
Drought-Resistant Plants vs Moisture-Loving Plants Illustration
Drought-resistant plants thrive in arid conditions by storing water in their leaves, stems, or roots, reducing dependency on frequent rainfall. Moisture-loving plants require consistently damp soil and high humidity, making them vulnerable during prolonged dry spells. Understanding the distinct water needs of these plants is crucial for sustainable landscaping and effective climate adaptation strategies.
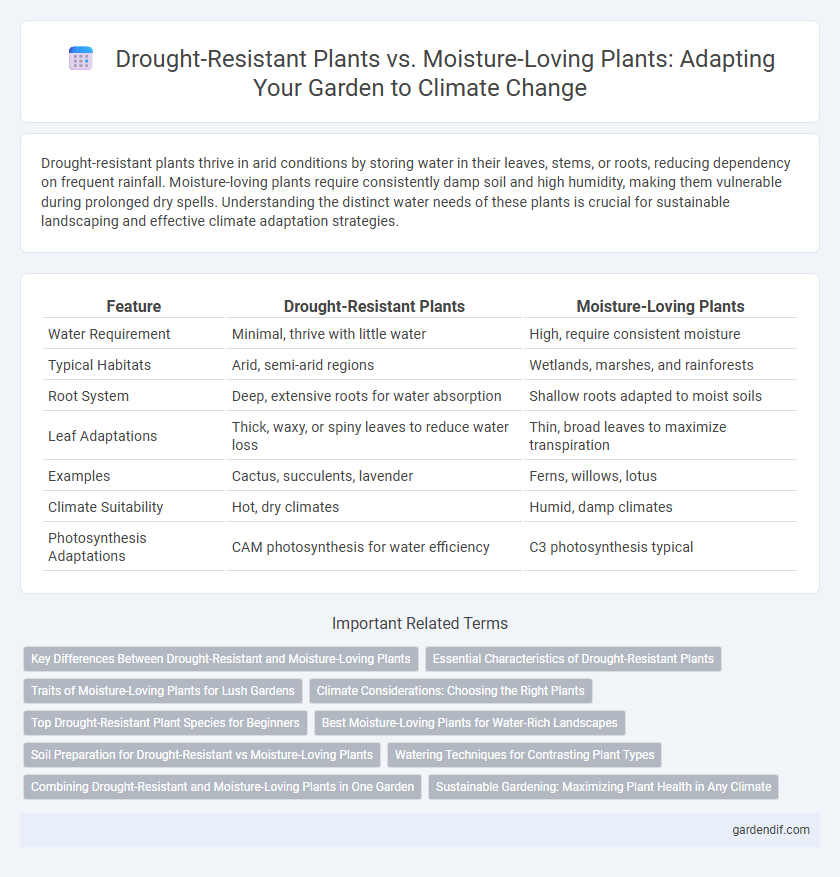
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drought-Resistant Plants | Moisture-Loving Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Water Requirement | Minimal, thrive with little water | High, require consistent moisture |
| Typical Habitats | Arid, semi-arid regions | Wetlands, marshes, and rainforests |
| Root System | Deep, extensive roots for water absorption | Shallow roots adapted to moist soils |
| Leaf Adaptations | Thick, waxy, or spiny leaves to reduce water loss | Thin, broad leaves to maximize transpiration |
| Examples | Cactus, succulents, lavender | Ferns, willows, lotus |
| Climate Suitability | Hot, dry climates | Humid, damp climates |
| Photosynthesis Adaptations | CAM photosynthesis for water efficiency | C3 photosynthesis typical |
Key Differences Between Drought-Resistant and Moisture-Loving Plants
Drought-resistant plants possess adaptations such as deep root systems, thick cuticles, and reduced leaf surfaces to minimize water loss, enabling survival in arid conditions. Moisture-loving plants thrive in consistently wet environments with shallow roots and broad leaves to maximize water uptake and transpiration. These fundamental physiological and morphological differences dictate their suitability for contrasting climate zones and inform sustainable landscaping and agricultural practices.
Essential Characteristics of Drought-Resistant Plants
Drought-resistant plants exhibit essential characteristics such as deep root systems that efficiently access underground water sources and thick, waxy cuticles that minimize water loss through evaporation. These plants often have reduced leaf surface areas or specialized leaf structures like spines to limit transpiration. Adaptations like CAM photosynthesis enable them to fix carbon dioxide at night, further conserving moisture in arid climates.
Traits of Moisture-Loving Plants for Lush Gardens
Moisture-loving plants thrive in consistently wet environments, exhibiting traits such as broad, thin leaves that facilitate efficient water absorption and transpiration. These plants typically develop extensive root systems near the soil surface to quickly uptake available moisture and often have softer stems and leaves that require ample hydration to maintain turgor pressure. Their natural adaptation to high humidity and saturated soils supports vibrant, lush gardens that demand steady moisture levels and rich, well-draining substrates.
Climate Considerations: Choosing the Right Plants
Drought-resistant plants such as succulents, lavender, and agave thrive in arid climates by conserving water through deep root systems and thick leaves, making them ideal for regions with low rainfall and prolonged dry spells. Moisture-loving plants like ferns, water lilies, and willows require consistently high soil moisture and are better suited to humid, wet climates or areas with regular irrigation. Selecting the right plants based on regional climate and soil moisture availability enhances garden resilience, reduces water usage, and supports sustainable landscaping practices.
Top Drought-Resistant Plant Species for Beginners
Top drought-resistant plant species ideal for beginners include succulents like Aloe Vera and Agave, which store water efficiently in their leaves and thrive in arid conditions. Lavender and Rosemary are hardy herbs known for their low water requirements and resilience in hot climates. These species are excellent choices for sustainable gardening, reducing water consumption while enhancing landscape biodiversity.
Best Moisture-Loving Plants for Water-Rich Landscapes
Moisture-loving plants such as cattails, marsh marigolds, and water lilies thrive in water-rich landscapes, playing a crucial role in maintaining wetland ecosystems. These plants enhance soil stability, support biodiversity by providing habitat for aquatic wildlife, and improve water quality through natural filtration processes. Selecting native moisture-loving species optimizes landscape resilience against flooding and sustains ecological balance in climate-sensitive regions.
Soil Preparation for Drought-Resistant vs Moisture-Loving Plants
Soil preparation for drought-resistant plants involves enhancing drainage and incorporating organic matter like compost to improve water retention without oversaturation, creating a well-aerated environment. In contrast, moisture-loving plants thrive in soils rich in organic material that retain consistent moisture, often requiring the addition of peat moss or mulch to maintain hydration. Proper soil pH adjustment is essential for both types, with drought-resistant plants favoring slightly alkaline to neutral soils and moisture-loving plants preferring slightly acidic conditions for optimal nutrient absorption.
Watering Techniques for Contrasting Plant Types
Drought-resistant plants require infrequent but deep watering to encourage root growth and increase water absorption, typically every 1-2 weeks depending on soil and climate conditions. Moisture-loving plants demand consistent, shallow watering to maintain high soil moisture levels, often needing daily or every-other-day irrigation to prevent stress and promote healthy leaves. Using drip irrigation or soaker hoses helps tailor watering schedules to these contrasting needs, conserving water while optimizing plant health.
Combining Drought-Resistant and Moisture-Loving Plants in One Garden
Combining drought-resistant plants like succulents and lavender with moisture-loving species such as ferns and hostas creates a dynamic garden that optimizes water usage and enhances biodiversity. This approach allows efficient irrigation by grouping plants based on their water needs, reducing overall water consumption while maintaining lush greenery. Strategic plant selection and soil management promote resilience against fluctuating climate conditions, ensuring sustained garden health through droughts and wetter periods.
Sustainable Gardening: Maximizing Plant Health in Any Climate
Drought-resistant plants such as succulents and native grasses thrive by conserving water, making them ideal for sustainable gardening in arid climates. Moisture-loving plants like ferns and marsh marigolds require consistent hydration and are best suited for regions with ample rainfall or well-irrigated gardens. Selecting the appropriate plant species based on local climate and soil moisture ensures optimal plant health while minimizing water usage and environmental impact.
Drought-Resistant Plants vs Moisture-Loving Plants Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com