
Goosegrass vs foxtail Illustration
Goosegrass and foxtail are common grassy weeds that thrive in lawns and gardens, often competing with desirable plants for nutrients and water. Goosegrass has a distinctive flattened stem and grows in dense clumps, while foxtail is recognizable by its bushy, tail-like seed heads that can cause irritation when handled. Effective weed control strategies target these differences, using selective herbicides and proper lawn maintenance to reduce their spread and impact.
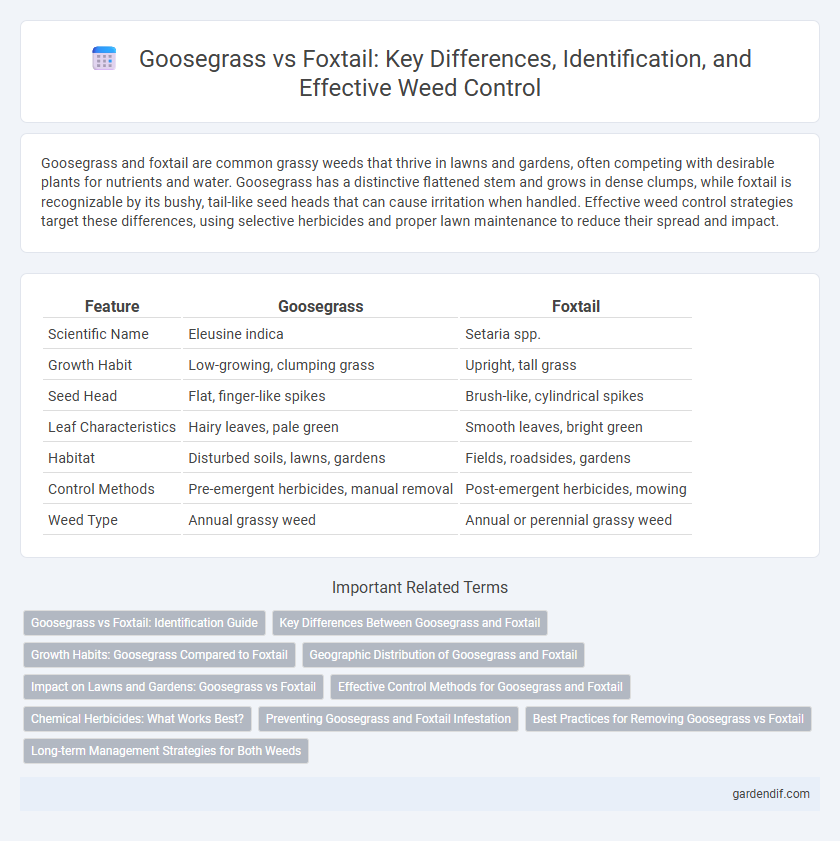
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Goosegrass | Foxtail |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Eleusine indica | Setaria spp. |
| Growth Habit | Low-growing, clumping grass | Upright, tall grass |
| Seed Head | Flat, finger-like spikes | Brush-like, cylindrical spikes |
| Leaf Characteristics | Hairy leaves, pale green | Smooth leaves, bright green |
| Habitat | Disturbed soils, lawns, gardens | Fields, roadsides, gardens |
| Control Methods | Pre-emergent herbicides, manual removal | Post-emergent herbicides, mowing |
| Weed Type | Annual grassy weed | Annual or perennial grassy weed |
Goosegrass vs Foxtail: Identification Guide
Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) features flat, white-striped leaves with distinct finger-like seed heads that contrast with foxtail's (Setaria spp.) bushy, cylindrical seed heads and hairy leaf surfaces. Identifying goosegrass involves noting its prostrate growth habit and smooth, shiny leaf blades compared to foxtail's upright posture and rough texture. Accurate recognition of these differences is crucial for effective weed management in turfgrass and agricultural systems.
Key Differences Between Goosegrass and Foxtail
Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) and foxtail (Setaria spp.) differ primarily in leaf texture and seed head structure; goosegrass features flat, rough leaves with a distinct white mid-vein, while foxtail has softer, hairy leaves and bristly seed heads resembling foxtails. Goosegrass spreads mainly through stolons forming dense mats, whereas foxtail propagates via seeds, leading to scattered infestations. Both weeds thrive in disturbed soils but vary in tolerance to herbicides and environmental conditions, influencing control strategies.
Growth Habits: Goosegrass Compared to Foxtail
Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) exhibits a prostrate, spreading growth habit that allows it to form dense mats close to the ground, contrasting with the upright and clump-forming growth typical of foxtail species (Setaria spp.). Goosegrass produces short, stiff stems that radiate from a central crown, aiding its persistence in compacted soils, whereas foxtail grows taller with erect, branched stems that can reach over three feet in height. These distinct growth habits influence their competitive strategies in agricultural and turf settings, with goosegrass often dominating areas of heavy traffic and foxtail thriving in disturbed, open soils.
Geographic Distribution of Goosegrass and Foxtail
Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) thrives primarily in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, notably across Asia, Africa, and the southern United States, favoring disturbed soils and urban environments. Foxtail species, including Setaria viridis and Setaria pumila, display a broader geographic distribution across temperate to tropical zones, prevalent in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, often infesting agricultural fields and grasslands. Their overlapping ranges contribute to competition in crop fields, with localized climatic factors influencing the predominance of either weed.
Impact on Lawns and Gardens: Goosegrass vs Foxtail
Goosegrass and foxtail both pose significant threats to lawns and gardens by aggressively competing for nutrients, water, and sunlight, leading to weakened turf and stunted plant growth. Goosegrass thrives in compacted, high-traffic soils, often creating bare patches that invite further weed invasion, while foxtail's rapid seed production and spreading habit smother desirable plants and reduce crop yields. Effective weed management strategies must address each species' unique growth patterns to protect the health and aesthetics of lawns and gardens.
Effective Control Methods for Goosegrass and Foxtail
Effective control methods for goosegrass (Eleusine indica) and foxtail (Setaria spp.) include pre-emergent herbicides such as pendimethalin and prodiamine, which prevent seed germination. Post-emergent options like quinclorac and ACCase inhibitors target actively growing plants, offering selective suppression in turfgrass and row crops. Integrated weed management combining cultural practices, herbicide rotation to avoid resistance, and proper mowing height enhances long-term control of both weed species.
Chemical Herbicides: What Works Best?
Goosegrass (Eleusine indica) and foxtail (Setaria spp.) respond differently to chemical herbicides due to their distinct growth habits and resistance profiles. Glyphosate effectively controls goosegrass when applied at early post-emergence stages, while foxtail species often require selective grass herbicides such as clethodim or sethoxydim for optimal suppression. Resistance management strategies emphasize rotating herbicide modes of action to maintain efficacy against both weed species.
Preventing Goosegrass and Foxtail Infestation
Effective prevention of goosegrass and foxtail infestation hinges on maintaining dense turf and proper lawn care practices such as regular mowing and adequate irrigation to reduce weed seed germination. Pre-emergent herbicides applied in early spring target weed seeds before they sprout, minimizing infestation risks for both goosegrass and foxtail. Monitoring soil health and promptly removing emerging weed seedlings further strengthens control efforts, ensuring a healthy, weed-resistant lawn ecosystem.
Best Practices for Removing Goosegrass vs Foxtail
Effectively removing goosegrass requires a targeted pre-emergent herbicide applied early in the growing season combined with consistent mechanical weed control such as hand pulling or mowing to prevent seed spread. Foxtail control benefits from post-emergent herbicides that target broad-leaf weeds and grasses, along with maintaining healthy turf or crop density to outcompete foxtail seedlings. Integrated weed management practices including crop rotation, proper irrigation, and soil fertility management improve long-term control of both goosegrass and foxtail infestations.
Long-term Management Strategies for Both Weeds
Effective long-term management of goosegrass (Eleusine indica) and foxtail (Setaria spp.) relies on integrated weed control strategies combining cultural, mechanical, and chemical methods. Crop rotation and maintaining competitive, healthy turf or crops reduce weed establishment by limiting resources essential for weed growth. Regular monitoring, timely herbicide applications targeting early growth stages, and preventing seed set significantly minimize reinfestation and seedbank buildup for both species.
Goosegrass vs foxtail Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com