
Grass weeds vs Broadleaf weeds Illustration
Grass weeds and broadleaf weeds differ primarily in their leaf structure and growth patterns, with grass weeds having narrow, blade-like leaves and broadleaf weeds exhibiting wider, more varied leaf shapes. Effective weed control requires species-specific strategies, as grass weeds tend to thrive in turfgrass and cereal crops, while broadleaf weeds often invade garden beds and lawns. Understanding these differences ensures targeted herbicide use and maintenance practices that promote healthy plant growth and minimize weed competition.
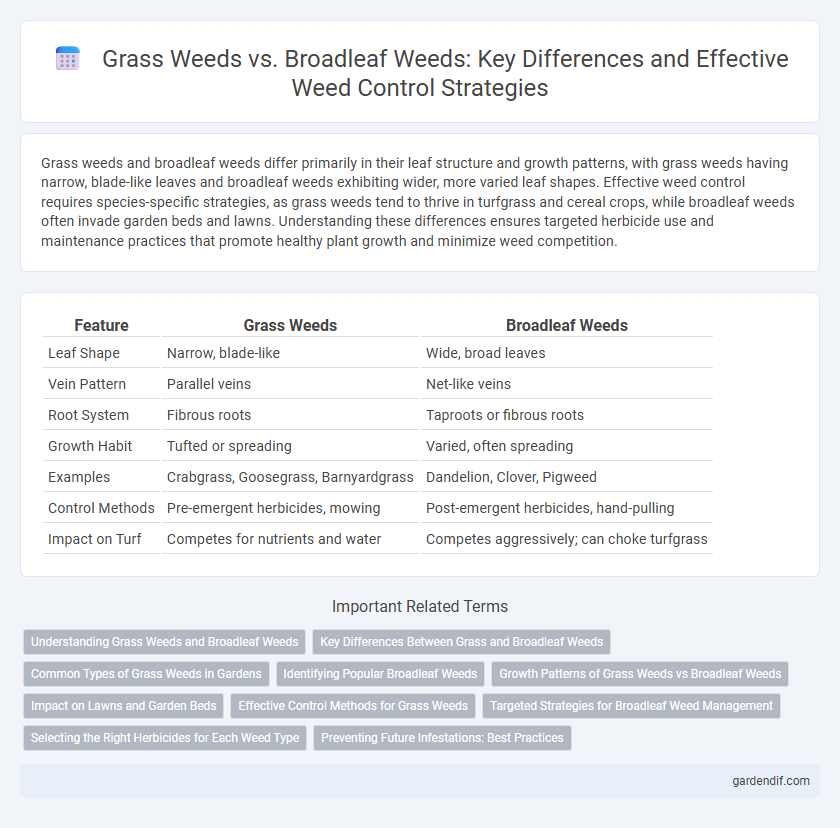
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Grass Weeds | Broadleaf Weeds |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, blade-like | Wide, broad leaves |
| Vein Pattern | Parallel veins | Net-like veins |
| Root System | Fibrous roots | Taproots or fibrous roots |
| Growth Habit | Tufted or spreading | Varied, often spreading |
| Examples | Crabgrass, Goosegrass, Barnyardgrass | Dandelion, Clover, Pigweed |
| Control Methods | Pre-emergent herbicides, mowing | Post-emergent herbicides, hand-pulling |
| Impact on Turf | Competes for nutrients and water | Competes aggressively; can choke turfgrass |
Understanding Grass Weeds and Broadleaf Weeds
Grass weeds belong to the Poaceae family and exhibit narrow, blade-like leaves with parallel veins, making them visually distinct from broadleaf weeds. Broadleaf weeds are characterized by wider leaves with net-like veins and often display prominent flowers or seed structures. Proper identification of these weed types allows for targeted herbicide application and effective weed management in lawns and agricultural settings.
Key Differences Between Grass and Broadleaf Weeds
Grass weeds have narrow, blade-like leaves with parallel veins, typically belonging to the Poaceae family, while broadleaf weeds feature wider leaves with net-like veins from various families such as Asteraceae. Grass weeds grow in clumps with hollow stems and produce seeds in spikelets, contrasting with broadleaf weeds that often have solid stems and produce seeds in flowering heads. Identifying these characteristics helps select appropriate herbicides, as grass-specific herbicides target grass weeds, whereas broadleaf herbicides control broadleaf weed species effectively.
Common Types of Grass Weeds in Gardens
Common types of grass weeds in gardens include crabgrass, goosegrass, and quackgrass, known for their aggressive growth and rapid spread. Crabgrass thrives in warm-season conditions, forming dense mats that outcompete desirable lawn grasses. Quackgrass features extensive rhizomes, making it difficult to eradicate and a persistent problem for garden beds and lawns.
Identifying Popular Broadleaf Weeds
Popular broadleaf weeds such as dandelions, clover, and chickweed can be identified by their wide, flat leaves and distinctive flower shapes, contrasting the narrow blades of grass weeds like crabgrass and foxtail. Dandelions feature bright yellow flowers and deeply toothed leaves, clover presents trifoliate leaf clusters with small white or pink blossoms, and chickweed has small white star-shaped flowers and oval leaves. Recognizing these characteristics is essential for selecting effective herbicides that target broadleaf weeds without harming grass lawns.
Growth Patterns of Grass Weeds vs Broadleaf Weeds
Grass weeds exhibit narrow, blade-like leaves with parallel venation and typically grow in dense clusters, often spreading via stolons or rhizomes that enable rapid colonization. Broadleaf weeds display wider leaves with net-like venation patterns and usually grow individually or sparsely, relying on seed dispersal for expansion rather than creeping growth. Understanding these distinct growth patterns is essential for targeted weed management strategies and effective herbicide application.
Impact on Lawns and Garden Beds
Grass weeds like crabgrass and goosegrass aggressively invade lawns, competing with turfgrass for nutrients and water, resulting in patchy, uneven turf. Broadleaf weeds such as dandelions and clover thrive in garden beds, disrupting plant growth by monopolizing sunlight and soil resources, often leading to reduced flower and vegetable yields. Effectively identifying and managing these weed types is crucial to maintaining healthy lawns and vibrant garden beds.
Effective Control Methods for Grass Weeds
Effective control methods for grass weeds include the use of selective herbicides such as sethoxydim and fluazifop-p-butyl, which target grassy species without harming broadleaf plants. Cultural practices like maintaining thick, healthy turf through proper mowing, irrigation, and fertilization suppress grass weed establishment by reducing available resources. Mechanical control involving repeated cultivation or hand-pulling can also reduce grass weed populations when combined with integrated management strategies.
Targeted Strategies for Broadleaf Weed Management
Broadleaf weed management requires targeted strategies such as the use of selective herbicides like 2,4-D or dicamba, which effectively control dicotyledonous weeds without harming grass species. Integrated approaches combining cultural practices, including crop rotation and turfgrass competition, enhance control by reducing broadleaf weed seed banks. Monitoring weed populations and applying treatments at the early growth stages maximize herbicide efficacy and minimize environmental impact.
Selecting the Right Herbicides for Each Weed Type
Selecting the right herbicide for grass weeds versus broadleaf weeds requires understanding their distinct biological characteristics. Grass weed herbicides typically contain active ingredients like sethoxydim or fluazifop that target narrow-leaved monocots, while broadleaf weed herbicides often include 2,4-D or dicamba for controlling dicotyledonous plants. Accurate identification of the weed type and using selective herbicides enhances weed management efficiency and reduces crop damage.
Preventing Future Infestations: Best Practices
Preventing future infestations of grass weeds and broadleaf weeds requires regular lawn maintenance, including proper mowing height to discourage weed growth and consistent watering that targets grass roots instead of shallow soil. Applying pre-emergent herbicides during early spring effectively inhibits weed seed germination, reducing the risk of both grass and broadleaf weed establishment. Incorporating overseeding with competitive grass varieties strengthens lawn density, minimizing open spaces where weeds can take hold.
Grass weeds vs Broadleaf weeds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com