
Frost dates vs planting dates Illustration
Understanding frost dates is essential for determining optimal planting dates to protect crops from cold damage. Planting too early risks exposure to late frosts, which can harm seedlings and reduce yield. Aligning planting schedules with local frost data ensures healthier plants and maximizes growth potential.
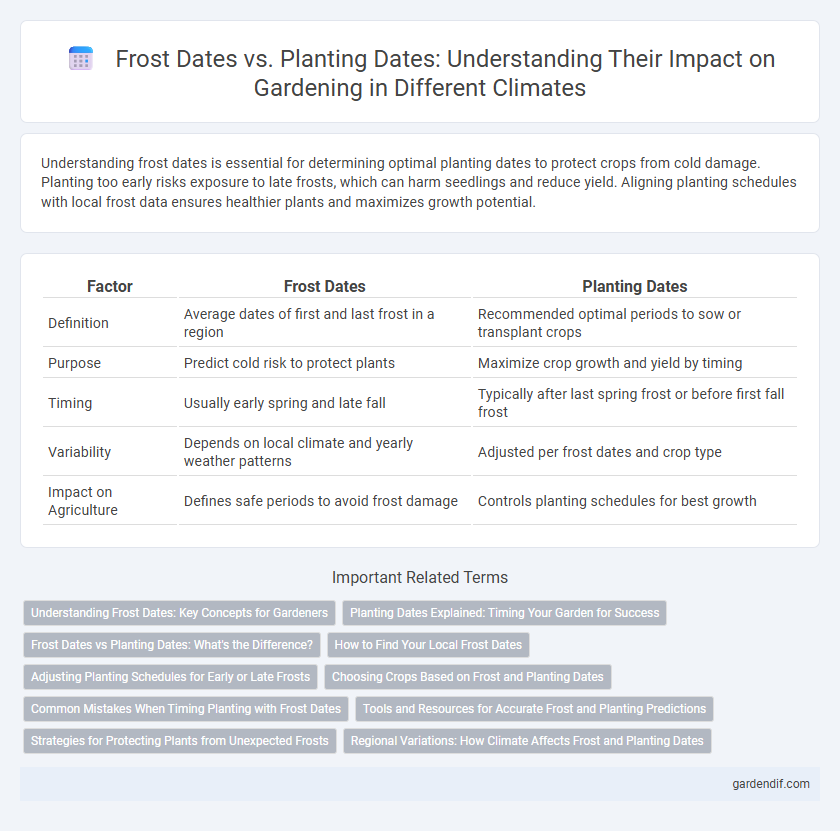
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Frost Dates | Planting Dates |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Average dates of first and last frost in a region | Recommended optimal periods to sow or transplant crops |
| Purpose | Predict cold risk to protect plants | Maximize crop growth and yield by timing |
| Timing | Usually early spring and late fall | Typically after last spring frost or before first fall frost |
| Variability | Depends on local climate and yearly weather patterns | Adjusted per frost dates and crop type |
| Impact on Agriculture | Defines safe periods to avoid frost damage | Controls planting schedules for best growth |
Understanding Frost Dates: Key Concepts for Gardeners
Frost dates indicate the average last occurrence of frost in spring and the first in fall, providing critical guidance for optimal planting times to protect sensitive plants. Gardeners use these dates to schedule seed sowing and transplanting, ensuring young plants avoid frost damage that can stunt growth or kill seedlings. Understanding the local climate's frost patterns helps maximize crop yield, extend growing seasons, and improve garden success.
Planting Dates Explained: Timing Your Garden for Success
Frost dates mark the average first and last occurrence of frost, crucial for determining safe planting periods to avoid cold damage. Knowing your region's frost dates helps gardeners select optimal planting dates, ensuring seedlings mature during favorable temperatures. Timing your garden based on frost data maximizes plant survival and enhances crop yield by aligning growth cycles with climate conditions.
Frost Dates vs Planting Dates: What's the Difference?
Frost dates mark the average last spring freeze and first fall freeze, crucial for determining safe planting windows to avoid crop damage. Planting dates refer to the optimal time frame when soil and weather conditions support seed germination and growth, often set after the last frost date in spring. Understanding the distinction between frost dates and planting dates helps gardeners and farmers maximize yield by aligning crop schedules with local climate patterns.
How to Find Your Local Frost Dates
To determine your local frost dates, consult the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and historical climate data from sources such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Local agricultural extension offices and online frost date calculators provide region-specific averages for the last spring frost and first fall frost, critical for planning optimal planting schedules. Tracking these dates helps gardeners and farmers minimize crop damage by timing planting and harvesting according to the typical frost period in their area.
Adjusting Planting Schedules for Early or Late Frosts
Adjusting planting schedules to account for local frost dates is crucial for optimizing crop survival and yield. Planting too early risks damage from late frosts, while delayed planting could shorten the growing season and reduce productivity. Using regional climate data and frost date predictions allows farmers to time plantings to minimize frost exposure and maximize growth potential.
Choosing Crops Based on Frost and Planting Dates
Understanding frost dates is crucial for selecting crops with optimal growing periods that avoid cold damage and maximize yield. Early planting dates should align with the average last frost date to ensure sensitive plants like tomatoes and peppers are not exposed to freezing temperatures. Crops with higher frost tolerance, such as kale and spinach, can be planted closer to or even before the last frost date to extend the growing season.
Common Mistakes When Timing Planting with Frost Dates
Misinterpreting frost dates can lead to planting too early, exposing seedlings to lethal late frost damage or too late, reducing the growing season and crop yield potential. Many gardeners mistake the last spring frost for a guaranteed safe planting date without considering microclimates or unusual weather variations. Ignoring local frost zone variations and the specific cold tolerance of plant species often results in poor timing and plant loss.
Tools and Resources for Accurate Frost and Planting Predictions
Accurate frost and planting date predictions rely on advanced climate modeling tools such as the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) frost date calculators. These resources integrate historical weather data, soil temperature trends, and local microclimate factors to provide tailored planting schedules that minimize crop damage risk. Leveraging GIS-based platforms and real-time climate sensors enhances precision for gardeners and farmers aiming to optimize planting success.
Strategies for Protecting Plants from Unexpected Frosts
Effective strategies for protecting plants from unexpected frosts include using frost cloths, mulching, and installing windbreaks to reduce cold air exposure. Employing techniques like watering soil before frost can also retain heat and protect root systems during sudden temperature drops. Monitoring local frost date forecasts enables gardeners to adjust planting schedules and implement timely frost protection measures to safeguard plant health.
Regional Variations: How Climate Affects Frost and Planting Dates
Frost dates vary significantly across regions due to differences in climate patterns, influencing the timing of safe planting periods for gardeners and farmers. Warmer climates typically experience later frost dates in spring and earlier frost dates in fall, extending the growing season, while colder regions have shorter frost-free intervals limiting planting options. Understanding local frost date data is essential for optimizing planting schedules and maximizing crop yields in diverse climatic zones.
Frost dates vs planting dates Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com