
Shoulder seasons vs Peak seasons Illustration
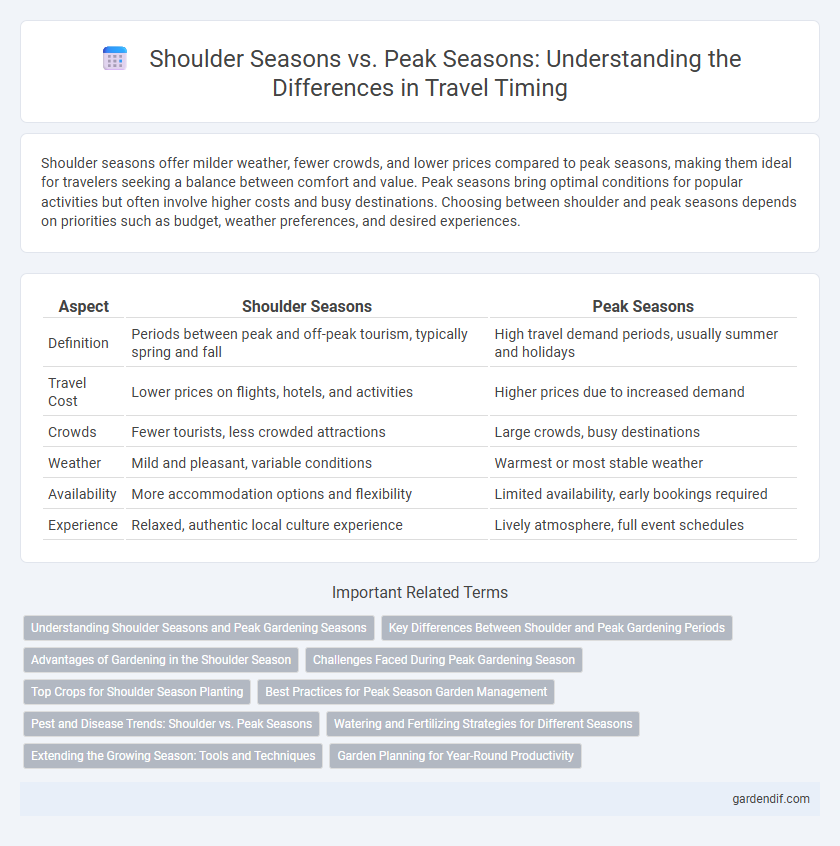
Shoulder seasons offer milder weather, fewer crowds, and lower prices compared to peak seasons, making them ideal for travelers seeking a balance between comfort and value. Peak seasons bring optimal conditions for popular activities but often involve higher costs and busy destinations. Choosing between shoulder and peak seasons depends on priorities such as budget, weather preferences, and desired experiences.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shoulder Seasons | Peak Seasons |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Periods between peak and off-peak tourism, typically spring and fall | High travel demand periods, usually summer and holidays |
| Travel Cost | Lower prices on flights, hotels, and activities | Higher prices due to increased demand |
| Crowds | Fewer tourists, less crowded attractions | Large crowds, busy destinations |
| Weather | Mild and pleasant, variable conditions | Warmest or most stable weather |
| Availability | More accommodation options and flexibility | Limited availability, early bookings required |
| Experience | Relaxed, authentic local culture experience | Lively atmosphere, full event schedules |
Understanding Shoulder Seasons and Peak Gardening Seasons
Shoulder seasons, typically spring and autumn, offer milder weather and less crowded conditions ideal for planting diverse garden crops with moderate water and sunlight needs. Peak gardening seasons in summer provide optimal warmth and longer daylight, promoting rapid growth and flowering for heat-loving plants like tomatoes and peppers. Understanding these seasonal dynamics helps optimize planting schedules and resource use for more productive, sustainable gardens.
Key Differences Between Shoulder and Peak Gardening Periods
Shoulder seasons in gardening occur during early spring and late fall, offering moderate temperatures and reduced pest activity, which promote steady plant growth with less maintenance. Peak seasons typically correspond to late spring through summer, characterized by optimal sunlight and warmth, resulting in accelerated growth but increased demand for watering and pest control. Understanding these key differences helps gardeners optimize planting schedules and resource allocation for healthier, more productive gardens.
Advantages of Gardening in the Shoulder Season
Gardening in the shoulder season offers moderate temperatures, reducing plant stress and promoting healthier growth compared to the intense heat of peak seasons. Soil moisture is often more consistent, decreasing the need for frequent watering and supporting stronger root development. Pest and disease pressures tend to be lower, allowing for a more sustainable and productive gardening experience.
Challenges Faced During Peak Gardening Season
Peak gardening seasons bring challenges such as increased pest infestations and higher water demands, stressing both plants and resources. Gardeners often face labor shortages due to heightened maintenance needs and time-sensitive tasks like pruning and harvesting. Soil nutrient depletion and disease outbreaks also become more prevalent, requiring vigilant management strategies.
Top Crops for Shoulder Season Planting
Shoulder seasons offer an ideal climate for cultivating cool-season vegetables like lettuce, spinach, and broccoli, which thrive in moderate temperatures and shorter daylight. Peak seasons favor warm-season crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers that require longer growing periods and higher heat levels. Understanding the top crops tailored for shoulder season planting can maximize yield and extend harvest periods beyond traditional peak season limits.
Best Practices for Peak Season Garden Management
Peak season garden management requires focused watering schedules to prevent plant stress during high heat and humidity periods. Maximizing mulching around plants conserves soil moisture and suppresses weed growth, essential for maintaining garden health. Regular monitoring for pests and diseases ensures early detection and treatment, safeguarding the garden's productivity and appearance.
Pest and Disease Trends: Shoulder vs. Peak Seasons
Pest and disease prevalence often intensifies during peak seasons due to favorable warm and humid conditions, accelerating reproduction cycles and infestation rates. Shoulder seasons typically exhibit lower pest pressures as temperature fluctuations and reduced host availability disrupt pest lifecycles, resulting in fewer outbreaks. Agricultural management strategies must adjust to these seasonal variations to optimize pest control and minimize crop damage effectively.
Watering and Fertilizing Strategies for Different Seasons
Watering and fertilizing strategies vary significantly between shoulder seasons and peak seasons due to differences in temperature and plant growth rates. During shoulder seasons, moderate watering is recommended to maintain soil moisture without causing waterlogging, paired with balanced fertilization to support gradual growth. In peak seasons, increased watering frequency and nutrient-rich fertilizers are essential to meet the higher metabolic demands and rapid development of plants.
Extending the Growing Season: Tools and Techniques
Extending the growing season involves using tools such as row covers, cold frames, and high tunnels to protect plants from frost and temperature fluctuations during shoulder seasons. Season extension techniques like using hoop houses and plastic mulches can enhance crop productivity by creating microclimates that support plant growth beyond traditional peak seasons. These methods help optimize yield and provide fresh produce during early spring and late fall shoulder seasons, maximizing the agricultural calendar.
Garden Planning for Year-Round Productivity
Shoulder seasons offer moderate temperatures and balanced rainfall, ideal for planting cool-season crops such as kale, spinach, and broccoli to extend garden productivity beyond peak growing times. In contrast, peak seasons bring intense heat and rapid plant growth, requiring efficient watering schedules and heat-tolerant varieties like tomatoes and peppers to maximize yield. Strategic crop rotation and soil enrichment during shoulder seasons enhance soil health, ensuring continuous harvests throughout varying climatic conditions.
Shoulder seasons vs Peak seasons Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com