
Manual weeding vs chemical weeding Illustration
Manual weeding offers precise removal of unwanted plants without harming surrounding crops, making it an eco-friendly and sustainable option for small-scale gardens. Chemical weeding, using herbicides, provides efficient and rapid control of broad weed infestations but carries risks of soil degradation and potential harm to non-target plants and beneficial organisms. Choosing between manual and chemical weeding depends on factors such as scale, environmental impact, labor availability, and long-term crop health.
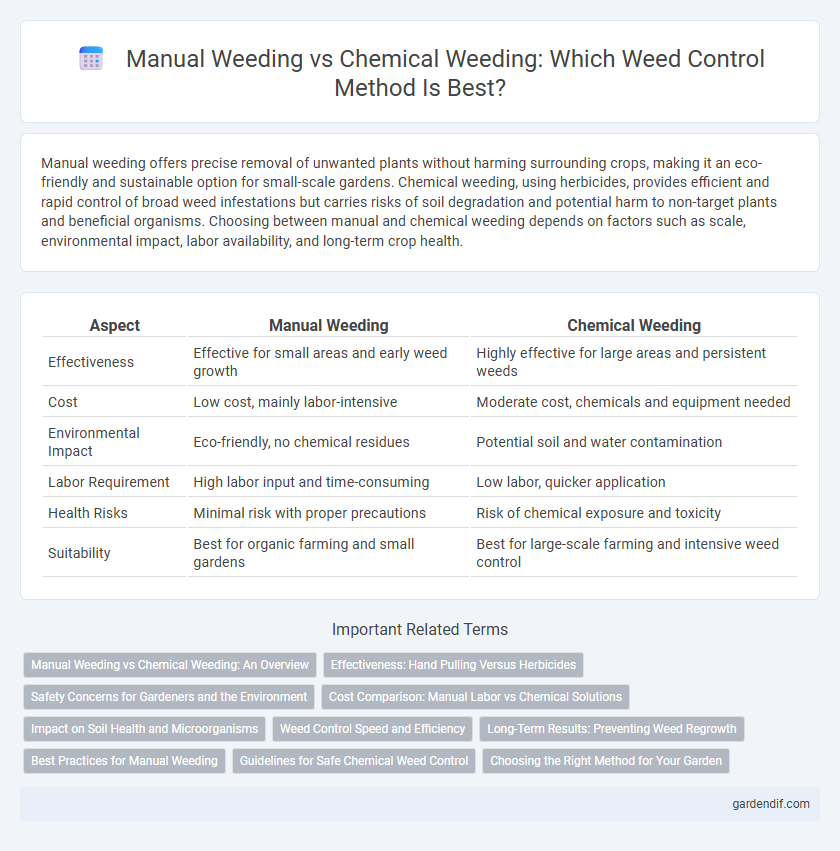
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manual Weeding | Chemical Weeding |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Effective for small areas and early weed growth | Highly effective for large areas and persistent weeds |
| Cost | Low cost, mainly labor-intensive | Moderate cost, chemicals and equipment needed |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no chemical residues | Potential soil and water contamination |
| Labor Requirement | High labor input and time-consuming | Low labor, quicker application |
| Health Risks | Minimal risk with proper precautions | Risk of chemical exposure and toxicity |
| Suitability | Best for organic farming and small gardens | Best for large-scale farming and intensive weed control |
Manual Weeding vs Chemical Weeding: An Overview
Manual weeding involves physically removing weeds by hand or with tools, offering precision and minimal environmental impact, which is ideal for small gardens and organic farming systems. Chemical weeding uses herbicides to control weed growth efficiently over large areas but poses risks such as soil contamination, development of resistant weed species, and potential harm to non-target plants and wildlife. Choosing between manual and chemical weeding depends on factors like land size, crop type, environmental concerns, and labor availability.
Effectiveness: Hand Pulling Versus Herbicides
Hand pulling effectively removes weeds by uprooting them and preventing immediate regrowth, but it is labor-intensive and less practical for large areas. Herbicides offer widespread weed control with rapid results, targeting specific plant species chemically to inhibit growth or kill weeds efficiently. Effectiveness depends on weed type, infestation level, and environmental conditions, with herbicides providing consistent control while manual weeding supports organic and sustainable practices.
Safety Concerns for Gardeners and the Environment
Manual weeding eliminates exposure to harmful chemicals, reducing health risks such as skin irritation and respiratory problems for gardeners. Chemical weeding poses potential environmental hazards, including soil contamination and harm to beneficial insects, water sources, and local biodiversity. Choosing manual methods supports ecological balance and ensures safer conditions for both gardeners and surrounding ecosystems.
Cost Comparison: Manual Labor vs Chemical Solutions
Manual weeding demands significant labor hours and higher recurring costs due to wages and slower weed removal rates, especially in large-scale agriculture. Chemical weed control involves upfront expenses for herbicide purchase and application equipment but often proves more cost-effective over time by reducing labor intensity and enabling faster weed management. Comparing both methods highlights that chemical solutions offer better scalability and lower per-acre costs, while manual weeding remains economically viable for small plots or organic farming practices.
Impact on Soil Health and Microorganisms
Manual weeding preserves soil structure and biodiversity by minimizing disturbance to soil microorganisms essential for nutrient cycling and plant health. Chemical weeding often disrupts microbial communities, reducing soil fertility and impairing beneficial bacteria and fungi that support plant growth. Long-term reliance on herbicides can lead to soil degradation, while manual weeding promotes sustainable soil ecosystem balance.
Weed Control Speed and Efficiency
Manual weeding offers precise removal of weeds, but it is labor-intensive and slower compared to chemical methods, making it less efficient for large-scale weed control. Chemical weeding provides rapid and broad-spectrum weed suppression, significantly increasing control speed and reducing labor costs. However, chemical herbicides may pose environmental risks and require careful application to avoid crop damage.
Long-Term Results: Preventing Weed Regrowth
Manual weeding offers precise removal of weeds by uprooting them completely, reducing the chance of regrowth over time and promoting healthier soil structure. Chemical weeding provides faster, broad-spectrum weed control, but may lead to residual herbicide build-up that can affect soil microbiota and promote resistant weed species. Integrating manual weeding with strategic chemical applications often yields sustainable, long-term weed management by preventing regrowth and minimizing environmental impact.
Best Practices for Manual Weeding
Manual weeding involves physically removing unwanted plants by hand or with tools, offering precise control and reducing chemical use. Best practices for manual weeding include regularly inspecting garden beds, uprooting weeds before they flower and seed, and maintaining soil moisture to ease weed removal. Consistent manual weeding promotes healthier crops, minimizes soil disturbance, and supports sustainable weed management.
Guidelines for Safe Chemical Weed Control
Safe chemical weed control requires strict adherence to label instructions, including the correct dosage, timing, and application methods to minimize environmental impact and human health risks. Protective clothing such as gloves, masks, and long sleeves must be worn to prevent direct contact with herbicides, while avoiding application during windy or rainy conditions reduces chemical drift and runoff. Proper disposal of containers and unused chemicals, along with storage in a secure, well-ventilated area, ensures safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden
Manual weeding offers precise removal of unwanted plants without harming surrounding crops, ideal for small gardens or organic practices. Chemical weeding provides fast and broad-spectrum control, suitable for larger areas but requires careful selection of herbicides to avoid damaging desirable plants. Evaluate garden size, weed types, and environmental impact to choose the most effective and sustainable weeding method.
Manual weeding vs chemical weeding Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com