
Corn vs bean beetle Illustration
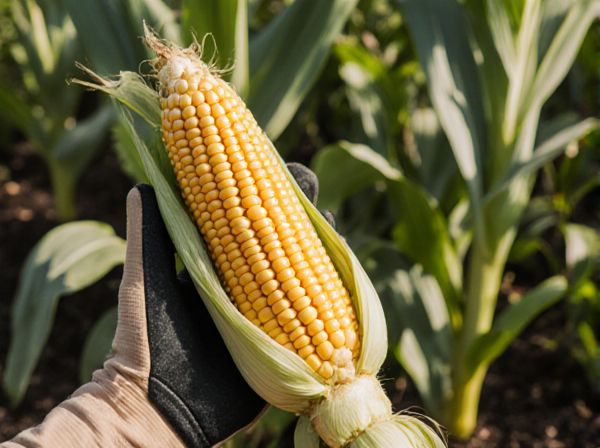
Corn beetles and bean beetles are common pests that target different crops, with corn beetles primarily infesting maize and bean beetles attacking various legume species. Both species cause significant damage by feeding on plants, but corn beetles often impact the stalks and leaves while bean beetles focus on the pods and seeds. Effective pest management requires identifying the specific beetle type to apply targeted treatments and prevent crop losses.
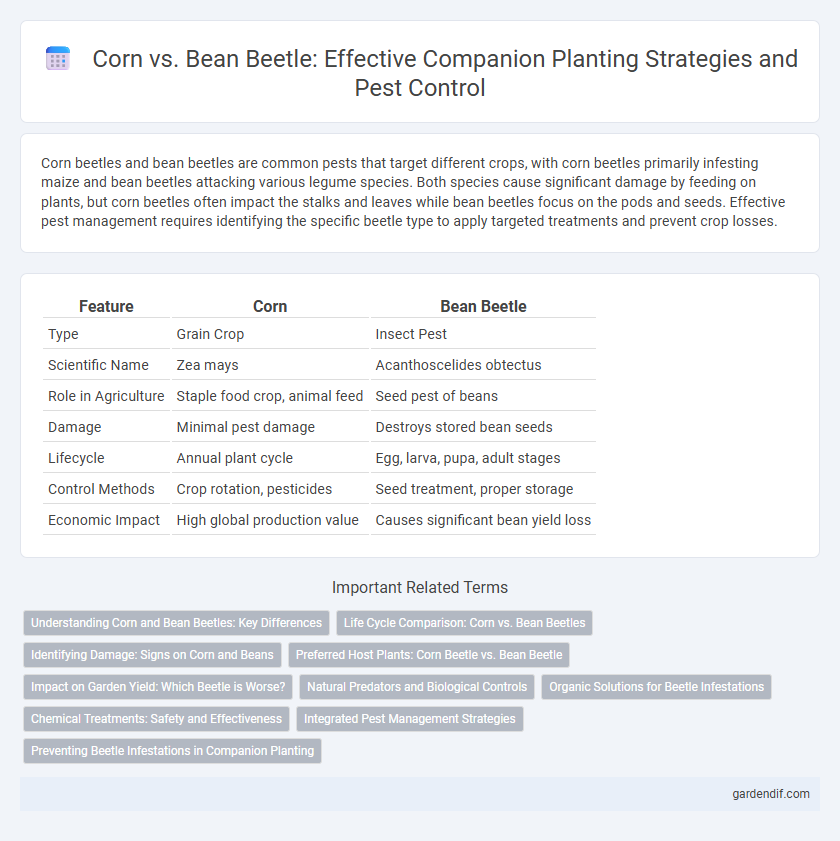
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corn | Bean Beetle |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Grain Crop | Insect Pest |
| Scientific Name | Zea mays | Acanthoscelides obtectus |
| Role in Agriculture | Staple food crop, animal feed | Seed pest of beans |
| Damage | Minimal pest damage | Destroys stored bean seeds |
| Lifecycle | Annual plant cycle | Egg, larva, pupa, adult stages |
| Control Methods | Crop rotation, pesticides | Seed treatment, proper storage |
| Economic Impact | High global production value | Causes significant bean yield loss |
Understanding Corn and Bean Beetles: Key Differences
Corn beetles and bean beetles differ primarily in their host preferences and damage patterns, with corn beetles targeting maize crops by feeding on silks and kernels, while bean beetles focus on leguminous plants, feeding on leaves and pods. Identification is facilitated by noting corn beetles' elongated bodies and bronze coloring versus the more rounded, spotted appearance of bean beetles. Understanding these distinctions aids in implementing targeted pest control strategies to protect crop yields effectively.
Life Cycle Comparison: Corn vs. Bean Beetles
Corn beetles undergo a complete metamorphosis with four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult, typically completing their life cycle within 30 to 45 days. Bean beetles also experience complete metamorphosis but tend to have a shorter life cycle, often finishing development in about 20 to 30 days, allowing multiple generations per season. Differences in life cycle duration influence the timing and strategy for pest management in crops where corn and beans are grown together.
Identifying Damage: Signs on Corn and Beans
Corn damage caused by corn rootworms typically appears as feeding scars and tunnels on roots, leading to stunted growth and lodging. Bean beetle damage is characterized by skeletonized leaves with small holes, often combined with yellowing and wilting in bean plants. Identifying these specific signs on corn and beans helps in timely pest management and crop protection.
Preferred Host Plants: Corn Beetle vs. Bean Beetle
The corn beetle primarily targets corn plants, thriving on the nutrient-rich stalks and leaves of Zea mays, which provide ideal conditions for feeding and reproduction. In contrast, the bean beetle favors leguminous plants such as common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), where it inflicts damage by consuming pods and seeds, significantly impacting crop yield. Understanding these beetles' host preferences aids in developing targeted pest management strategies tailored to protect specific crops effectively.
Impact on Garden Yield: Which Beetle is Worse?
Corn beetles primarily target maize plants, causing extensive leaf damage that significantly reduces photosynthesis and can lead to yield losses of up to 30%. Bean beetles infest legume crops, damaging pods and seeds, which directly diminishes both quantity and quality of bean harvests by up to 40%. Comparing the two, bean beetles generally impose a greater negative impact on garden yield due to their direct destruction of edible parts, making them more detrimental in mixed crop gardens.
Natural Predators and Biological Controls
Natural predators of corn and bean beetles include lady beetles, lacewings, and parasitic wasps that help maintain pest populations in agricultural settings. Biological controls such as entomopathogenic fungi and nematodes effectively reduce beetle infestations by targeting their larval and adult stages. Employing crop rotation and intercropping with pest-repellent plants enhances the impact of these natural enemies, fostering sustainable pest management.
Organic Solutions for Beetle Infestations
Corn and bean beetle infestations can be effectively managed using organic solutions such as neem oil, diatomaceous earth, and beneficial insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps. Crop rotation with non-host plants disrupts beetle life cycles, reducing population buildup without chemical inputs. Incorporating companion planting with marigolds and garlic further deters beetles, promoting a healthy, pest-resistant garden ecosystem.
Chemical Treatments: Safety and Effectiveness
Chemical treatments for corn and bean beetles require careful selection due to varying insecticide susceptibility. Pyrethroids and neonicotinoids demonstrate effectiveness against corn borers but can harm beneficial insects critical in companion planting. Targeted application of systemic insecticides minimizes ecological impact while maintaining control efficacy for both pests.
Integrated Pest Management Strategies
Corn and bean beetles require targeted integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to minimize crop damage and maximize yield. Utilizing crop rotation, resistant varieties, and biological controls such as natural predators effectively reduces beetle populations without heavy reliance on chemical pesticides. Monitoring beetle populations through regular field scouting and applying selective insecticides only when economic thresholds are reached supports sustainable pest management.
Preventing Beetle Infestations in Companion Planting
Corn and bean beetles can be effectively managed through companion planting using species like marigolds and nasturtiums, which repel these pests naturally. Intercropping with aromatic herbs such as basil and rosemary creates a disruptive environment that reduces beetle infestations on corn and beans. Implementing these companion plants promotes healthy crop growth by minimizing chemical interventions and supporting biodiversity in the garden.
Corn vs bean beetle Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com