
Marigolds vs nematodes Illustration
Marigolds are effective companion plants known for their natural ability to repel nematodes, microscopic pests that attack plant roots and reduce crop yields. The roots of marigolds release chemicals that disrupt the life cycle of nematodes, thereby protecting nearby plants from infestation. Planting marigolds around susceptible crops creates a natural barrier, improving soil health and promoting stronger, pest-resistant growth.
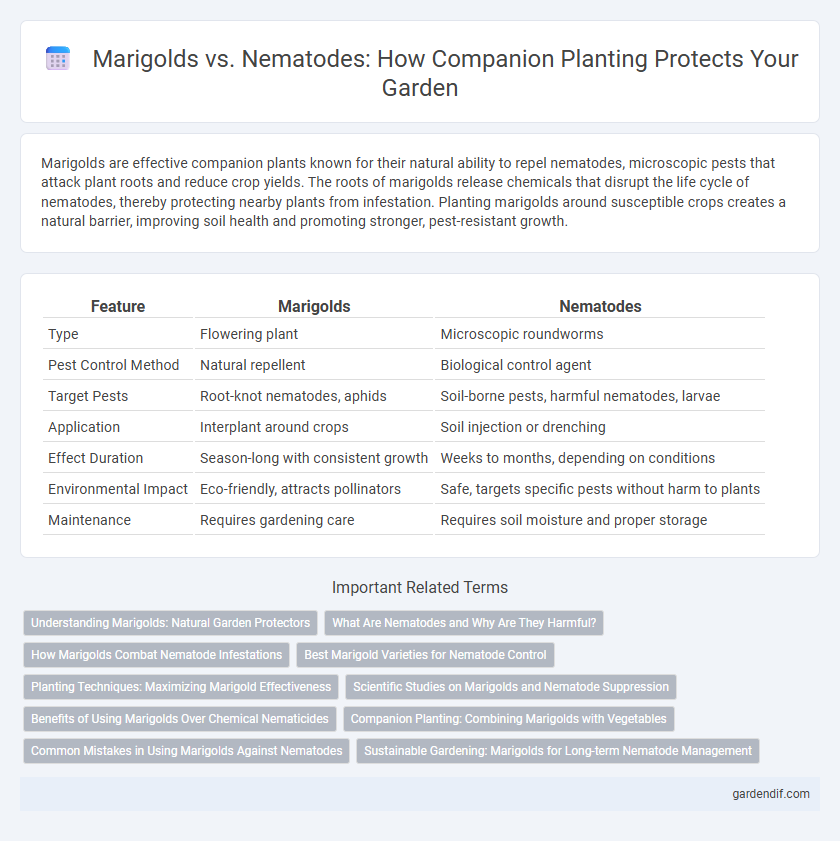
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Marigolds | Nematodes |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Flowering plant | Microscopic roundworms |
| Pest Control Method | Natural repellent | Biological control agent |
| Target Pests | Root-knot nematodes, aphids | Soil-borne pests, harmful nematodes, larvae |
| Application | Interplant around crops | Soil injection or drenching |
| Effect Duration | Season-long with consistent growth | Weeks to months, depending on conditions |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, attracts pollinators | Safe, targets specific pests without harm to plants |
| Maintenance | Requires gardening care | Requires soil moisture and proper storage |
Understanding Marigolds: Natural Garden Protectors
Marigolds release thiophenes, natural compounds that effectively repel nematodes and prevent root damage in vegetable gardens. These vibrant flowers act as biological nematicides, disrupting nematode life cycles and reducing soil-borne pest populations without harmful chemicals. Growing marigolds alongside susceptible plants boosts garden health and promotes sustainable pest management.
What Are Nematodes and Why Are They Harmful?
Nematodes are microscopic roundworms commonly found in soil, some of which act as plant parasites damaging roots and limiting nutrient uptake. Harmful nematodes, such as root-knot nematodes, cause gall formation that stunts plant growth and reduces crop yields. Marigolds release natural biofumigants that suppress nematode populations, making them an effective companion plant for nematode management.
How Marigolds Combat Nematode Infestations
Marigolds produce thiophenes, natural compounds that are toxic to root-knot nematodes, disrupting their life cycle and preventing infestation. Their root exudates repel nematodes and inhibit egg hatching, effectively reducing nematode populations in the soil. Planting marigolds as companion plants creates a protective barrier for susceptible crops by decreasing nematode damage and improving overall soil health.
Best Marigold Varieties for Nematode Control
Tagetes erecta, Tagetes patula, and Tagetes tenuifolia represent the best marigold varieties for nematode control, known for their natural biofumigant properties that suppress root-knot nematode populations. These marigolds release thiophene compounds from their roots, which are toxic to nematodes and help improve soil health by reducing nematode density. Planting these species in crop rotation or as border plants can effectively protect vegetable gardens and fields from nematode-related damage.
Planting Techniques: Maximizing Marigold Effectiveness
Planting marigolds in staggered rows around susceptible crops creates a natural barrier that disrupts nematode movement, enhancing soil protection. Incorporating marigolds as a green manure or intercropped within vegetable beds increases root exudate concentration, which suppresses nematode populations effectively. Timing marigold planting to precede or coincide with nematode-prone crops maximizes root zone coverage, reducing nematode infestation and improving crop health.
Scientific Studies on Marigolds and Nematode Suppression
Scientific studies demonstrate that marigolds (Tagetes spp.) effectively suppress root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) by releasing bioactive compounds such as alpha-terthienyl that inhibit nematode egg hatch and juvenile development. Experimental results highlight marigold species like Tagetes patula as particularly potent in reducing nematode populations in agricultural soils. Field trials confirm that incorporating marigold cover crops can significantly decrease nematode-induced crop damage, enhancing soil health and plant vigor.
Benefits of Using Marigolds Over Chemical Nematicides
Marigolds suppress harmful nematodes naturally by releasing bioactive compounds from their roots that disrupt nematode reproduction and survival, offering an eco-friendly alternative to chemical nematicides. Their use improves soil health and promotes beneficial soil microorganisms, enhancing overall plant growth without the toxic residues associated with synthetic chemicals. Marigolds reduce reliance on chemical treatments, making them a sustainable and effective companion plant for nematode management in agricultural and garden ecosystems.
Companion Planting: Combining Marigolds with Vegetables
Marigolds are effective in companion planting as they emit thiophenes, natural compounds that repel root-knot nematodes harmful to vegetables like tomatoes and peppers. Interplanting marigolds with susceptible crops helps reduce nematode populations in the soil, improving plant health and yield. Research shows that Tagetes species, especially Tagetes patula, provide significant nematode suppression, making them a valuable ally in sustainable vegetable gardening.
Common Mistakes in Using Marigolds Against Nematodes
Common mistakes in using marigolds against nematodes include planting the wrong species, such as Tagetes erecta instead of Tagetes patula, which is less effective in nematode control. Another frequent error is not timing the planting correctly; marigolds must be grown for at least 8 weeks before nematode host plants to reduce nematode populations effectively. Overlooking soil conditions and density can also limit marigold efficacy, as sparse planting or poor soil health diminishes their nematode-repellent properties.
Sustainable Gardening: Marigolds for Long-term Nematode Management
Marigolds (Tagetes spp.) effectively suppress root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) through natural biofumigants released by their roots, making them a sustainable choice for long-term nematode management. These companion plants reduce nematode populations without harmful chemicals, promoting healthier soil biodiversity and organic gardening practices. Integrating marigolds into crop rotations and garden beds enhances nematode control while supporting sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
Marigolds vs nematodes Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com