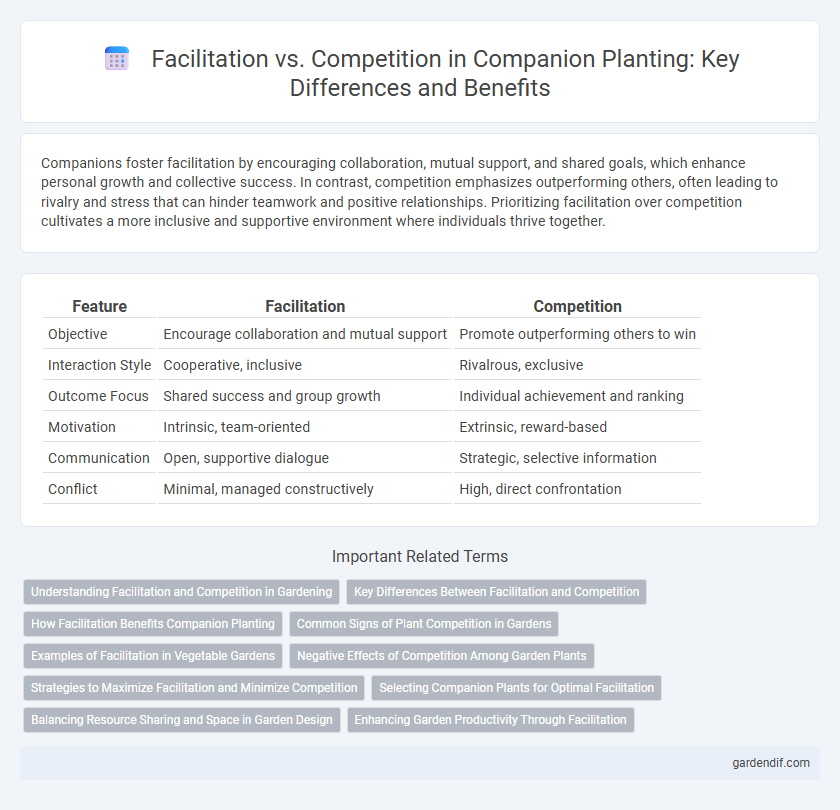
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facilitation | Competition |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Encourage collaboration and mutual support | Promote outperforming others to win |
| Interaction Style | Cooperative, inclusive | Rivalrous, exclusive |
| Outcome Focus | Shared success and group growth | Individual achievement and ranking |
| Motivation | Intrinsic, team-oriented | Extrinsic, reward-based |
| Communication | Open, supportive dialogue | Strategic, selective information |
| Conflict | Minimal, managed constructively | High, direct confrontation |
Understanding Facilitation and Competition in Gardening
Facilitation in gardening occurs when certain plants improve the growth conditions for neighboring species by providing shade, retaining moisture, or enriching soil nutrients, promoting a healthier ecosystem. Competition arises when plants vie for the same limited resources such as sunlight, water, and soil nutrients, potentially inhibiting each other's growth. Understanding these interactions enables gardeners to design plant combinations that enhance overall productivity and biodiversity within the garden environment.
Key Differences Between Facilitation and Competition
Facilitation occurs when one species benefits another without causing harm, enhancing growth or survival through positive interactions, while competition involves species vying for the same limited resources, negatively impacting at least one participant. In ecological contexts, facilitation often promotes biodiversity and ecosystem stability, whereas competition can lead to resource partitioning and evolutionary adaptations. Key differences hinge on the nature of interactions: facilitation is mutually beneficial or neutral, whereas competition is antagonistic, influencing species distribution and community structure.
How Facilitation Benefits Companion Planting
Facilitation in companion planting enhances plant growth by improving nutrient uptake, attracting beneficial insects, and deterring pests through natural means. This mutual support reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting a healthier and more sustainable garden ecosystem. Plants like beans enrich soil nitrogen for nearby crops, demonstrating how facilitation optimizes overall plant health and yield.
Common Signs of Plant Competition in Gardens
Common signs of plant competition in gardens include stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced flowering, all indicating nutrient or light deficiencies. Overcrowding often leads to root entanglement and uneven moisture distribution, stressing weaker plants. Effective facilitation involves strategic spacing and selecting complementary species to promote coexistence and overall garden health.
Examples of Facilitation in Vegetable Gardens
Facilitation in vegetable gardens occurs when certain plants enhance the growth or health of others, such as planting marigolds alongside tomatoes to deter harmful nematodes or intercropping basil with peppers to improve flavor and repel pests. Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting nearby leafy greens like lettuce and spinach, leading to increased yields. Sunflowers can provide natural shade for cucumbers, protecting them from excessive heat and promoting better growth.
Negative Effects of Competition Among Garden Plants
Competition among garden plants often leads to reduced growth and lower yields due to limited resources like water, nutrients, and sunlight. Root systems may become entangled, causing stress and inhibiting proper nutrient uptake, while taller plants overshadow smaller ones, diminishing photosynthesis. This interference ultimately weakens plant health, increases susceptibility to diseases, and decreases overall garden productivity.
Strategies to Maximize Facilitation and Minimize Competition
Companion animals enhance social facilitation by encouraging positive interactions and cooperative behaviors, which can be maximized through structured joint activities and environmental enrichment that promote shared goals. Minimizing competition requires careful resource allocation, such as providing multiple feeding stations and separate resting areas to reduce territorial disputes and stress. Strategic monitoring of behavior patterns and timely intervention helps maintain harmony, ensuring the companion environment supports facilitation over rivalry.
Selecting Companion Plants for Optimal Facilitation
Selecting companion plants that maximize facilitation involves identifying species that improve each other's growth by enhancing nutrient availability, providing pest control, or offering shade and support. Examples include planting nitrogen-fixing legumes alongside heavy feeders like maize to boost soil fertility, or pairing marigolds with tomatoes to repel pests naturally. Understanding specific plant interactions and microclimate effects ensures optimal resource use and higher crop yields through strategic companion planting.
Balancing Resource Sharing and Space in Garden Design
Balancing resource sharing and space in garden design enhances companion planting by optimizing sunlight, water, and nutrient distribution among plants. Strategic facilitation promotes mutual growth benefits, while controlled competition prevents overcrowding and resource depletion. Effective garden layouts ensure diverse plant compatibility, supporting ecosystem health and maximizing yield.
Enhancing Garden Productivity Through Facilitation
Facilitation in garden productivity emphasizes mutual benefits where companion plants improve growth conditions, nutrient availability, and pest resistance for each other. For example, legumes fix nitrogen into the soil, enriching it for neighboring plants like tomatoes, which in turn provide shade and support. This cooperative strategy boosts overall yield and resilience compared to competitive planting, which often reduces resource access and plant health.
Facilitation vs competition Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com