
Rain gauge vs soil moisture meter Illustration
A rain gauge measures the amount of precipitation over a specific period, providing essential data for irrigation planning and weather monitoring. A soil moisture meter detects the water content in soil, helping gardeners and farmers optimize watering schedules to prevent over- or under-watering. Both tools are crucial for effective water management but serve distinct purposes in assessing environmental moisture levels.
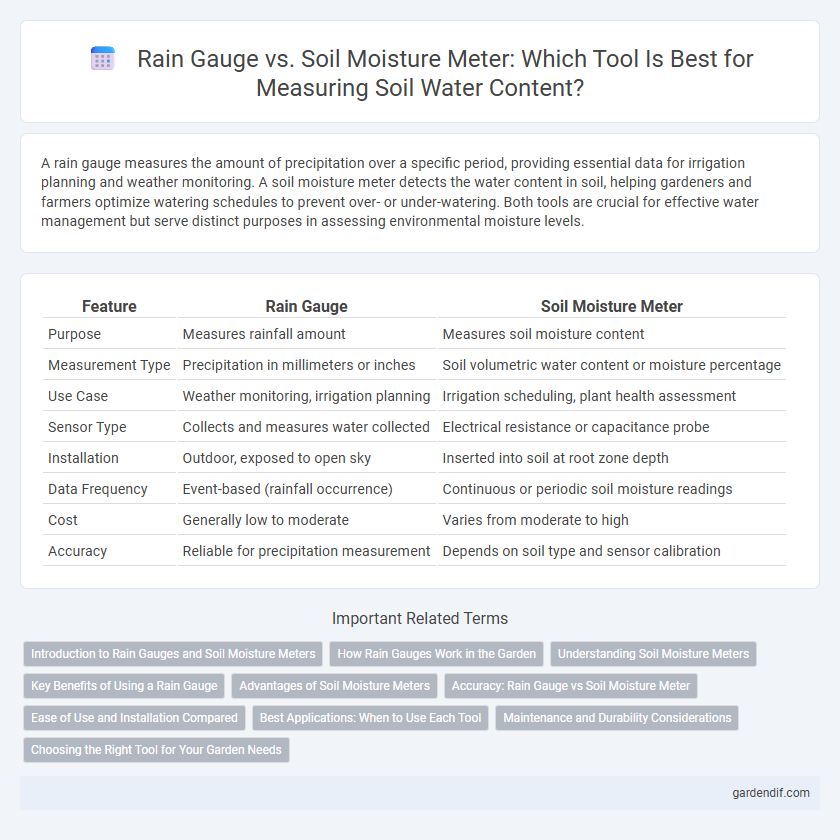
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rain Gauge | Soil Moisture Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures rainfall amount | Measures soil moisture content |
| Measurement Type | Precipitation in millimeters or inches | Soil volumetric water content or moisture percentage |
| Use Case | Weather monitoring, irrigation planning | Irrigation scheduling, plant health assessment |
| Sensor Type | Collects and measures water collected | Electrical resistance or capacitance probe |
| Installation | Outdoor, exposed to open sky | Inserted into soil at root zone depth |
| Data Frequency | Event-based (rainfall occurrence) | Continuous or periodic soil moisture readings |
| Cost | Generally low to moderate | Varies from moderate to high |
| Accuracy | Reliable for precipitation measurement | Depends on soil type and sensor calibration |
Introduction to Rain Gauges and Soil Moisture Meters
Rain gauges measure precipitation levels by collecting and quantifying rainfall, providing critical data for weather monitoring and agricultural planning. Soil moisture meters assess the water content within soil, enabling precise irrigation management and promoting optimal plant health. Both tools are essential for effective water resource management in environmental science and farming practices.
How Rain Gauges Work in the Garden
Rain gauges measure precipitation by collecting and quantifying rainwater in a calibrated container, providing precise data on rainfall amounts. Gardeners use rain gauges to monitor natural water input, helping them adjust irrigation schedules efficiently and avoid overwatering. This tool complements soil moisture meters, which assess water content directly in the soil for optimal plant health management.
Understanding Soil Moisture Meters
Soil moisture meters measure the volumetric water content in soil by using probes that detect electrical resistance or capacitance, providing precise readings essential for optimal irrigation management. Unlike rain gauges, which only record precipitation levels, soil moisture meters offer real-time data on water availability directly in the root zone, helping prevent overwatering or underwatering. Advanced models also feature digital displays and app connectivity for tracking soil health trends, making them invaluable for agriculture and gardening.
Key Benefits of Using a Rain Gauge
A rain gauge provides precise measurement of rainfall, enabling accurate tracking of precipitation levels essential for effective water management and irrigation planning. It helps prevent both overwatering and underwatering by delivering real-time data on rainfall amounts, reducing water waste and promoting healthier plant growth. Using a rain gauge also supports environmental monitoring and weather prediction efforts, enhancing agricultural decision-making and sustainability.
Advantages of Soil Moisture Meters
Soil moisture meters provide precise, real-time measurements of soil water content, enabling targeted irrigation and water conservation for healthier plant growth. Unlike rain gauges, which only measure precipitation, soil moisture meters assess actual soil conditions, improving efficiency in agriculture, landscaping, and gardening. Accurate soil moisture data helps prevent overwatering and underwatering, reducing plant stress and optimizing resource use.
Accuracy: Rain Gauge vs Soil Moisture Meter
Rain gauges provide precise measurements of precipitation by collecting and quantifying rainfall, typically with accuracy levels within 0.2 millimeters. Soil moisture meters measure volumetric water content in the soil, using sensors that can vary in accuracy depending on soil type and calibration, often ranging between 2% to 5% error margin. The accuracy of rain gauges is generally higher and more consistent for rainfall data, whereas soil moisture meters require careful calibration to achieve reliable moisture readings.
Ease of Use and Installation Compared
Rain gauges are typically easier to install, requiring simple placement in an open area to collect precipitation without complex setup. Soil moisture meters often need insertion into the soil at specific depths, which can be more involved and require periodic calibration for accuracy. Users seeking straightforward installation and minimal maintenance generally prefer rain gauges over soil moisture meters.
Best Applications: When to Use Each Tool
Rain gauges are best used for measuring precipitation levels to inform irrigation scheduling and prevent waterlogging in agricultural fields, gardens, or landscapes. Soil moisture meters provide precise readings of soil water content, ensuring optimal hydration for plants by guiding targeted watering practices, particularly in drought-prone or controlled growing environments. Use rain gauges to monitor rainfall patterns, while soil moisture meters are essential for assessing actual soil dryness to avoid over- or under-watering.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Rain gauges, designed primarily with weather-resistant materials such as UV-stabilized plastics or stainless steel, require minimal maintenance and can withstand prolonged exposure to rain and sun without significant wear. Soil moisture meters, often featuring delicate sensors and electronic components, demand careful cleaning after each use to prevent soil buildup and occasional battery replacements to ensure accurate readings. Durability-wise, rain gauges typically outlast soil moisture meters in outdoor conditions due to their simpler construction and less frequent need for calibration.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Garden Needs
Rain gauges accurately measure precipitation levels to help determine watering schedules, while soil moisture meters assess the water content directly in the soil for precise irrigation management. Selecting the right tool depends on your garden's specific needs: rain gauges are ideal for tracking rainfall patterns, whereas soil moisture meters provide immediate soil conditions to prevent over or under-watering. Effective garden care combines understanding rainfall data with soil moisture measurements to optimize plant health and water usage.
Rain gauge vs soil moisture meter Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com