
Growing season extension vs Standard season Illustration
Extending the growing season allows for increased crop yields and more diverse plant cultivation by providing plants with additional time to mature. This method enhances food production efficiency compared to the standard season, which is limited by natural environmental conditions. Farmers can better manage resources and reduce the risk of crop failure by adapting to longer or shifted growing periods.
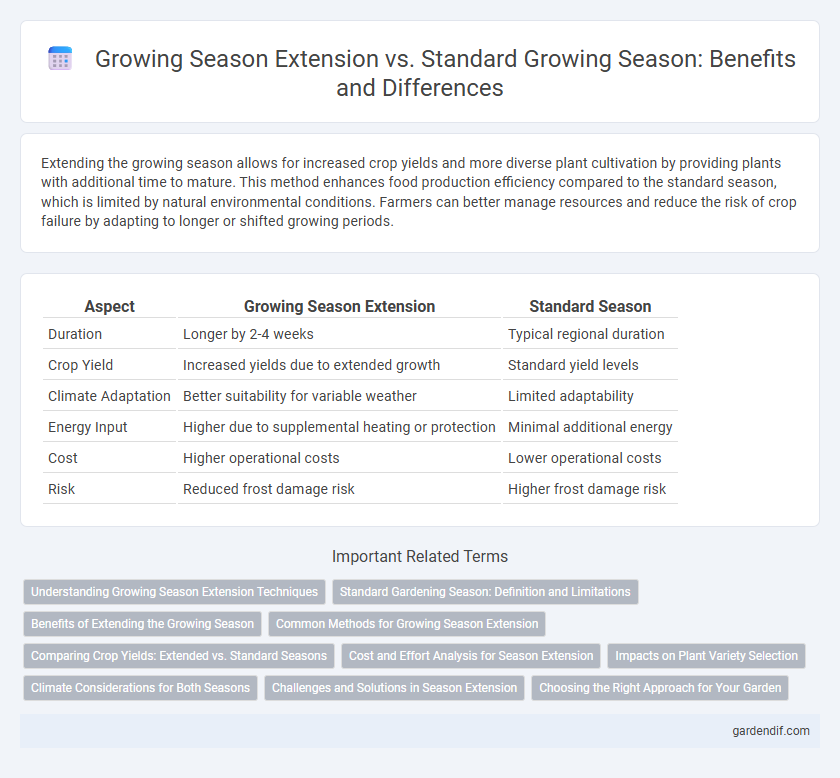
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Growing Season Extension | Standard Season |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Longer by 2-4 weeks | Typical regional duration |
| Crop Yield | Increased yields due to extended growth | Standard yield levels |
| Climate Adaptation | Better suitability for variable weather | Limited adaptability |
| Energy Input | Higher due to supplemental heating or protection | Minimal additional energy |
| Cost | Higher operational costs | Lower operational costs |
| Risk | Reduced frost damage risk | Higher frost damage risk |
Understanding Growing Season Extension Techniques
Growing season extension techniques such as row covers, high tunnels, and greenhouses enable farmers to cultivate crops beyond the standard frost-free period, increasing yield potential. These methods modify microclimates by retaining heat and protecting plants from frost, pests, and wind, effectively prolonging the productive growing period. Understanding the specific benefits and limitations of each technique helps optimize crop selection and timing for enhanced agricultural productivity.
Standard Gardening Season: Definition and Limitations
Standard gardening season typically spans from spring to early fall, defined by frost-free periods suitable for most crops. Its limitations include vulnerability to unpredictable weather, short growing periods for some plants, and restricted crop diversity due to temperature constraints. Gardeners often face challenges with early frosts or late thaws that can curtail plant growth and reduce yields.
Benefits of Extending the Growing Season
Extending the growing season increases crop yields by providing plants with a longer period to mature, enhancing food production efficiency. It improves resource utilization, allowing farmers to maximize land and labor investment throughout the year. Furthermore, extended growing periods offer greater resilience against climate variability, reducing risks associated with unpredictable weather patterns.
Common Methods for Growing Season Extension
Common methods for growing season extension include the use of high tunnels, row covers, and cold frames, which provide frost protection and maintain warmer soil temperatures. The application of plastic mulch and windbreaks further enhances temperature regulation and moisture retention, promoting earlier planting and later harvesting. These techniques collectively increase crop yield potential and improve production consistency compared to a standard growing season.
Comparing Crop Yields: Extended vs. Standard Seasons
Extended growing seasons significantly increase crop yields by providing plants with prolonged exposure to optimal temperature, sunlight, and moisture conditions. Crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens often produce 20-30% higher yields during extended seasons compared to standard seasons due to accelerated growth cycles and reduced stress periods. Improved yield efficiency during extended seasons supports higher profitability and resource utilization for farmers.
Cost and Effort Analysis for Season Extension
Extending the growing season typically incurs higher initial costs due to investments in infrastructure such as greenhouses, row covers, or heating systems, which are absent in standard season cultivation. The increased effort includes labor for monitoring temperature control, pest management, and crop protection against unexpected weather fluctuations, making it more resource-intensive than conventional methods. Despite these expenses, a well-managed season extension can yield multiple harvests and higher overall productivity, potentially offsetting the increased costs over time.
Impacts on Plant Variety Selection
Extending the growing season allows farmers to choose a wider range of plant varieties that thrive in longer periods of favorable temperatures and daylight, enhancing crop diversity and yield potential. Standard season constraints often limit selection to varieties with shorter maturation periods or greater stress tolerance, potentially reducing genetic variety and adaptability. Access to extended growing conditions supports the cultivation of both traditional and novel species, promoting innovation in agricultural practices and food security.
Climate Considerations for Both Seasons
Growing season extension techniques enable crops to thrive beyond traditional climate constraints by leveraging controlled environments or protective structures, which mitigate temperature fluctuations and frost risks. Standard growing seasons rely heavily on natural climate patterns, making them vulnerable to unpredictable weather events such as late frosts or early heatwaves that can reduce crop yields. Climate considerations for both involve monitoring temperature thresholds, soil moisture levels, and daylight duration to optimize growth cycles and enhance agricultural productivity.
Challenges and Solutions in Season Extension
Extending the growing season faces challenges such as fluctuating temperatures, increased pest pressures, and unpredictable weather patterns that can impact crop growth and yield stability. Solutions include the use of advanced greenhouse technologies, frost protection methods like row covers and wind machines, as well as implementing crop varieties genetically optimized for tolerance to temperature extremes. Integrating precision agriculture tools and soil moisture monitoring also enhances resource efficiency and mitigates risks associated with longer growing seasons.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Garden
Growing season extension methods such as row covers, cold frames, and greenhouses enable gardeners to cultivate plants beyond the limitations of a standard season, increasing yields and diversity. Assessing local climate patterns, crop types, and resource availability helps determine whether extending the growing season or adhering to traditional planting schedules best suits your garden's goals. Implementing season extension techniques optimizes plant growth conditions, resulting in healthier crops and prolonged harvest periods.
Growing season extension vs Standard season Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com