
Dynamic accumulators vs Soil builders Illustration
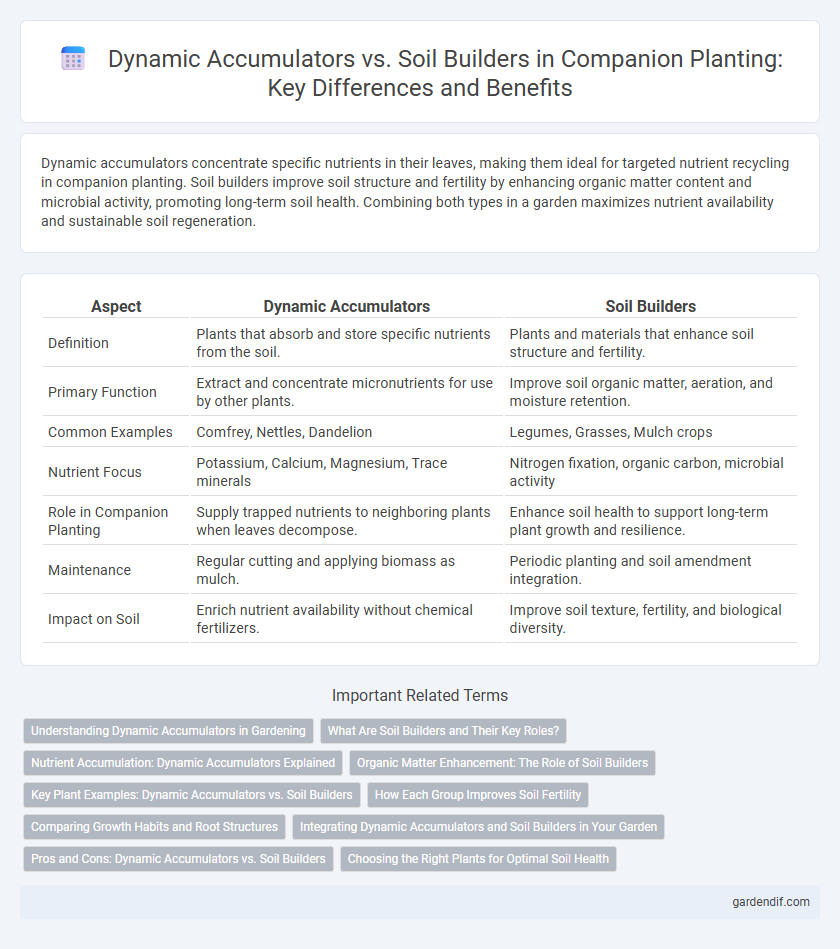
Dynamic accumulators concentrate specific nutrients in their leaves, making them ideal for targeted nutrient recycling in companion planting. Soil builders improve soil structure and fertility by enhancing organic matter content and microbial activity, promoting long-term soil health. Combining both types in a garden maximizes nutrient availability and sustainable soil regeneration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dynamic Accumulators | Soil Builders |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants that absorb and store specific nutrients from the soil. | Plants and materials that enhance soil structure and fertility. |
| Primary Function | Extract and concentrate micronutrients for use by other plants. | Improve soil organic matter, aeration, and moisture retention. |
| Common Examples | Comfrey, Nettles, Dandelion | Legumes, Grasses, Mulch crops |
| Nutrient Focus | Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Trace minerals | Nitrogen fixation, organic carbon, microbial activity |
| Role in Companion Planting | Supply trapped nutrients to neighboring plants when leaves decompose. | Enhance soil health to support long-term plant growth and resilience. |
| Maintenance | Regular cutting and applying biomass as mulch. | Periodic planting and soil amendment integration. |
| Impact on Soil | Enrich nutrient availability without chemical fertilizers. | Improve soil texture, fertility, and biological diversity. |
Understanding Dynamic Accumulators in Gardening
Dynamic accumulators are plants that absorb and store specific nutrients from the soil, enriching it when their foliage or roots decompose. Unlike general soil builders, these plants target particular minerals such as potassium, calcium, or nitrogen, enhancing soil fertility in a focused manner. Incorporating dynamic accumulators in companion planting strategies optimizes nutrient cycling and supports sustainable garden ecosystems.
What Are Soil Builders and Their Key Roles?
Soil builders are plants that enhance soil fertility and structure by fixing nitrogen, increasing organic matter, and promoting beneficial microbial activity. Key roles of soil builders include improving nutrient cycling, enhancing water retention, and reducing soil erosion, which supports healthier companion crops. Examples of effective soil builders include legumes like clover and vetch, which enrich soil with nitrogen critical for plant growth.
Nutrient Accumulation: Dynamic Accumulators Explained
Dynamic accumulators are plants specifically chosen for their ability to mine and concentrate essential nutrients like potassium, calcium, and magnesium from the soil, making them accessible for companion plants. Unlike general soil builders that improve soil structure and organic matter broadly, dynamic accumulators target nutrient enrichment by storing minerals in their leaves and roots. Incorporating these plants in companion planting cycles boosts nutrient cycling efficiency, enhancing overall soil fertility and plant health.
Organic Matter Enhancement: The Role of Soil Builders
Soil builders play a crucial role in enhancing organic matter by breaking down plant residues and increasing microbial activity, which improves soil structure and nutrient availability. Unlike dynamic accumulators that primarily concentrate specific nutrients from the subsoil, soil builders contribute to overall soil fertility by adding diverse organic compounds and promoting humus formation. This process boosts water retention and supports healthy root development, essential for sustainable companion planting.
Key Plant Examples: Dynamic Accumulators vs. Soil Builders
Dynamic accumulators such as comfrey, nettle, and yarrow concentrate essential nutrients like potassium, calcium, and nitrogen in their leaves, making them ideal for nutrient cycling in companion planting. Soil builders like clover, alfalfa, and lupine improve soil structure and fertility by fixing nitrogen and increasing organic matter through deep root systems. Combining dynamic accumulators with soil builders enhances overall soil health by replenishing specific nutrients and improving soil texture for sustainable plant growth.
How Each Group Improves Soil Fertility
Dynamic accumulators enhance soil fertility by mining deep nutrients from subsoil layers and concentrating them in their leaves, which release valuable minerals like potassium, calcium, and magnesium when decomposed. Soil builders improve fertility by increasing organic matter through extensive root systems and biomass production, promoting microbial activity and enhancing soil structure for better nutrient retention. Together, dynamic accumulators provide targeted nutrient replenishment while soil builders sustain long-term soil health and nutrient cycling.
Comparing Growth Habits and Root Structures
Dynamic accumulators develop deep, fibrous root systems that extract and store nutrients from subsoil layers, enhancing soil fertility by recycling minerals. Soil builders feature extensive, dense root networks that improve soil structure and organic matter through continuous biomass contribution. Comparing growth habits, dynamic accumulators grow rapidly to access and deposit nutrients, while soil builders establish persistent root mats that promote long-term soil aeration and microbial activity.
Integrating Dynamic Accumulators and Soil Builders in Your Garden
Integrating dynamic accumulators and soil builders enhances garden fertility by combining nutrient mining and organic matter enrichment. Dynamic accumulators like comfrey pull deep minerals to the surface, while soil builders such as legumes improve soil structure and nitrogen content. This synergy promotes healthier plants and sustainable soil health for long-term garden productivity.
Pros and Cons: Dynamic Accumulators vs. Soil Builders
Dynamic accumulators enhance soil fertility by mining deep nutrients and bringing them to the surface, improving nutrient availability for companion plants, but they may tie up nitrogen temporarily during decomposition. Soil builders, such as compost and cover crops, boost organic matter and microbial life, promoting long-term soil structure and health, though they require more time and space to implement effectively. Balancing dynamic accumulators with soil builders optimizes nutrient cycling and soil vitality for sustainable companion planting systems.
Choosing the Right Plants for Optimal Soil Health
Dynamic accumulators, such as comfrey and nettle, are plants that extract and concentrate specific nutrients from the soil, making them available for future use when their leaves decompose. Soil builders like legumes not only fix nitrogen but also enhance soil structure through root biomass and organic matter. Selecting the right combination of dynamic accumulators and soil builders tailored to your garden's nutrient needs and soil type ensures optimal soil health and sustainable plant growth.
Dynamic accumulators vs Soil builders Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com