
shade cloth vs garden netting Illustration
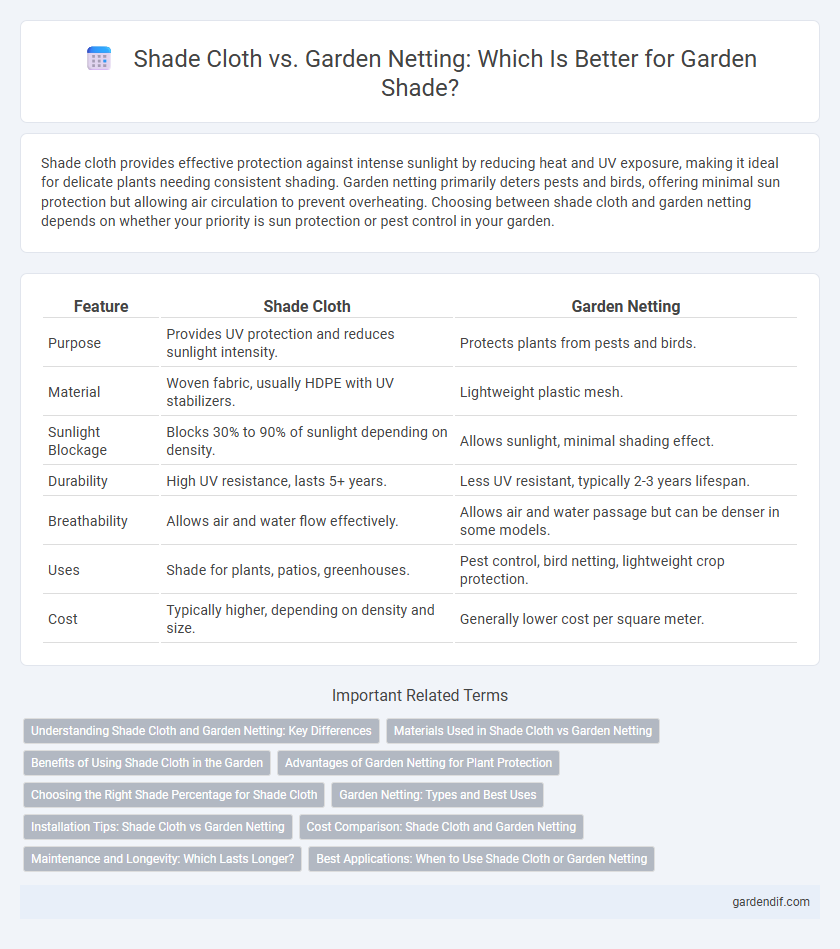
Shade cloth provides effective protection against intense sunlight by reducing heat and UV exposure, making it ideal for delicate plants needing consistent shading. Garden netting primarily deters pests and birds, offering minimal sun protection but allowing air circulation to prevent overheating. Choosing between shade cloth and garden netting depends on whether your priority is sun protection or pest control in your garden.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shade Cloth | Garden Netting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides UV protection and reduces sunlight intensity. | Protects plants from pests and birds. |
| Material | Woven fabric, usually HDPE with UV stabilizers. | Lightweight plastic mesh. |
| Sunlight Blockage | Blocks 30% to 90% of sunlight depending on density. | Allows sunlight, minimal shading effect. |
| Durability | High UV resistance, lasts 5+ years. | Less UV resistant, typically 2-3 years lifespan. |
| Breathability | Allows air and water flow effectively. | Allows air and water passage but can be denser in some models. |
| Uses | Shade for plants, patios, greenhouses. | Pest control, bird netting, lightweight crop protection. |
| Cost | Typically higher, depending on density and size. | Generally lower cost per square meter. |
Understanding Shade Cloth and Garden Netting: Key Differences
Shade cloth is a tightly woven or knitted fabric designed primarily to reduce sunlight intensity and provide temperature control for plants, whereas garden netting serves mainly as a protective barrier against pests, birds, and debris without significantly affecting light levels. Shade cloth offers varying shade percentages, usually ranging from 30% to 90%, tailored to specific plant needs, while garden netting typically features a more open mesh structure allowing maximum sunlight penetration. Understanding these functional differences helps gardeners choose the appropriate material for plant health, growth optimization, and environmental protection.
Materials Used in Shade Cloth vs Garden Netting
Shade cloth is typically made from woven or knitted polyethylene or polypropylene fibers, offering UV resistance and durability to protect plants from excessive sunlight. Garden netting is often constructed from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or nylon, designed with a more open mesh structure to allow air circulation while deterring pests. The difference in materials affects tensile strength, light filtration, and longevity under outdoor conditions, making shade cloth better for controlling sunlight intensity and garden netting ideal for plant protection and ventilation.
Benefits of Using Shade Cloth in the Garden
Shade cloth provides superior UV protection and temperature control compared to garden netting, promoting healthier plant growth and reducing heat stress. Its durable, tightly woven fabric blocks excessive sunlight while allowing air circulation, preventing fungal diseases and leaf scorch. Shade cloth also extends the growing season by protecting plants from harsh environmental elements, ensuring optimal garden productivity.
Advantages of Garden Netting for Plant Protection
Garden netting offers superior ventilation and light penetration compared to traditional shade cloth, promoting healthier plant growth by preventing overheating and allowing essential sunlight. It effectively protects plants from pests, birds, and harsh weather conditions while maintaining optimal airflow. The durability and flexibility of garden netting make it a cost-effective, versatile solution for safeguarding diverse types of crops and garden plants.
Choosing the Right Shade Percentage for Shade Cloth
When selecting the right shade percentage for shade cloth, consider the specific needs of your plants and climate; typical shade percentages range from 30% to 90%, with lower percentages allowing more sunlight for seedlings and higher percentages providing maximum protection for sensitive plants. Shade cloth offers durable UV protection and better airflow compared to garden netting, which is primarily designed to keep pests away rather than regulate light intensity. Matching the shade cloth percentage to your garden's sun exposure ensures optimal growth and prevents heat stress or insufficient light absorption.
Garden Netting: Types and Best Uses
Garden netting comes in various types including insect netting, bird netting, and support netting, each designed to protect plants from pests, birds, and to aid plant growth respectively. Insect netting features fine mesh to keep out small pests without restricting airflow or sunlight, making it ideal for vegetable gardens and delicate plants. Bird netting has larger holes to prevent birds from accessing fruit trees and berry bushes, while support netting is used to provide structural support for climbing plants such as peas and beans.
Installation Tips: Shade Cloth vs Garden Netting
When installing shade cloth, secure it tautly using heavy-duty staples or UV-resistant zip ties to wooden or metal frames, ensuring maximum durability under sun exposure. Garden netting requires frequent tension adjustments and softer fasteners, like plastic clips, to prevent tearing from wind or wildlife movement. Proper anchoring and overlap techniques for both materials prevent gaps, ensuring effective protection for plants.
Cost Comparison: Shade Cloth and Garden Netting
Shade cloth generally costs more per square foot than garden netting due to its durable woven fabric designed for UV protection. Garden netting is typically less expensive because it serves primarily as a physical barrier against pests and debris rather than providing significant shade. Evaluating long-term investment, shade cloth offers better sun protection and longevity, while garden netting provides a budget-friendly solution for basic plant safeguarding.
Maintenance and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Shade cloth generally offers greater durability and requires less frequent replacement compared to garden netting, as it is made from UV-stabilized materials designed to withstand prolonged sun exposure without significant degradation. Garden netting tends to be more susceptible to tearing and damage from wind or pests, resulting in a shorter lifespan and increased maintenance needs. Proper installation and seasonal care can extend the longevity of both, but shade cloth typically outperforms garden netting in maintenance efficiency and long-term resilience.
Best Applications: When to Use Shade Cloth or Garden Netting
Shade cloth is ideal for controlling sunlight exposure and reducing heat in greenhouses, nurseries, and outdoor patios, effectively protecting plants from intense UV rays and promoting healthy growth. Garden netting excels in providing physical barriers against pests and birds, safeguarding fruits, vegetables, and flowers without significantly altering light levels. Choosing between shade cloth and garden netting depends on whether the primary goal is managing light and temperature or preventing pest damage.
shade cloth vs garden netting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com