
Succession planting vs Single-season planting Illustration
Succession planting maximizes garden yield by staggering crop planting times to provide continuous harvests throughout the growing season. This method contrasts with single-season planting, where all crops are sown simultaneously and harvested once, limiting production to a specific period. By utilizing succession planting, gardeners can enhance food supply, reduce waste, and better adapt to changing weather conditions.
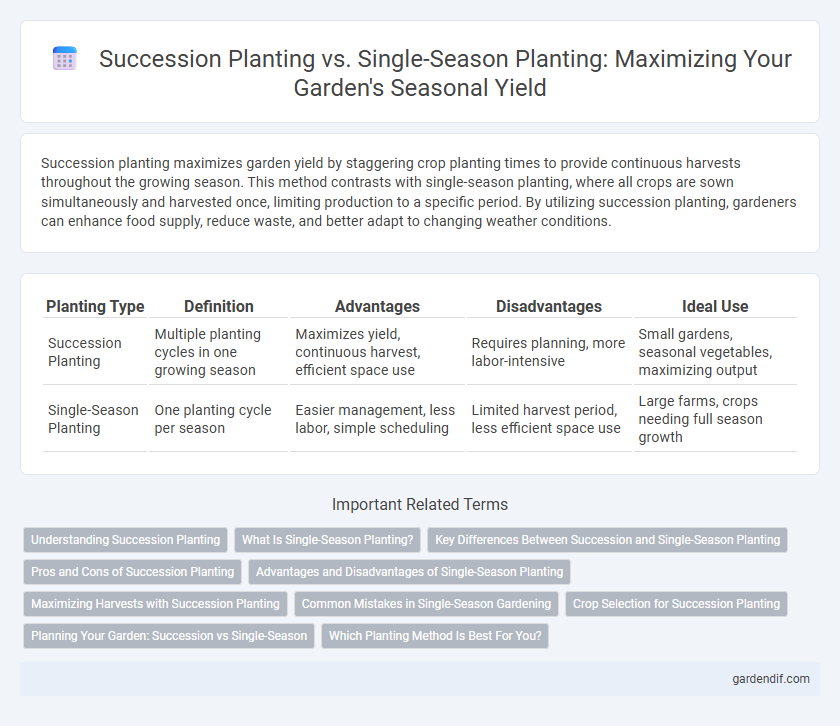
Table of Comparison
| Planting Type | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Succession Planting | Multiple planting cycles in one growing season | Maximizes yield, continuous harvest, efficient space use | Requires planning, more labor-intensive | Small gardens, seasonal vegetables, maximizing output |
| Single-Season Planting | One planting cycle per season | Easier management, less labor, simple scheduling | Limited harvest period, less efficient space use | Large farms, crops needing full season growth |
Understanding Succession Planting
Succession planting maximizes garden productivity by staggering crop planting dates, enabling continuous harvest throughout multiple seasons rather than harvesting once. This method reduces downtime between crops and optimizes space by planting fast-growing vegetables immediately after early crops mature. Gardeners benefit from increased yields and diversified produce, contrasting single-season planting where crops are sown and harvested only once per growing period.
What Is Single-Season Planting?
Single-season planting involves sowing seeds or transplanting crops once per growing season, resulting in a single harvest cycle. This method suits climates with distinct growing periods and reduces labor by timing planting and harvesting within a fixed timeframe. Crop selection for single-season planting emphasizes varieties that mature within the local season length to maximize yield and quality.
Key Differences Between Succession and Single-Season Planting
Succession planting involves sowing crops in intervals to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the growing season, enhancing garden productivity and maximizing yield. Single-season planting, by contrast, consists of planting a crop once during the growing season, resulting in a single, larger harvest. Key differences include timing, crop turnover rate, and the ability to extend harvest periods, with succession planting allowing repeated cycles of growth and harvest compared to the one-time output in single-season planting.
Pros and Cons of Succession Planting
Succession planting maximizes garden yield by staggering crop planting times, ensuring continuous harvests and efficient space use throughout multiple growing seasons. This method reduces the risk of total crop failure by diversifying harvest periods, but requires careful planning and more management effort compared to single-season planting. However, succession planting can strain soil nutrients faster, necessitating more frequent soil amendments and monitoring to maintain productivity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Single-Season Planting
Single-season planting offers the advantage of focused crop management, reducing complexity in pest and nutrient control during a defined growing period. However, it limits harvest frequency, potentially decreasing overall yield compared to succession planting, which maximizes production by staggering crops. The risk of crop failure due to weather or pests is higher in single-season planting since it relies on a single harvest window.
Maximizing Harvests with Succession Planting
Succession planting strategically spaces crop plantings to extend harvest periods and maximize yield within a single growing season. This method increases garden productivity by staggering planting times, allowing continuous production of vegetables like lettuce, beans, and carrots. Compared to single-season planting, which yields a one-time harvest, succession planting efficiently utilizes space and resources, providing fresh produce over a longer timeframe.
Common Mistakes in Single-Season Gardening
Single-season planting often leads to common mistakes such as inefficient space utilization and shorter harvest periods due to limited crop variety. Gardeners frequently overlook the benefits of staggered planting, resulting in soil nutrient depletion and increased pest vulnerability. Succession planting maximizes productivity by ensuring continuous harvests, better soil health, and pest management through crop rotation and varied planting schedules.
Crop Selection for Succession Planting
Crop selection for succession planting prioritizes fast-maturing, space-efficient varieties such as radishes, lettuce, and bush beans to optimize garden productivity across seasons. Choosing compatible crops with staggered harvest times supports continuous yield and maximizes soil nutrient use. These selections contrast with single-season planting, which often favors crops needing longer growth periods like tomatoes or squash.
Planning Your Garden: Succession vs Single-Season
Succession planting maximizes garden yield by staggering crop cycles, enabling continuous harvests throughout the growing season. Single-season planting, on the other hand, dedicates the garden space to one crop at a time, which simplifies management but limits total output. Careful planning considers crop maturity rates and seasonal climate to optimize space, soil health, and overall productivity.
Which Planting Method Is Best For You?
Succession planting maximizes garden yields by staggering crop cycles, allowing continuous harvests throughout the growing season, ideal for gardeners seeking extended fresh produce. Single-season planting simplifies management with one planting and harvest per season, best suited for those with limited time or space. Choosing the best method depends on your available resources, desired harvest frequency, and crop preferences, balancing effort with productivity.
Succession planting vs Single-season planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com