
Interseasonal Gardening vs Intrasessional Gardening Illustration
Interseasonal gardening involves cultivating plants between different seasons, allowing for crop rotation and maximizing yield throughout the year. Intrasessional gardening focuses on growing plants within a single season, optimizing conditions for rapid growth and harvest. Understanding these approaches enhances productivity by aligning planting schedules with seasonal weather patterns and soil conditions.
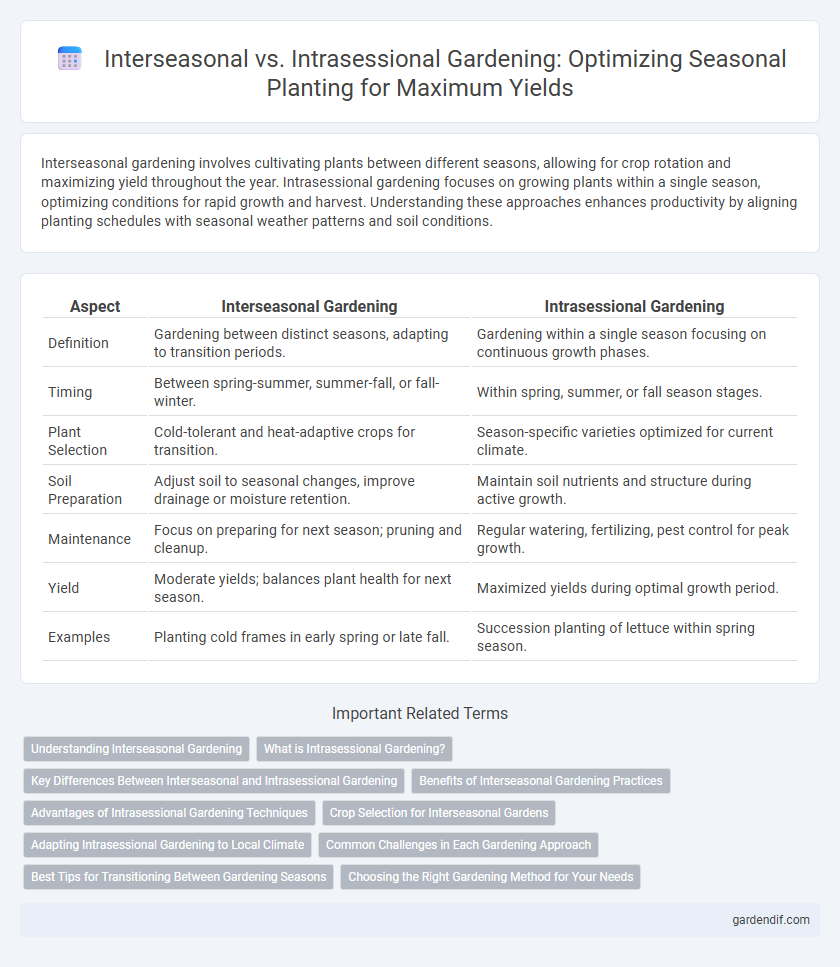
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Interseasonal Gardening | Intrasessional Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gardening between distinct seasons, adapting to transition periods. | Gardening within a single season focusing on continuous growth phases. |
| Timing | Between spring-summer, summer-fall, or fall-winter. | Within spring, summer, or fall season stages. |
| Plant Selection | Cold-tolerant and heat-adaptive crops for transition. | Season-specific varieties optimized for current climate. |
| Soil Preparation | Adjust soil to seasonal changes, improve drainage or moisture retention. | Maintain soil nutrients and structure during active growth. |
| Maintenance | Focus on preparing for next season; pruning and cleanup. | Regular watering, fertilizing, pest control for peak growth. |
| Yield | Moderate yields; balances plant health for next season. | Maximized yields during optimal growth period. |
| Examples | Planting cold frames in early spring or late fall. | Succession planting of lettuce within spring season. |
Understanding Interseasonal Gardening
Interseasonal gardening involves cultivating plants between traditional growing seasons, leveraging microclimates and controlled environments to extend productive periods. This method optimizes crop yield by selecting resilient varieties and employing techniques such as season extenders, greenhouses, or cold frames. Understanding interseasonal gardening enables gardeners to maximize space and resource efficiency while maintaining steady food production year-round.
What is Intrasessional Gardening?
Intrasessional gardening involves cultivating plants within the same growing season by selecting varieties that mature at different times, allowing multiple harvests before the season ends. This method maximizes yield from a single season by staggering planting dates and using fast-growing crops suited to the existing climatic conditions. It contrasts with interseasonal gardening, which focuses on growing crops between distinct seasons to extend production throughout the year.
Key Differences Between Interseasonal and Intrasessional Gardening
Interseasonal gardening involves cultivating plants during the transitional periods between primary growing seasons, maximizing yield in mild climates or with controlled environments. Intrasessional gardening focuses on planting successive crops within a single growing season to maintain continuous harvest and soil health. Key differences include timing and crop rotation strategies, with interseasonal gardening bridging gaps between seasons and intrasessional gardening optimizing space and resources within one season.
Benefits of Interseasonal Gardening Practices
Interseasonal gardening leverages transitional periods between traditional planting seasons to maximize crop yield and garden productivity. This practice extends the growing season, allowing for continuous harvests and improved soil health through diverse crop rotations. Enhanced pest management and resource efficiency are additional benefits of interseasonal gardening compared to intrasessional methods focused strictly within single growing seasons.
Advantages of Intrasessional Gardening Techniques
Intrasessional gardening techniques leverage short growth cycles within a single season, maximizing yield by allowing multiple planting and harvesting phases. These methods optimize resource use, reduce pest build-up, and improve soil health through crop rotation and intercropping. Enhanced flexibility in crop selection also leads to greater resilience against unpredictable weather patterns.
Crop Selection for Interseasonal Gardens
Interseasonal gardening emphasizes crop selection that thrives between traditional growing seasons, including cold-tolerant and fast-maturing varieties such as kale, spinach, and radishes. Choosing crops with flexible growing requirements ensures continuous harvests during transitional weather and variable temperature conditions. Strategic crop rotation and soil management enhance productivity and reduce pest buildup in interseasonal gardens.
Adapting Intrasessional Gardening to Local Climate
Intrasessional gardening involves cultivating crops within the same season to maximize yields and adapt to specific climatic conditions. Adapting intrasessional gardening techniques to local climate requires selecting crop varieties with appropriate growth cycles and employing precise planting schedules aligned with temperature and rainfall patterns. Understanding microclimates and soil characteristics enhances resilience and ensures optimal growth during varying seasonal phases.
Common Challenges in Each Gardening Approach
Interseasonal gardening faces challenges such as fluctuating temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns that can stress plants during transitional periods between seasons. Intrasessional gardening often struggles with soil nutrient depletion and pest buildup due to continuous planting within a single season. Both approaches require careful planning and adaptive strategies to manage these environmental and biological stresses effectively.
Best Tips for Transitioning Between Gardening Seasons
Maximize garden productivity by selecting hardy, season-appropriate plants that thrive during transition periods, such as kale for late fall and early spring. Improve soil health by incorporating organic matter and adjusting pH levels to accommodate changing temperature and moisture conditions between seasons. Use row covers and mulch to protect seedlings from unexpected frosts and maintain consistent soil temperatures during interseasonal shifts.
Choosing the Right Gardening Method for Your Needs
Interseasonal gardening extends planting periods by utilizing techniques such as cold frames or greenhouses to grow crops between traditional seasons, maximizing yield and variety. Intrasessional gardening focuses on optimizing planting within a specific growing season by selecting crops suited to that season's temperature and daylight conditions, ensuring peak growth and harvesting efficiency. Choosing the right method depends on factors like climate, available space, crop selection, and desired harvest frequency.
Interseasonal Gardening vs Intrasessional Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com