
Light Shade Plants vs Heavy Shade Plants Illustration
Light shade plants thrive in areas with filtered sunlight or partial shade, requiring at least a few hours of indirect light daily to maintain healthy growth and vibrant foliage. Heavy shade plants are adapted to low-light environments, flourishing under dense canopies or on north-facing slopes where sunlight is minimal. Understanding the specific light requirements of shade plants ensures optimal placement, enhances garden vitality, and promotes balanced ecosystem development.
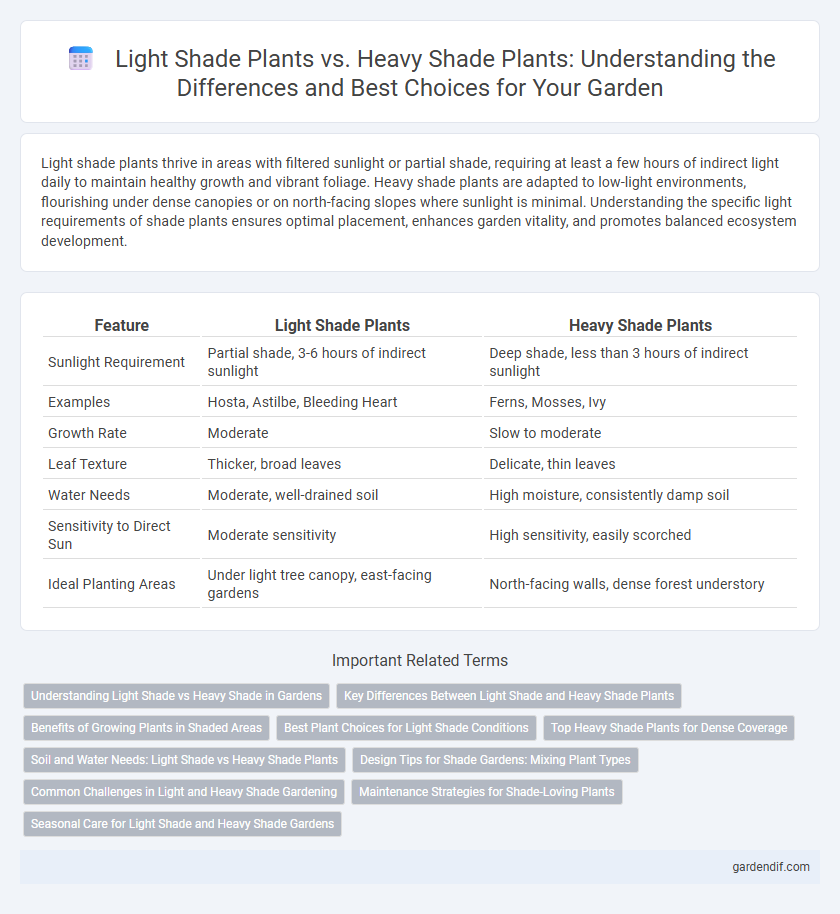
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light Shade Plants | Heavy Shade Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Sunlight Requirement | Partial shade, 3-6 hours of indirect sunlight | Deep shade, less than 3 hours of indirect sunlight |
| Examples | Hosta, Astilbe, Bleeding Heart | Ferns, Mosses, Ivy |
| Growth Rate | Moderate | Slow to moderate |
| Leaf Texture | Thicker, broad leaves | Delicate, thin leaves |
| Water Needs | Moderate, well-drained soil | High moisture, consistently damp soil |
| Sensitivity to Direct Sun | Moderate sensitivity | High sensitivity, easily scorched |
| Ideal Planting Areas | Under light tree canopy, east-facing gardens | North-facing walls, dense forest understory |
Understanding Light Shade vs Heavy Shade in Gardens
Light shade plants thrive in areas receiving filtered sunlight or partial morning sun, making them ideal for garden spots with dappled light or brief sun exposure. Heavy shade plants are adapted to low-light environments, flourishing under dense canopies or shaded structures where direct sunlight is minimal or absent. Understanding the specific light requirements helps gardeners select suitable plants that promote healthy growth and vibrant foliage in varying shade conditions.
Key Differences Between Light Shade and Heavy Shade Plants
Light shade plants require filtered sunlight, thriving in dappled or partial shade with moderate light levels, while heavy shade plants adapt to low-light conditions, often found beneath dense tree canopies or north-facing walls. Light shade plants typically include species like ferns and impatiens, which perform well with indirect sunlight, whereas heavy shade plants such as hostas and mosses are adapted to minimal light exposure and higher humidity. These differences affect their photosynthesis rates, growth patterns, and placement in garden designs to ensure optimal health and aesthetics.
Benefits of Growing Plants in Shaded Areas
Growing light shade plants, such as ferns and impatiens, enhances garden biodiversity by thriving in partial sunlight and promoting healthy soil conditions. Heavy shade plants like hostas and astilbes are ideal for dense shaded areas, conserving moisture and preventing soil erosion while providing lush foliage. Both types improve air quality, reduce garden heat, and create cool, comfortable outdoor microclimates that support diverse wildlife habitats.
Best Plant Choices for Light Shade Conditions
Light shade plants such as hostas, ferns, and astilbes thrive in environments with 2-4 hours of indirect sunlight, making them ideal for garden areas that receive filtered or dappled light. These plants are adapted to partial sunlight and moderate moisture, ensuring vibrant foliage and healthy growth without direct sun exposure. Selecting shade-tolerant perennials like hellebores and coral bells optimizes garden aesthetics and plant vitality in light shade conditions.
Top Heavy Shade Plants for Dense Coverage
Top heavy shade plants like Japanese Maple, Camellia, and Rhododendron provide dense coverage ideal for deep shade areas, thriving with limited sunlight. These plants feature lush foliage and vibrant blooms that enhance garden privacy and aesthetic appeal under heavy canopy conditions. Cultivating these species ensures robust growth in dense shade while maintaining soil moisture and reducing weed competition.
Soil and Water Needs: Light Shade vs Heavy Shade Plants
Light shade plants thrive in well-drained soil with moderate moisture, requiring consistent watering but avoiding waterlogged conditions to maintain healthy growth. Heavy shade plants prefer richer, moisture-retentive soil that stays damp longer, benefiting from higher humidity and more frequent watering to support their low-light adaptation. Understanding these distinct soil and water needs is crucial for optimizing plant health and growth in varying shade environments.
Design Tips for Shade Gardens: Mixing Plant Types
Combining light shade plants like hostas and ferns with heavy shade plants such as astilbes and foamflowers creates layered textures and diverse foliage in shade gardens. Position taller heavy shade plants in the background to provide depth while placing light shade plants in front for visual interest and brightness. Incorporate varied leaf shapes and colors to enhance contrast and ensure year-round appeal in shady garden areas.
Common Challenges in Light and Heavy Shade Gardening
Light shade plants often struggle with inconsistent sunlight, leading to uneven growth and susceptibility to pests, while heavy shade plants face challenges such as limited photosynthesis and increased moisture retention, which can cause root rot. Soil quality frequently becomes an issue in both conditions, requiring careful amendment to ensure adequate drainage and nutrient availability. Managing these environmental stressors is crucial for maintaining healthy foliage and preventing common diseases associated with shade gardens.
Maintenance Strategies for Shade-Loving Plants
Light shade plants, such as hostas and ferns, require moderate watering and well-drained soil to prevent root rot, while heavy shade plants like mosses and astilbes thrive with consistent moisture and organic mulch to retain humidity. Regular pruning and removing dead foliage enhance airflow and reduce disease risks for both light and heavy shade plants. Optimizing soil nutrients through slow-release fertilizers supports healthy growth in low-light environments, ensuring lush, shade-tolerant garden displays.
Seasonal Care for Light Shade and Heavy Shade Gardens
Light shade plants thrive with moderate sunlight and require regular watering during spring and summer, while heavy shade plants benefit from consistent moisture and protection from harsh sun, especially in hot seasons. Seasonal care for light shade gardens includes pruning to enhance airflow and applying mulch to retain soil moisture in warmer months. Heavy shade gardens demand less frequent pruning but need soil enrichment and careful monitoring for fungal diseases during damp fall and winter months.
Light Shade Plants vs Heavy Shade Plants Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com